-
IP addresses are NOT logged in this forum so there's no point asking. Please note that this forum is full of homophobes, racists, lunatics, schizophrenics & absolute nut jobs with a smattering of geniuses, Chinese chauvinists, Moderate Muslims and last but not least a couple of "know-it-alls" constantly sprouting their dubious wisdom. If you believe that content generated by unsavory characters might cause you offense PLEASE LEAVE NOW! Sammyboy Admin and Staff are not responsible for your hurt feelings should you choose to read any of the content here. The OTHER forum is HERE so please stop asking.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Chitchat Opium and China Military threads
- Thread starter democracy my butt
- Start date
- Joined
- Aug 8, 2008
- Messages
- 6,070
- Points
- 83
https://www.rt.com/op-ed/465539-china-defense-military-white-paper/
China sees new era of ‘shared destiny’ with US no longer in the driving seat
Darius Shahtahmasebi
Darius Shahtahmasebi is a New Zealand-based legal and political analyst who focuses on US foreign policy in the Middle East, Asia and Pacific region. He is fully qualified as a lawyer in two international jurisdictions.
Published time: 1 Aug, 2019 08:55
China sees new era of ‘shared destiny’ with US no longer in the driving seat
A J-10 fighter jet of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Air Force's August 1st aerobatics team © Global Look Press / Xinhua / Yu Yongde
Follow RT on
RT
The release of China’s white paper on defense demonstrates to the world an increasingly confident and more assertive China, actively preparing for major shifts on a predominantly US-led global chessboard.
As well as the US, other crucial players on the world stage also have their eyes on China’s military posture.
One such country is India. Cutting straight to the chase, the white paper’s most obvious and arguably most relevant reference to India is a sentence that states the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) will “take effective measures to create favourable conditions for the peaceful resolution of the Donglang (Doklam) standoff.”
For those with difficulty recalling, in August 2017 India and China engaged in a brief skirmish in Doklam, on the Indo-Tibetan border. While seriously underreported by the mainstream media, the two nations continue to maintain a tense border standoff, with troops on both sides stationed just meters apart. However, it should be noted that the skirmishes in 2017 were effectively ended when both parties disengaged by mutual agreement.
The recently published white paper also confirmed the deployment of a Type 15 tank, much lighter than tanks deployed in China’s northern and western regions and purpose-built for mountain warfare. As the paper also makes numerous references to the mobilization and mobility of the PLA, such a low-weight Chinese tank may help in this regard. Deployment of this tank on the Sino-Indian border is almost certainly something New Delhi will become increasingly concerned at.
Read more
Joint India-China Moon exploration could mend relations & counter US space dominance Joint India-China Moon exploration could mend relations & counter US space dominance
Barely a day after the Chinese defense ministry released the white paper, Navy Chief Admiral Karambir Singh said that India was watching carefully, after noting that a lot of resources had shifted to China’s navy from other branches of the PLA. According to Singh, this all fits in as part of China’s intention to “become a global power.” Singh indicated that India would be required to respond within its own budget and the constraints that it has.
At the end of last year, Indian media reported that India was taking steps to counter China’s “strategic footprint” in the Indian Ocean, approving the construction of 56 new warships and six submarines for its navy over the next decade. India’s aim is to have 200 ships and 500 aircraft by the year 2050. According to the India Times, the country’s Navy has designed more than 90 warships across 19 different classes. As Singh recently said “we require long-term fiscal support to build a navy, that is the only way we can plan.”
That being said, China’s white paper’s reception has the potential to be interpreted in many contradicting ways, as the remaining references to India are not openly hostile or otherwise critical. As I discussed last year, there have been many signs that, despite the growing competition between New Delhi and Beijing, the two nations are finding ways to work together and minimize tensions that are likely to arise, whether they concern freedom of navigation, China’s closeness with Pakistan, or the growing question of Afghanistan and who can best exploit the mineral-rich war-torn nation.
Since then, there have been further indications that India is purposely and conscientiously avoiding ways in which it can outright provoke China, including and especially with regard to the South China Sea. In fact, Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s official position now seems to be that the Indo-Pacific is inclusive and not a “strategy or as a club of limited numbers.” Given that India sits firmly on the side of US-allied nations, it is clear that India does not seek to formally or officially exclude China from this zone. At the end of the day, India is becoming increasingly unlikely to be able to match China’s growing military prowess.
Given this context, it is unlikely that China’s white paper on defense will irk India to an extent which would not have been expected from India in the first place. Compared to, say, the ever-increasing US-China dispute, the competition between India and China appears to suggest a competition which can at least be contained for the foreseeable future.
Read more
US planning military infrastructure in Australia, amid tensions with Beijing US planning military infrastructure in Australia, amid tensions with Beijing
For example, just last month the US Department of Defense quietly released its Indo-Pacific Strategy Report (with the laughable subtitle: “Preparedness, Partnerships, and Promoting a Networked Region.” With chapters entitled “The People’s Republic of China as a Revisionist Power” and “Russia as a Revitalized Malign Actor”, Beijing’s white paper on defense begins to look quite tame indeed. As the US document states, “the core diagnosis of the National Defense Strategy is that DoD’s military advantage vis-à-vis China and Russia is eroding and, if inadequately addressed, it will undermine our ability to deter aggression and coercion.”
The report identifies China as being more confident and assertive, and more willing to “accept friction” in pursuit of its expanding foreign policy strategy. The US –by its own admission– is unable to deal alone with the threat that a rising China presents.
“The challenges we face in the Indo-Pacific extend beyond what any single country can address alone,” the report states. “The Department seeks to cooperate with like-minded allies and partners to address common challenges.”
It is in this framework that China’s white paper on defense likewise focuses heavily on the Asia-Pacific region, hotly contested by the US and its allies as well.
In 2015, President Xi Jinping made a concise declaration that China does not intend to pursue militarization of the features located in the South China Sea, such as those seen at the Spratly Islands. And yet, the white paper appears to have flipped that on its head, as it clearly refers to China’s “right to install to build infrastructure and deploy necessary defensive capabilities on the islands and reefs in the South China Sea.”
The US, China also argues, “is strengthening its Asia-Pacific military alliances and reinforcing military deployment and intervention.” The white paper notably singles out South Korea, Japan and Australia as fitting in this category of alliances. What may be the most cause for concern throughout the entire white paper, however, is the fact that China appears to be undeterred even in the face of this growing military alliance.
Read more
China to build ‘world-class’ military in new strategy as US ‘stirs up rivalry’ between major powers China to build ‘world-class’ military in new strategy as US ‘stirs up rivalry’ between major powers
“Asia-Pacific countries are increasingly aware that they are members of a community with shared destiny,” the white paper states, perhaps the single-most important sentence of the entire white paper.
On the face of it, it is unclear what Beijing is referring to. However, as far as some people and their sources are concerned, at the very least China is hinting that the region shares the destiny of what will become “the end of a US-led alliance system.”
While this all seems to be part and parcel of the inevitable decline of the American empire and the understandable rise of an ambitious competitor, I have suspicions of my own that the US is unlikely to surrender its throne to China without a fight, and an ever-looming showdown between these two nuclear powers is really what should be concerning us in the long run.
China sees new era of ‘shared destiny’ with US no longer in the driving seat
Darius Shahtahmasebi
Darius Shahtahmasebi is a New Zealand-based legal and political analyst who focuses on US foreign policy in the Middle East, Asia and Pacific region. He is fully qualified as a lawyer in two international jurisdictions.
Published time: 1 Aug, 2019 08:55
China sees new era of ‘shared destiny’ with US no longer in the driving seat
A J-10 fighter jet of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Air Force's August 1st aerobatics team © Global Look Press / Xinhua / Yu Yongde
Follow RT on
RT
The release of China’s white paper on defense demonstrates to the world an increasingly confident and more assertive China, actively preparing for major shifts on a predominantly US-led global chessboard.
As well as the US, other crucial players on the world stage also have their eyes on China’s military posture.
One such country is India. Cutting straight to the chase, the white paper’s most obvious and arguably most relevant reference to India is a sentence that states the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) will “take effective measures to create favourable conditions for the peaceful resolution of the Donglang (Doklam) standoff.”
For those with difficulty recalling, in August 2017 India and China engaged in a brief skirmish in Doklam, on the Indo-Tibetan border. While seriously underreported by the mainstream media, the two nations continue to maintain a tense border standoff, with troops on both sides stationed just meters apart. However, it should be noted that the skirmishes in 2017 were effectively ended when both parties disengaged by mutual agreement.
The recently published white paper also confirmed the deployment of a Type 15 tank, much lighter than tanks deployed in China’s northern and western regions and purpose-built for mountain warfare. As the paper also makes numerous references to the mobilization and mobility of the PLA, such a low-weight Chinese tank may help in this regard. Deployment of this tank on the Sino-Indian border is almost certainly something New Delhi will become increasingly concerned at.
Read more
Joint India-China Moon exploration could mend relations & counter US space dominance Joint India-China Moon exploration could mend relations & counter US space dominance
Barely a day after the Chinese defense ministry released the white paper, Navy Chief Admiral Karambir Singh said that India was watching carefully, after noting that a lot of resources had shifted to China’s navy from other branches of the PLA. According to Singh, this all fits in as part of China’s intention to “become a global power.” Singh indicated that India would be required to respond within its own budget and the constraints that it has.
At the end of last year, Indian media reported that India was taking steps to counter China’s “strategic footprint” in the Indian Ocean, approving the construction of 56 new warships and six submarines for its navy over the next decade. India’s aim is to have 200 ships and 500 aircraft by the year 2050. According to the India Times, the country’s Navy has designed more than 90 warships across 19 different classes. As Singh recently said “we require long-term fiscal support to build a navy, that is the only way we can plan.”
That being said, China’s white paper’s reception has the potential to be interpreted in many contradicting ways, as the remaining references to India are not openly hostile or otherwise critical. As I discussed last year, there have been many signs that, despite the growing competition between New Delhi and Beijing, the two nations are finding ways to work together and minimize tensions that are likely to arise, whether they concern freedom of navigation, China’s closeness with Pakistan, or the growing question of Afghanistan and who can best exploit the mineral-rich war-torn nation.
Since then, there have been further indications that India is purposely and conscientiously avoiding ways in which it can outright provoke China, including and especially with regard to the South China Sea. In fact, Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s official position now seems to be that the Indo-Pacific is inclusive and not a “strategy or as a club of limited numbers.” Given that India sits firmly on the side of US-allied nations, it is clear that India does not seek to formally or officially exclude China from this zone. At the end of the day, India is becoming increasingly unlikely to be able to match China’s growing military prowess.
Given this context, it is unlikely that China’s white paper on defense will irk India to an extent which would not have been expected from India in the first place. Compared to, say, the ever-increasing US-China dispute, the competition between India and China appears to suggest a competition which can at least be contained for the foreseeable future.
Read more
US planning military infrastructure in Australia, amid tensions with Beijing US planning military infrastructure in Australia, amid tensions with Beijing
For example, just last month the US Department of Defense quietly released its Indo-Pacific Strategy Report (with the laughable subtitle: “Preparedness, Partnerships, and Promoting a Networked Region.” With chapters entitled “The People’s Republic of China as a Revisionist Power” and “Russia as a Revitalized Malign Actor”, Beijing’s white paper on defense begins to look quite tame indeed. As the US document states, “the core diagnosis of the National Defense Strategy is that DoD’s military advantage vis-à-vis China and Russia is eroding and, if inadequately addressed, it will undermine our ability to deter aggression and coercion.”
The report identifies China as being more confident and assertive, and more willing to “accept friction” in pursuit of its expanding foreign policy strategy. The US –by its own admission– is unable to deal alone with the threat that a rising China presents.
“The challenges we face in the Indo-Pacific extend beyond what any single country can address alone,” the report states. “The Department seeks to cooperate with like-minded allies and partners to address common challenges.”
It is in this framework that China’s white paper on defense likewise focuses heavily on the Asia-Pacific region, hotly contested by the US and its allies as well.
In 2015, President Xi Jinping made a concise declaration that China does not intend to pursue militarization of the features located in the South China Sea, such as those seen at the Spratly Islands. And yet, the white paper appears to have flipped that on its head, as it clearly refers to China’s “right to install to build infrastructure and deploy necessary defensive capabilities on the islands and reefs in the South China Sea.”
The US, China also argues, “is strengthening its Asia-Pacific military alliances and reinforcing military deployment and intervention.” The white paper notably singles out South Korea, Japan and Australia as fitting in this category of alliances. What may be the most cause for concern throughout the entire white paper, however, is the fact that China appears to be undeterred even in the face of this growing military alliance.
Read more
China to build ‘world-class’ military in new strategy as US ‘stirs up rivalry’ between major powers China to build ‘world-class’ military in new strategy as US ‘stirs up rivalry’ between major powers
“Asia-Pacific countries are increasingly aware that they are members of a community with shared destiny,” the white paper states, perhaps the single-most important sentence of the entire white paper.
On the face of it, it is unclear what Beijing is referring to. However, as far as some people and their sources are concerned, at the very least China is hinting that the region shares the destiny of what will become “the end of a US-led alliance system.”
While this all seems to be part and parcel of the inevitable decline of the American empire and the understandable rise of an ambitious competitor, I have suspicions of my own that the US is unlikely to surrender its throne to China without a fight, and an ever-looming showdown between these two nuclear powers is really what should be concerning us in the long run.
- Joined
- Mar 13, 2009
- Messages
- 170
- Points
- 18
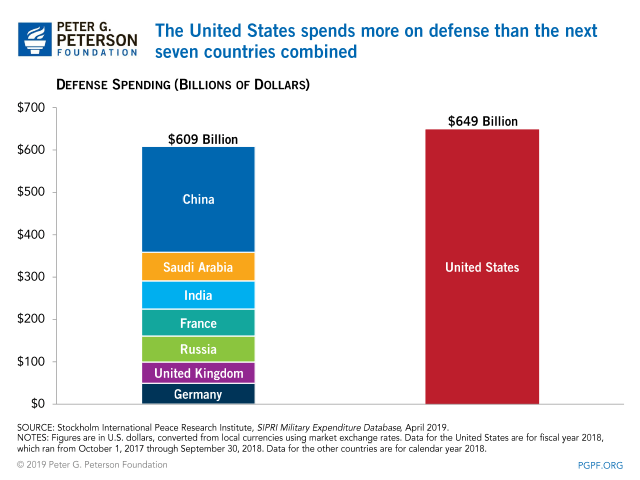
You China groupies are really deluded. The US defense budget is more than those of the next seven countries combined, and this year it went up by another $100 billion. China is not catching up anytime soon.
- Joined
- Jul 10, 2008
- Messages
- 64,816
- Points
- 113
I guess ah toing land don't need so much budget for defence. Like everything else in china, ah tiong can also build weapons at a fraction of the usual cost
Yes at a fraction of the cost to ensure that it breaks down after a few hours of use!!!!







I guess ah toing land don't need so much budget for defence. Like everything else in china, ah tiong can also build weapons at a fraction of the usual cost
Quality. Not quantity.

- Joined
- Jun 27, 2011
- Messages
- 3,715
- Points
- 113
Yes at a fraction of the cost to ensure that it breaks down after a few hours of use!!!!








- Joined
- Sep 22, 2008
- Messages
- 80,511
- Points
- 113
China is surrounded by US bases. There is no escape!
China is surrounded by US bases. There is no escape!
No worry. They have the Great Wall.

- Joined
- Nov 29, 2016
- Messages
- 5,674
- Points
- 63
Still dare fuck around at SCS?
PLA is too Civilized and Kind! Give a proper Carnage and Write New History in BLOOD. That is the ONLY CORRECT WAY TO REEDUCATE CHOW ANG MOH BANKRUPTED BEGGARS!
https://mil.news.sina.com.cn/jssd/2019-08-08/doc-ihytcerm9403927.shtml
英国海军有多寒酸 2次监视中国军舰竟要动用30%兵力
英国海军有多寒酸 2次监视中国军舰竟要动用30%兵力
215
 △“西安舰”于7月28日亮相俄罗斯2019年海军节阅兵
△“西安舰”于7月28日亮相俄罗斯2019年海军节阅兵
7月中旬,中国海军052C型驱逐舰“西安舰”通过英吉利海峡前往俄罗斯圣彼得堡,参加在那里举办的2019年俄海军节阅兵。
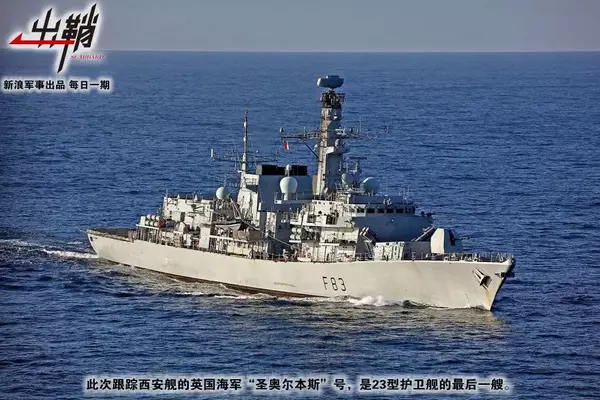
“西安舰”前往圣彼得堡本来是很“低调”的,可在英国皇家海军的帮忙造势下,“西安舰”北上的消息迅速引起外界的关注。“西安舰”由南向北穿越英吉利海峡期间,英国海军派出23型护卫舰“圣奥尔本斯”号对其进行持续监视,并将现场画面利用媒体传播了出去。
8月初,“西安舰”在参加完俄海军节活动后南下返回亚丁湾准备继续执行亚丁湾护航任务,在经过英吉利海峡期间又一次遭到英国海军的跟踪监视。执行监视任务的依然是23型护卫舰,但船却换成了“威斯敏斯特”号。

2艘护卫舰轮流监视“西安舰”,相比之前英国海军用扫雷舰招待俄罗斯海军,“西安舰”的“待遇”似乎好了不少。可这是表象,英国皇家海军的现状依然不尽如人意。英国海军现有主战舰艇仅19艘,分别是13艘23型护卫舰和6艘45型驱逐舰。单论服役规模的话远不及英吉利海峡对岸的“安静美男子”——法国,法国人极少在英吉利海峡干监视别人的事儿。
但实事求是的说,以英国当前的国力19艘驱护舰的规模也不能算太少,在世界上也能混个“十强”,虽然和前几位相差实在太远。尴尬的是,即便是这19艘舰艇也仅有9艘处于可调动状态,这当中还有3艘已经或正在前往海外部署。
 △监控“西安舰”的“威斯敏斯特”号护卫舰,注意它都经过了升级,顶部的新型三坐标雷达是一个明显特征
△监控“西安舰”的“威斯敏斯特”号护卫舰,注意它都经过了升级,顶部的新型三坐标雷达是一个明显特征
也就是说,英国海军目前仅有6艘驱护舰级别的主力战舰在英国自家水域。2次监视“西安舰”,英国海军出动了“三成多”的可用兵力。那么,剩下的舰艇在干嘛呢?
英国海军当前可用的舰艇主要是23型护卫舰,13艘中有7艘可用,其余6艘5艘在进行延寿升级,另1艘则纯粹趴窝等待进行延寿升级。由于新一代的26型护卫舰最快也要到2020年代中期才能服役,31型护卫舰更是遥遥无期,英国海军唯一的选择是维持住当前的23型护卫舰队。
 △部分换装“海受体”导弹的23型护卫舰防空能力将大大提升
△部分换装“海受体”导弹的23型护卫舰防空能力将大大提升
英国早前便已经决定对全部13艘23型护卫舰进行全面延寿升级,只是为了省钱,每艘舰艇的升级内容并不一致,以正在延寿的5艘为例,其中2艘将同时更新“海受体”舰空导弹和2087型拖曳阵列声呐、1艘仅换装“海受体”舰空导弹、1艘仅换装2087型拖曳阵列声呐纳、另一艘则只进行延寿。现役7艘23型的改装也与之类似,可见,即便是老舰艇的升级对于当前拮据的英国也得“精打细算”。
 △45型驱逐舰服役已经整10天,却至今仍不完美
△45型驱逐舰服役已经整10天,却至今仍不完美
45型驱逐舰自服役以来就问题不断,目前仍处于解决问题的状态当中,6艘中有4艘45型因为“不好不坏”而尴尬的处于不同“趴窝”状态:首舰“勇敢”号目前仍在等待决定是进行改装升级或是返回继续服役,做出决定似乎非常“艰难”,该舰不明不白的从2017年等到了现在,中间有一段时间这一堂堂防空驱逐舰还被作为训练舰使用;2号舰“不屈”号的状态最为“光明正大”,目前正在进行改装升级,预计2021年重返海军服役;3号舰“钻石”号和5号舰“防卫者”号都在进行维护,其中后者的维护则已经进行1年多的时间,预计于今年底重新服役。(作者署名:北国防务)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/74937389
 我军西安舰是怎么让英国军舰“变瞎”的?
我军西安舰是怎么让英国军舰“变瞎”的?

新浪军事
已认证的官方帐号
无可靠信息来源
为了避免对您造成误导,请谨慎甄别
中国海军052C西安舰目前正对欧洲多国展开访问之旅,继7月1日抵达法国土伦港进行军事交流之后,15日又转往荷兰鹿特丹港进行休整补给。据“中国军网”官方微信号消息,就在抵达鹿特丹前的14日,西安舰在英吉利海峡曾遭到英国护卫舰“圣奥尔本斯”号的跟踪监视。但期间“圣奥尔本斯”号护卫舰的雷达却失灵,并遭到反向锁定,最后不得不放弃了跟踪监视。那么英国军舰在跟踪时雷达为何会失灵,这又反应了我国军舰怎样的电子战水平?本期《出鞘》就来谈西安舰电子对抗英国军舰。

结合外媒报道可知,西安舰一抵近英吉利海峡附近时,英国海军就打开了岸基雷达,全程监视西安舰的活动轨迹,并随后派出23型护卫舰“圣奥尔本斯”号一路尾随西安舰。但就在西安舰驶离英吉利海峡时,“圣奥尔本斯”号的雷达却突然失灵了,西安舰的坐标位置消失在屏幕之中。于是英舰立即启动制导雷达,试图重新搜索西安舰的位置,但此时制导雷达却受到了强烈的电磁干扰,完全无法正常启用。
更让英国军舰船员惊讶的是,“圣奥尔本斯”号还遭到了西安舰的反向锁定。一般制导雷达的反向锁定,也就意味着该舰已经被西安舰瞄准。于是“圣奥尔本斯”号紧急掉头,不再对西安舰进行跟踪监视,但直到返回海峡后制导雷达才恢复正常。而在西安舰这边,据悉7月18日结束在荷兰鹿特丹港的短暂休整补给之后,已经转往俄罗斯波罗的海舰队的驻地喀琅施塔得,可能将参加俄军举行的海上阅舰式。
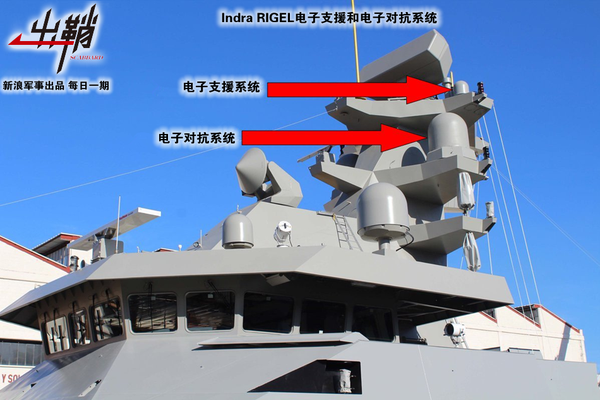
从媒体的报道来看,“圣奥尔本斯”号在跟踪监视过程中无疑是遭到了西安舰的电子干扰。人们常说的电子战,是指利用电磁能和定向能控制电磁频谱攻击敌方的任何军事行动,电子对抗是组成电子战的三个重要方面之一(电子战包括电子支援/电子侦察ESM、电子对抗ECM和电子反对抗ECCM),即利用己方电子设备,削弱和破坏敌方电子设备的使用效能。与之相对应的是电子反对抗,即用一定的技术手段来消除敌军电子对抗的有害影响,保证己方电子设备的正常工作。
一般舰艇上的电子对抗装备可分为无源干扰和有源干扰两大类,其中前者的作用原理是利用一定技术措施改变雷达电磁波正常传播条件、改变目标的二次辐射特性、投放反射物等造成对雷达的干扰,根据实施的方法和用途又可分为压制式和欺骗式两大类。其中压制式干扰主要是箔条干扰,而欺骗式干扰主要包括箔条干扰弹、伪装和雷达诱饵等。由于技术简单,无源干扰是最早被应用于舰艇电子对抗的软干扰手段,例如箔条干扰在二战期间就已经被运用。
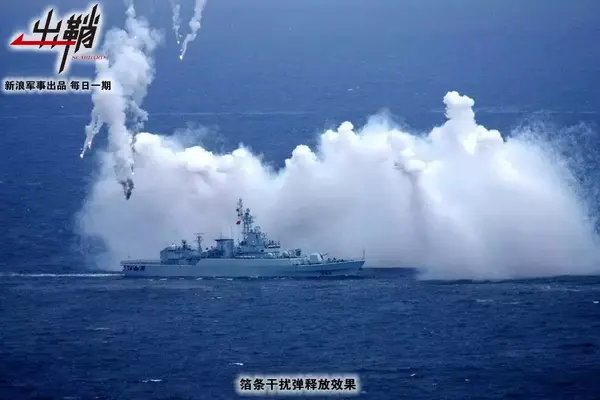

箔条一般由长度为半波长倍数(因为半波长对电磁波谐振反射最强,有效反射面最大)的铝丝或涂铝玻璃丝制成,使用时会被诱饵发射器发射出去,并在气流的作用下散开形成箔条云,在雷达的显示器上形成很强的类似噪声的乱杂波干扰波形,从而掩护目标回波。箔条干扰在针对早期反舰导弹所使用的雷达导引头时效果十分显著,例如在第四次中东战争中,以色列海军就通过装备在水面舰艇上的箔条干扰系统,成功让叙利亚舰艇发射的52枚“冥河”反舰导弹无一命中目标。
而箔条干扰弹则是一种欺骗式干扰技术,当雷达或雷达制导导弹跟踪被保护的舰艇或飞机时,箔条干扰弹能形成比回波大几倍的干扰箔条云回波,并使雷达或雷达制导导弹跟踪干扰箔条云,从而使被保护的舰艇或飞机摆脱跟踪。除了箔条干扰弹之外,欺骗性干扰技术还有雷达诱饵,它是应用具有很强的雷达反射面的雷达诱饵(如角反射器或龙伯透镜反射器等),把雷达对目标的跟踪引到跟踪雷达诱饵上。一般舰艇会在舰尾牵着长为几公里或几十公里的绳索,并将雷达诱饵拖在舰船的后面,使雷达跟踪雷达诱饵而丢失目标。

但随着舰载雷达和反舰导弹火控雷达导引头抗干扰能力的提升,性能单一的无源干扰开始越来越不能满足需求,因此之后各国海军又开发出了有源干扰手段——舰载雷达有源干扰和舷外有源干扰诱饵等。雷达有源干扰可分为噪声干扰和欺骗干扰两种,前者通过发射大功率的噪声信号来掩盖或淹没敌方雷达的目标回波,使敌方雷达无法正常工作;而后者虽然允许敌方雷达探测到目标,但获得的却不是目标的准确信息,而是失真的距离、方位和速度等参数。
舰载雷达有源干扰机自上世纪70年代开始应用之后,目前已经在各类水面舰艇上得到了普遍应用,而且基本同时具备噪声干扰和欺骗干扰两种功能。西方海军经典的舰载有源干扰电子战系统包括AN/SLQ-32系列和“牛顿-C”等,而我国海军虽然在051G导弹驱逐舰上才开始装备825型舰载电子对抗系统,但目前也已经先后发展出了包括826型和726型等有源干扰舰载电子对抗系统,并且大量装备在了052D驱逐舰、054A护卫舰和071登陆舰等各型战舰上。
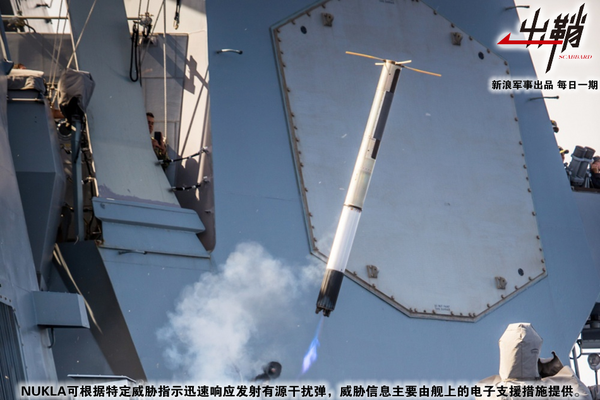

除了舰载雷达有源干扰外,还有一种比较特殊的有源干扰手段——舷外有源干扰诱饵。它可以简单理解为是一个与舰艇保持一定距离的有源干扰机,其优势在于作为一次性可消耗诱饵,可反制反舰导弹“干扰源寻的”模式所带来的威胁。目前比较有代表性的舷外有源干扰是英国“女妖”系统与美澳联合开发的NULKA系统,前者采用比较简单的降落伞滞空方式,而后者则使用了更先进的脉冲火箭发动机滞空方式。
美国海军如今很是重视NULKA这套系统,例如2016年在亚丁湾海域,美军的DDG-87 “梅森”号导弹驱逐舰就在遭遇胡赛武装的反舰导弹袭击时,动用NULKA系统配合ESSM与标准-2防空导弹对来袭导弹进行了有效的拦截防御。此外从美军主力驱逐舰伯克级的配置来看,也可以看出美国海军对这套舷外有源干扰系统的重视,因为目前有近一半的伯克级驱逐舰上的SLQ-32(V)2电子战系统是不具备有源干扰能力的,一般这些舰艇的舰载有源干扰主要依靠的就是NULKA系统。
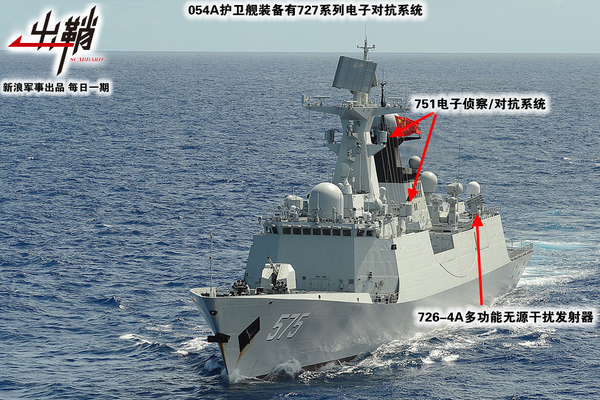

我军在舰载有源干扰系统方面最早的成果,是80年代初期研制的825系列电子对抗系统,它不仅曾装备于053护卫舰早期型以及部分051G驱逐舰,还曾作为053HT护卫舰的配套设备出口到泰国。之后我国又在参考“牛顿-C”系统的基础上,针对中小型水面舰艇作战需求,研制出了827系列电子对抗系统,它不仅曾装备053H2/H3护卫舰,还在051驱逐舰的现代化改装中被应用。目前在我军中小型水面舰艇上,827系列已经被727系列电子对抗系统所取代,例如054/054A护卫舰就装备了727系列,而且最新几艘054A护卫舰的727系统还改装了一种新型相控阵体制的有源干扰机。
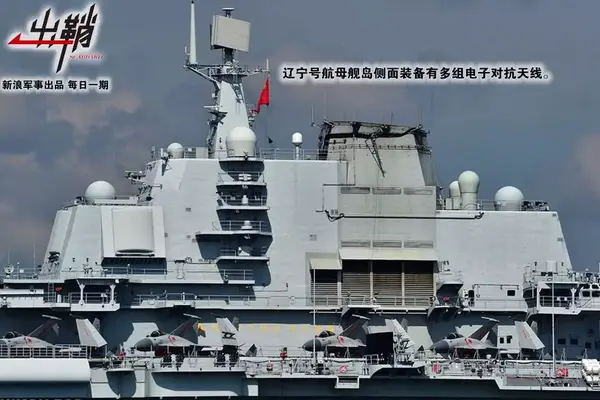
在大型水面舰艇电子对抗系统方面,我国也在参考了“弯刀”系统的基础上,开发出了826系列电子对抗系统,并在052驱逐舰上安装。不过826系列电子对抗系统有一个问题,那就是研制周期过长,并且现役舰艇可改装余地较小,因此后续很快就被726系列电子对抗系统所取代。这套系统主要装备于052C/D驱逐舰,其改进型号则装备于辽宁号航母和首艘国产航母,它的优点在于具备非常完善的雷达告警测频/测向功能,同时具备对各频段雷达信号的多种模式有源干扰能力,并且可以配合726-4系列干扰弹发射装置作业,可以达到对多批次、多模式攻击的组合干扰效果。

而在无源干扰手段这方面,我国则先后发展了945系列无源/光电对抗系统、946系列干扰弹发射装置、947系列干扰弹发射装置、726-4系列干扰弹发射装置和728系列干扰弹发射装置等。其中945系列的旋转式箔条/红外发射装置和烟雾弹发射装置曾装备于053H3型护卫舰,而945系列的固定式箔条/红外发射装置则装备于053H2G型护卫舰;946系列的15管干扰弹发射装置曾装备于051型驱逐舰;947系列的10管干扰弹发射装置曾装备于051B/C型驱逐舰,而16管干扰弹发射装置则装备于现今的辽宁号航母。
726-4系列干扰弹发射装置是目前我军舰艇主要装备的无源干扰设备,该系列主要包括3型,其中基本型每座发射装置共有三排共18个发射管,现装备于052B/C/D型驱逐舰、054型护卫舰和071型船坞登陆舰等;改进型的每座发射装置进一步增至四排共24个发射管,现已知装备于054A型护卫舰;而最新型号的726-4系列干扰弹发射装置据悉已经装备于055型导弹驱逐舰的舰尾直升机库上,虽然具体性能未知,但相信比改进型会有进一步提升。最后便是728系列干扰弹发射装置,该系列结构比较简单,因此多装备于022导弹艇和056护卫舰上。
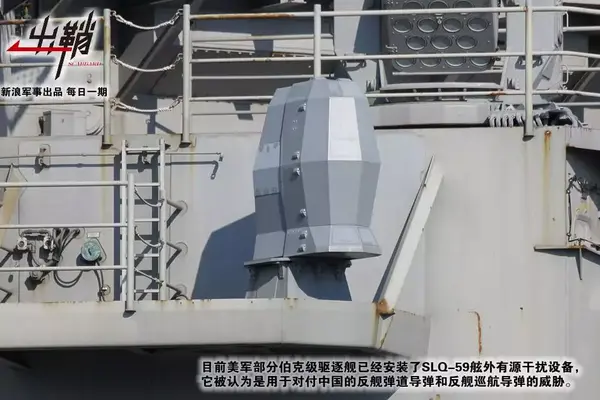

至于舷外有源干扰系统,虽然我国曾发展过947舰拖雷达诱饵,但由于一些原因最终未能实现装备,这也导致我军舰艇至今未装备性能堪比NULKA的舷外有源干扰系统。不过从某些不可靠的消息来源可知,我军舰艇近期似乎装备了与NULKA同类型的舷外有源干扰系统,但大概率依旧采用了类似“海妖”的降落伞滞空方式,并集成在了726-4系列干扰弹发射装置中。虽然这种模式距离美军NULKA系统的脉冲火箭发动机滞空方式尚有一定技术差距,不过至少算是解决了有无问题,将来未必不会改进。
回到此次事件来看,西安舰估计是采用了舰上装备的726系列电子对抗系统,对英国军舰的雷达进行了干扰。而从具体效果来看,726系列的表现还算是不错的,这也从侧面印证了我军舰载电子对抗系统所取得的不俗成就。当然我们也要看到,英国海军此次派出的是一艘老旧的23型护卫舰,战力配置根本无法与我052C级相比,所以不能就此认为我军舰载电子战系统已经赶超西方最先进水平。那么本期《出鞘》就到这里,我们下期再见。
发布于 2019-07-24
中华神盾
中国海军
军事
Https://mil.news.sina.com.cn/jssd/2019-08-08/doc-ihytcerm9403927.shtml
How cold is the British Navy? 2 times to monitor Chinese warships to use 30% of the troops
How cold is the British Navy? 2 times to monitor Chinese warships to use 30% of the troops
215
△ "Xi'an Ship" debuted on July 28th Russia's 2019 Navy Festival parade △ "Xi'an Ship" debuted on July 28th Russia's 2019 Navy Festival military parade
In mid-July, the Chinese Navy 052C destroyer "Xi'an Ship" traveled through the English Channel to St. Petersburg, Russia, to participate in the 2019 Russian Navy Festival parade.
The "Xi'an Ship" to St. Petersburg was originally a "low-key". Under the help of the British Royal Navy, the news of the "Xi'an Ship" north quickly attracted the attention of the outside world. During the "Xi'an Ship" crossing the English Channel from south to north, the British Navy sent a 23-type frigate "St. Albans" to continuously monitor it and spread the scene footage using the media.
At the beginning of August, the "Xi'an Ship" returned to the Gulf of Aden after attending the Russian Navy Festival and was ready to continue the escort mission in the Gulf of Aden. It was once again monitored by the British Navy during the passage of the English Channel. The type 23 frigate was still performing the surveillance mission, but the ship was replaced by the Westminster.
The two frigates took turns to monitor the "Xi'an Ship". Compared with the British Navy's use of minesweepers to entertain the Russian Navy, the "treatment" of the "Xi'an Ship" seems to be much better. But this is the appearance, the status quo of the Royal Navy is still not satisfactory. The British Navy currently has only 19 main battleships, 13 13-type frigates and 6 Type 45 destroyers. The scale of service alone is far less than the "quiet and beautiful man" on the other side of the English Channel - France, the French rarely monitor other people's affairs in the English Channel.
But to be realistic, the size of the 19 national frigates in the United Kingdom can not be too small, and the world can also mix a "top ten", although it is too far from the previous ones. What is embarrassing is that even 9 of the 19 ships are in a state of motion, and three of them have already been deployed overseas.
△Monitor the "Westminster" frigate of the "Xi'an Ship", note that it has been upgraded, the new three-coordinate radar at the top is a distinct feature
In other words, the British Navy currently has only six main destroyer-class battleships in the UK's own waters. Two times to monitor the "Xi'an Ship", the British Navy dispatched a "three percent" of available troops. So what are the remaining ships doing?
The currently available ships of the British Navy are mainly Type 23 frigates, 7 of which are available, and the remaining 6 are upgraded for life extensions, while the other is simply waiting for life extensions. Since the new generation of Type 26 frigates will not be operational until the mid-2020s, the Type 31 frigates are far from being in sight. The only choice for the British Navy is to maintain the current Type 23 escort fleet.
△ Partial replacement of the "Sea Receptor" missile type 23 frigate air defense capability will greatly enhance the △ part of the "sea receptor" missile type 23 frigate air defense capability will be greatly improved
The United Kingdom has already decided to carry out a full life extension upgrade for all 13 Type 23 frigates, just to save money. The upgrade content of each ship is not consistent. For example, 5 ships that are in the process of extending life, 2 of which will be updated at the same time. The "Ship" missile and the 2087 type towed array sonar, one only replaces the "Sea Receptor" ship-to-air missile, one only replaces the 2087 type towed array sonar, and the other only extends life. The modification of the current 7 Type 23 models is similar. It can be seen that even the upgrade of the old ships has to be "finely calculated" for the current UK.
The △45 destroyer has been in service for 10 days, but it is still not perfect. The Δ45 destroyer has been in service for 10 days, but it is still not perfect.
The Type 45 destroyer has been in constant problem since its service. It is still in a state of solving the problem. Four of the six ships are in a different "armpit" state because of "not bad or not bad": the first ship "Brave" It is still waiting for the decision to upgrade or return to service. It seems very difficult to make a decision. The ship has not waited until 2017, and there is a time when the air defense destroyer is also used as training. The ship is used; the No. 2 ship "Unyielding" is the most "bright and straight", and is currently undergoing modification and upgrading. It is expected to return to the Navy in 2021; the No. 3 "Diamond" and the No. 5 "Defender" are in progress. Maintenance, the maintenance of the latter has been carried out for more than a year and is expected to be re-commissioned by the end of this year. (Author's signature: Northern Defense)
Https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/74937389
How did the Chinese Xi’an ship “transform” the British warships? How did the Chinese Xi’an ship “transform” the British warships?
Sina military
Sina military
Certified official account
No reliable source of information
In order to avoid misleading you, please be careful
The Chinese Navy 052C Xi'an is currently on a tour of many European countries. After arriving in Toulon, France on July 1 for military exchanges, it was transferred to the port of Rotterdam in the Netherlands on the 15th for replenishment. According to the official micro-signal news of the "China Military Network", on the 14th before arriving in Rotterdam, the Xi'an ship was under surveillance by the British frigate "St. Albans" in the English Channel. However, during the period, the radar of the "Saint Albans" frigate failed, and was reverse locked, and finally had to give up tracking and surveillance. Then why did the radar fail when the British warships were tracking, which reflected the level of electronic warfare of our warships? This issue of "Sheathing" comes to talk about the Xi'an ship electronic war against British warships.
In combination with foreign media reports, when the Xi'an ship approached the English Channel, the British Navy opened the shore-based radar to monitor the trajectory of the Xi'an ship, and then dispatched the 23-type frigate "St. Albans" to follow Xi'an. Ship. But when the Xi'an ship sailed off the English Channel, the radar of St. Albans suddenly failed, and the coordinates of the Xi'an ship disappeared into the screen. So the British ship immediately started the guidance radar, trying to re-search the location of the Xi'an ship, but at this time the guided radar was subjected to strong electromagnetic interference and could not be activated normally.
To the surprise of the British warship crew, the "St. Albans" was also reversed by the Xi'an ship. The reverse locking of the general guided radar means that the ship has been targeted by the Xi'an ship. So "St. Albans" turned around urgently, no longer tracking and monitoring the Xi'an ship, but the guided radar did not return to normal until the return to the strait. On the Xi'an side of the ship, it is reported that after the short replenishment in the port of Rotterdam, the Netherlands, on July 18, it has been transferred to the Karststadt, the resident of the Russian Baltic Fleet, and may participate in the maritime warship style held by the Russian army.
According to media reports, the "St. Albans" was undoubtedly subject to electronic interference from the Xi'an ship during the tracking and monitoring process. People often say that electronic warfare refers to any military action that uses electromagnetic energy and directed energy to control the electromagnetic spectrum to attack the enemy. Electronic warfare is one of the three important aspects that constitute electronic warfare (electronic warfare includes electronic support/electronic reconnaissance ESM, Electronic countermeasures against ECM and electronic opposition to anti-ECCM), that is, the use of their own electronic devices to weaken and destroy the use of enemy electronic devices. Corresponding to this is electronic opposition, that is, using certain technical means to eliminate the harmful effects of enemy electronic countermeasures and to ensure the normal operation of their own electronic equipment.
The electronic countermeasure equipment on general ships can be divided into two categories: passive interference and active interference. The former principle is to use certain technical measures to change the normal propagation conditions of radar electromagnetic waves, change the secondary radiation characteristics of targets, and place reflectors. The interference to the radar can be divided into two categories: suppressed and deceptive according to the method and use of the implementation. Among them, the suppression interference is mainly chaff interference, while the deceptive interference mainly includes chaff jamming, camouflage and radar bait. Due to the simplicity of the technology, passive interference is the first soft interference method used in ship electronic countermeasures. For example, chaff interference has been used during World War II.
The chaff is generally made of aluminum wire or aluminum-coated glass wire with a length of half a wavelength multiple (because the half-wavelength is the strongest for electromagnetic wave resonance reflection, and the effective reflection surface is the largest). When used, it is emitted by the bait emitter and acts in the airflow. The clouds are scattered to form a chaff cloud, which forms a strong noise-like clutter interference waveform on the radar display, thereby shielding the target echo. Chaff jamming is very effective when targeting radar seekers used in early anti-ship missiles. For example, in the Fourth Middle East War, the Israeli Navy successfully launched a Syrian warship through a chaff jamming system equipped on a surface ship. The 52 "Sty River" anti-ship missiles have no target.
The chaff jamming bomb is a deceptive jamming technique. When the radar or radar guided missile tracks the protected ship or aircraft, the chaff jamming bomb can form an interference foil cloud echo that is several times larger than the echo, and Enable radar or radar-guided missiles to track the chaotic cloud, thereby freeing the protected ship or aircraft from tracking. In addition to the chaff jamming, the deceptive jamming technology also has a radar decoy, which is a radar decoy with a strong radar reflecting surface (such as a corner reflector or a Lombor lens reflector) to track the radar to the target. Lead to the tracking radar bait. In general, ships will carry ropes of several kilometers or tens of kilometers at the end of the ship, and the radar bait will be dragged behind the ship, so that the radar tracks the radar bait and loses the target.
However, with the improvement of the anti-interference ability of the ship-borne radar and the anti-ship missile fire control radar seeker, the single-passive passive interference began to be unable to meet the demand. Therefore, the navies of the countries have developed active interference means. Shipborne radar active interference and outboard active interference bait. Radar active interference can be divided into two types: noise interference and deception interference. The former can cover or flood the target radar of the enemy radar by transmitting a high-power noise signal, so that the enemy radar can not work normally; while the latter allows the enemy radar. The target is detected, but the accurate information of the target is not obtained, but the parameters such as the distance, azimuth and speed of the distortion.
Since the application of the shipborne radar active jammer in the 1970s, it has been widely used in all kinds of surface ships, and basically has both noise interference and deception interference. The Western Navy's classic shipborne active jamming electronic warfare system includes the AN/SLQ-32 series and the "Newton-C", while the Chinese navy began to equip the 825-type shipborne electronic countermeasure system on the 051G guided missile destroyer. Active jammed electronic countermeasures systems including the 826 and 726 have been developed, and are heavily equipped on various types of warships such as the 052D destroyer, the 054A frigate and the 071 landing ship.
In addition to the active interference of the shipborne radar, there is a special kind of active interference means - the outboard active interference decoy. It can be simply understood as an active jammer that maintains a certain distance from the ship. Its advantage is that it can counter the threat posed by the “interference source-seeking” model of anti-ship missiles as a disposable consumable bait. At present, the representative outboard active interference is the NULKA system jointly developed by the British "banshee" system and the United States and Australia. The former adopts a relatively simple parachute stagnation mode, while the latter uses a more advanced pulse rocket engine stagnation mode.
The US Navy now attaches great importance to the NULKA system. For example, in the Gulf of Aden in 2016, the US military's DDG-87 "Mason" guided missile destroyer used the NULKA system to cooperate with ESSM and standards when it was attacked by Hussein's anti-ship missile. -2 air defense missiles have effectively intercepted the incoming missiles. In addition, from the configuration of the Burke-class destroyer of the US military, it can be seen that the US Navy attaches importance to this outboard active jamming system, because there are nearly half of the SLQ-32(V)2 on the Burke-class destroyer. The electronic warfare system does not have active interference capability. Generally, the shipboard active interference of these ships mainly relies on the NULKA system.
The earliest result of our military in the shipborne active jamming system was the 825 series electronic countermeasure system developed in the early 1980s. It was not only equipped with the early 053 frigate and some 051G destroyers, but also exported as an accessory equipment for the 053HT frigate. Thailand. Afterwards, based on the "Newton-C" system, China has developed the 827 series electronic countermeasure system for the combat demand of small and medium-sized surface ships. It has not only been equipped with 053H2/H3 frigates, but also in the modern modification of the 051 destroyer. application. At present, in our small and medium-sized surface ships, the 827 series has been replaced by the 727 series electronic countermeasure system. For example, the 054/054A frigate is equipped with the 727 series, and the latest 547A escort 727 system has also been modified with a new phase control. An active jammer of the array system.
In terms of the large-scale surface warship electronic countermeasure system, China has also developed the 826 series electronic countermeasure system based on the "curved knife" system and installed it on the 052 destroyer. However, there is a problem with the 826 series electronic countermeasures system, that is, the development cycle is too long, and the existing ship can be modified with a small room, so the follow-up is quickly replaced by the 726 series electronic countermeasure system. This system is mainly equipped with the 052C/D destroyer. Its improved model is equipped with the Liaoning aircraft carrier and the first domestic aircraft carrier. Its advantage is that it has a very perfect radar warning frequency/direction finding function, and has radar signals for each frequency band. The multi-mode active interference capability, and can work with the 726-4 series of jamming launchers, can achieve a combined interference effect on multi-batch, multi-mode attacks.
In terms of passive interference, China has developed 945 series passive/optical countermeasures system, 946 series interference bomb launcher, 947 series jammer launcher, 726-4 series jammer launcher and 728 series jammer Launcher, etc. The 945 series of rotating foil/infrared launchers and smoke bomb launchers were equipped with the 053H3 frigate, while the 945 series of fixed chaff/infrared launchers were equipped with the 053H2G frigate; the 946 series of 15 tube jams The launcher was once equipped with the Type 051 destroyer; the 10 tube jamming launcher of the 947 series was equipped with the 051B/C destroyer, and the 16-tube jam launcher was equipped with the current Liaoning carrier.
The 726-4 series jamming launcher is the passive interference equipment of the main equipment of our warships. The series mainly includes 3 types, of which the basic type has a total of 18 launch tubes in three rows. It is now equipped with 052B/C. /D destroyer, type 054 frigate and type 071 dock
PLA is too Civilized and Kind! Give a proper Carnage and Write New History in BLOOD. That is the ONLY CORRECT WAY TO REEDUCATE CHOW ANG MOH BANKRUPTED BEGGARS!
https://mil.news.sina.com.cn/jssd/2019-08-08/doc-ihytcerm9403927.shtml
英国海军有多寒酸 2次监视中国军舰竟要动用30%兵力
英国海军有多寒酸 2次监视中国军舰竟要动用30%兵力
215

7月中旬,中国海军052C型驱逐舰“西安舰”通过英吉利海峡前往俄罗斯圣彼得堡,参加在那里举办的2019年俄海军节阅兵。
“西安舰”前往圣彼得堡本来是很“低调”的,可在英国皇家海军的帮忙造势下,“西安舰”北上的消息迅速引起外界的关注。“西安舰”由南向北穿越英吉利海峡期间,英国海军派出23型护卫舰“圣奥尔本斯”号对其进行持续监视,并将现场画面利用媒体传播了出去。
8月初,“西安舰”在参加完俄海军节活动后南下返回亚丁湾准备继续执行亚丁湾护航任务,在经过英吉利海峡期间又一次遭到英国海军的跟踪监视。执行监视任务的依然是23型护卫舰,但船却换成了“威斯敏斯特”号。

2艘护卫舰轮流监视“西安舰”,相比之前英国海军用扫雷舰招待俄罗斯海军,“西安舰”的“待遇”似乎好了不少。可这是表象,英国皇家海军的现状依然不尽如人意。英国海军现有主战舰艇仅19艘,分别是13艘23型护卫舰和6艘45型驱逐舰。单论服役规模的话远不及英吉利海峡对岸的“安静美男子”——法国,法国人极少在英吉利海峡干监视别人的事儿。
但实事求是的说,以英国当前的国力19艘驱护舰的规模也不能算太少,在世界上也能混个“十强”,虽然和前几位相差实在太远。尴尬的是,即便是这19艘舰艇也仅有9艘处于可调动状态,这当中还有3艘已经或正在前往海外部署。

也就是说,英国海军目前仅有6艘驱护舰级别的主力战舰在英国自家水域。2次监视“西安舰”,英国海军出动了“三成多”的可用兵力。那么,剩下的舰艇在干嘛呢?
英国海军当前可用的舰艇主要是23型护卫舰,13艘中有7艘可用,其余6艘5艘在进行延寿升级,另1艘则纯粹趴窝等待进行延寿升级。由于新一代的26型护卫舰最快也要到2020年代中期才能服役,31型护卫舰更是遥遥无期,英国海军唯一的选择是维持住当前的23型护卫舰队。

英国早前便已经决定对全部13艘23型护卫舰进行全面延寿升级,只是为了省钱,每艘舰艇的升级内容并不一致,以正在延寿的5艘为例,其中2艘将同时更新“海受体”舰空导弹和2087型拖曳阵列声呐、1艘仅换装“海受体”舰空导弹、1艘仅换装2087型拖曳阵列声呐纳、另一艘则只进行延寿。现役7艘23型的改装也与之类似,可见,即便是老舰艇的升级对于当前拮据的英国也得“精打细算”。

45型驱逐舰自服役以来就问题不断,目前仍处于解决问题的状态当中,6艘中有4艘45型因为“不好不坏”而尴尬的处于不同“趴窝”状态:首舰“勇敢”号目前仍在等待决定是进行改装升级或是返回继续服役,做出决定似乎非常“艰难”,该舰不明不白的从2017年等到了现在,中间有一段时间这一堂堂防空驱逐舰还被作为训练舰使用;2号舰“不屈”号的状态最为“光明正大”,目前正在进行改装升级,预计2021年重返海军服役;3号舰“钻石”号和5号舰“防卫者”号都在进行维护,其中后者的维护则已经进行1年多的时间,预计于今年底重新服役。(作者署名:北国防务)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/74937389


新浪军事
已认证的官方帐号
无可靠信息来源
为了避免对您造成误导,请谨慎甄别
中国海军052C西安舰目前正对欧洲多国展开访问之旅,继7月1日抵达法国土伦港进行军事交流之后,15日又转往荷兰鹿特丹港进行休整补给。据“中国军网”官方微信号消息,就在抵达鹿特丹前的14日,西安舰在英吉利海峡曾遭到英国护卫舰“圣奥尔本斯”号的跟踪监视。但期间“圣奥尔本斯”号护卫舰的雷达却失灵,并遭到反向锁定,最后不得不放弃了跟踪监视。那么英国军舰在跟踪时雷达为何会失灵,这又反应了我国军舰怎样的电子战水平?本期《出鞘》就来谈西安舰电子对抗英国军舰。

结合外媒报道可知,西安舰一抵近英吉利海峡附近时,英国海军就打开了岸基雷达,全程监视西安舰的活动轨迹,并随后派出23型护卫舰“圣奥尔本斯”号一路尾随西安舰。但就在西安舰驶离英吉利海峡时,“圣奥尔本斯”号的雷达却突然失灵了,西安舰的坐标位置消失在屏幕之中。于是英舰立即启动制导雷达,试图重新搜索西安舰的位置,但此时制导雷达却受到了强烈的电磁干扰,完全无法正常启用。
更让英国军舰船员惊讶的是,“圣奥尔本斯”号还遭到了西安舰的反向锁定。一般制导雷达的反向锁定,也就意味着该舰已经被西安舰瞄准。于是“圣奥尔本斯”号紧急掉头,不再对西安舰进行跟踪监视,但直到返回海峡后制导雷达才恢复正常。而在西安舰这边,据悉7月18日结束在荷兰鹿特丹港的短暂休整补给之后,已经转往俄罗斯波罗的海舰队的驻地喀琅施塔得,可能将参加俄军举行的海上阅舰式。

从媒体的报道来看,“圣奥尔本斯”号在跟踪监视过程中无疑是遭到了西安舰的电子干扰。人们常说的电子战,是指利用电磁能和定向能控制电磁频谱攻击敌方的任何军事行动,电子对抗是组成电子战的三个重要方面之一(电子战包括电子支援/电子侦察ESM、电子对抗ECM和电子反对抗ECCM),即利用己方电子设备,削弱和破坏敌方电子设备的使用效能。与之相对应的是电子反对抗,即用一定的技术手段来消除敌军电子对抗的有害影响,保证己方电子设备的正常工作。
一般舰艇上的电子对抗装备可分为无源干扰和有源干扰两大类,其中前者的作用原理是利用一定技术措施改变雷达电磁波正常传播条件、改变目标的二次辐射特性、投放反射物等造成对雷达的干扰,根据实施的方法和用途又可分为压制式和欺骗式两大类。其中压制式干扰主要是箔条干扰,而欺骗式干扰主要包括箔条干扰弹、伪装和雷达诱饵等。由于技术简单,无源干扰是最早被应用于舰艇电子对抗的软干扰手段,例如箔条干扰在二战期间就已经被运用。

箔条一般由长度为半波长倍数(因为半波长对电磁波谐振反射最强,有效反射面最大)的铝丝或涂铝玻璃丝制成,使用时会被诱饵发射器发射出去,并在气流的作用下散开形成箔条云,在雷达的显示器上形成很强的类似噪声的乱杂波干扰波形,从而掩护目标回波。箔条干扰在针对早期反舰导弹所使用的雷达导引头时效果十分显著,例如在第四次中东战争中,以色列海军就通过装备在水面舰艇上的箔条干扰系统,成功让叙利亚舰艇发射的52枚“冥河”反舰导弹无一命中目标。
而箔条干扰弹则是一种欺骗式干扰技术,当雷达或雷达制导导弹跟踪被保护的舰艇或飞机时,箔条干扰弹能形成比回波大几倍的干扰箔条云回波,并使雷达或雷达制导导弹跟踪干扰箔条云,从而使被保护的舰艇或飞机摆脱跟踪。除了箔条干扰弹之外,欺骗性干扰技术还有雷达诱饵,它是应用具有很强的雷达反射面的雷达诱饵(如角反射器或龙伯透镜反射器等),把雷达对目标的跟踪引到跟踪雷达诱饵上。一般舰艇会在舰尾牵着长为几公里或几十公里的绳索,并将雷达诱饵拖在舰船的后面,使雷达跟踪雷达诱饵而丢失目标。

但随着舰载雷达和反舰导弹火控雷达导引头抗干扰能力的提升,性能单一的无源干扰开始越来越不能满足需求,因此之后各国海军又开发出了有源干扰手段——舰载雷达有源干扰和舷外有源干扰诱饵等。雷达有源干扰可分为噪声干扰和欺骗干扰两种,前者通过发射大功率的噪声信号来掩盖或淹没敌方雷达的目标回波,使敌方雷达无法正常工作;而后者虽然允许敌方雷达探测到目标,但获得的却不是目标的准确信息,而是失真的距离、方位和速度等参数。
舰载雷达有源干扰机自上世纪70年代开始应用之后,目前已经在各类水面舰艇上得到了普遍应用,而且基本同时具备噪声干扰和欺骗干扰两种功能。西方海军经典的舰载有源干扰电子战系统包括AN/SLQ-32系列和“牛顿-C”等,而我国海军虽然在051G导弹驱逐舰上才开始装备825型舰载电子对抗系统,但目前也已经先后发展出了包括826型和726型等有源干扰舰载电子对抗系统,并且大量装备在了052D驱逐舰、054A护卫舰和071登陆舰等各型战舰上。

除了舰载雷达有源干扰外,还有一种比较特殊的有源干扰手段——舷外有源干扰诱饵。它可以简单理解为是一个与舰艇保持一定距离的有源干扰机,其优势在于作为一次性可消耗诱饵,可反制反舰导弹“干扰源寻的”模式所带来的威胁。目前比较有代表性的舷外有源干扰是英国“女妖”系统与美澳联合开发的NULKA系统,前者采用比较简单的降落伞滞空方式,而后者则使用了更先进的脉冲火箭发动机滞空方式。
美国海军如今很是重视NULKA这套系统,例如2016年在亚丁湾海域,美军的DDG-87 “梅森”号导弹驱逐舰就在遭遇胡赛武装的反舰导弹袭击时,动用NULKA系统配合ESSM与标准-2防空导弹对来袭导弹进行了有效的拦截防御。此外从美军主力驱逐舰伯克级的配置来看,也可以看出美国海军对这套舷外有源干扰系统的重视,因为目前有近一半的伯克级驱逐舰上的SLQ-32(V)2电子战系统是不具备有源干扰能力的,一般这些舰艇的舰载有源干扰主要依靠的就是NULKA系统。

我军在舰载有源干扰系统方面最早的成果,是80年代初期研制的825系列电子对抗系统,它不仅曾装备于053护卫舰早期型以及部分051G驱逐舰,还曾作为053HT护卫舰的配套设备出口到泰国。之后我国又在参考“牛顿-C”系统的基础上,针对中小型水面舰艇作战需求,研制出了827系列电子对抗系统,它不仅曾装备053H2/H3护卫舰,还在051驱逐舰的现代化改装中被应用。目前在我军中小型水面舰艇上,827系列已经被727系列电子对抗系统所取代,例如054/054A护卫舰就装备了727系列,而且最新几艘054A护卫舰的727系统还改装了一种新型相控阵体制的有源干扰机。
在大型水面舰艇电子对抗系统方面,我国也在参考了“弯刀”系统的基础上,开发出了826系列电子对抗系统,并在052驱逐舰上安装。不过826系列电子对抗系统有一个问题,那就是研制周期过长,并且现役舰艇可改装余地较小,因此后续很快就被726系列电子对抗系统所取代。这套系统主要装备于052C/D驱逐舰,其改进型号则装备于辽宁号航母和首艘国产航母,它的优点在于具备非常完善的雷达告警测频/测向功能,同时具备对各频段雷达信号的多种模式有源干扰能力,并且可以配合726-4系列干扰弹发射装置作业,可以达到对多批次、多模式攻击的组合干扰效果。

而在无源干扰手段这方面,我国则先后发展了945系列无源/光电对抗系统、946系列干扰弹发射装置、947系列干扰弹发射装置、726-4系列干扰弹发射装置和728系列干扰弹发射装置等。其中945系列的旋转式箔条/红外发射装置和烟雾弹发射装置曾装备于053H3型护卫舰,而945系列的固定式箔条/红外发射装置则装备于053H2G型护卫舰;946系列的15管干扰弹发射装置曾装备于051型驱逐舰;947系列的10管干扰弹发射装置曾装备于051B/C型驱逐舰,而16管干扰弹发射装置则装备于现今的辽宁号航母。
726-4系列干扰弹发射装置是目前我军舰艇主要装备的无源干扰设备,该系列主要包括3型,其中基本型每座发射装置共有三排共18个发射管,现装备于052B/C/D型驱逐舰、054型护卫舰和071型船坞登陆舰等;改进型的每座发射装置进一步增至四排共24个发射管,现已知装备于054A型护卫舰;而最新型号的726-4系列干扰弹发射装置据悉已经装备于055型导弹驱逐舰的舰尾直升机库上,虽然具体性能未知,但相信比改进型会有进一步提升。最后便是728系列干扰弹发射装置,该系列结构比较简单,因此多装备于022导弹艇和056护卫舰上。

至于舷外有源干扰系统,虽然我国曾发展过947舰拖雷达诱饵,但由于一些原因最终未能实现装备,这也导致我军舰艇至今未装备性能堪比NULKA的舷外有源干扰系统。不过从某些不可靠的消息来源可知,我军舰艇近期似乎装备了与NULKA同类型的舷外有源干扰系统,但大概率依旧采用了类似“海妖”的降落伞滞空方式,并集成在了726-4系列干扰弹发射装置中。虽然这种模式距离美军NULKA系统的脉冲火箭发动机滞空方式尚有一定技术差距,不过至少算是解决了有无问题,将来未必不会改进。
回到此次事件来看,西安舰估计是采用了舰上装备的726系列电子对抗系统,对英国军舰的雷达进行了干扰。而从具体效果来看,726系列的表现还算是不错的,这也从侧面印证了我军舰载电子对抗系统所取得的不俗成就。当然我们也要看到,英国海军此次派出的是一艘老旧的23型护卫舰,战力配置根本无法与我052C级相比,所以不能就此认为我军舰载电子战系统已经赶超西方最先进水平。那么本期《出鞘》就到这里,我们下期再见。
发布于 2019-07-24
中华神盾
中国海军
军事
Https://mil.news.sina.com.cn/jssd/2019-08-08/doc-ihytcerm9403927.shtml
How cold is the British Navy? 2 times to monitor Chinese warships to use 30% of the troops
How cold is the British Navy? 2 times to monitor Chinese warships to use 30% of the troops
215
△ "Xi'an Ship" debuted on July 28th Russia's 2019 Navy Festival parade △ "Xi'an Ship" debuted on July 28th Russia's 2019 Navy Festival military parade
In mid-July, the Chinese Navy 052C destroyer "Xi'an Ship" traveled through the English Channel to St. Petersburg, Russia, to participate in the 2019 Russian Navy Festival parade.
The "Xi'an Ship" to St. Petersburg was originally a "low-key". Under the help of the British Royal Navy, the news of the "Xi'an Ship" north quickly attracted the attention of the outside world. During the "Xi'an Ship" crossing the English Channel from south to north, the British Navy sent a 23-type frigate "St. Albans" to continuously monitor it and spread the scene footage using the media.
At the beginning of August, the "Xi'an Ship" returned to the Gulf of Aden after attending the Russian Navy Festival and was ready to continue the escort mission in the Gulf of Aden. It was once again monitored by the British Navy during the passage of the English Channel. The type 23 frigate was still performing the surveillance mission, but the ship was replaced by the Westminster.
The two frigates took turns to monitor the "Xi'an Ship". Compared with the British Navy's use of minesweepers to entertain the Russian Navy, the "treatment" of the "Xi'an Ship" seems to be much better. But this is the appearance, the status quo of the Royal Navy is still not satisfactory. The British Navy currently has only 19 main battleships, 13 13-type frigates and 6 Type 45 destroyers. The scale of service alone is far less than the "quiet and beautiful man" on the other side of the English Channel - France, the French rarely monitor other people's affairs in the English Channel.
But to be realistic, the size of the 19 national frigates in the United Kingdom can not be too small, and the world can also mix a "top ten", although it is too far from the previous ones. What is embarrassing is that even 9 of the 19 ships are in a state of motion, and three of them have already been deployed overseas.
△Monitor the "Westminster" frigate of the "Xi'an Ship", note that it has been upgraded, the new three-coordinate radar at the top is a distinct feature
In other words, the British Navy currently has only six main destroyer-class battleships in the UK's own waters. Two times to monitor the "Xi'an Ship", the British Navy dispatched a "three percent" of available troops. So what are the remaining ships doing?
The currently available ships of the British Navy are mainly Type 23 frigates, 7 of which are available, and the remaining 6 are upgraded for life extensions, while the other is simply waiting for life extensions. Since the new generation of Type 26 frigates will not be operational until the mid-2020s, the Type 31 frigates are far from being in sight. The only choice for the British Navy is to maintain the current Type 23 escort fleet.
△ Partial replacement of the "Sea Receptor" missile type 23 frigate air defense capability will greatly enhance the △ part of the "sea receptor" missile type 23 frigate air defense capability will be greatly improved
The United Kingdom has already decided to carry out a full life extension upgrade for all 13 Type 23 frigates, just to save money. The upgrade content of each ship is not consistent. For example, 5 ships that are in the process of extending life, 2 of which will be updated at the same time. The "Ship" missile and the 2087 type towed array sonar, one only replaces the "Sea Receptor" ship-to-air missile, one only replaces the 2087 type towed array sonar, and the other only extends life. The modification of the current 7 Type 23 models is similar. It can be seen that even the upgrade of the old ships has to be "finely calculated" for the current UK.
The △45 destroyer has been in service for 10 days, but it is still not perfect. The Δ45 destroyer has been in service for 10 days, but it is still not perfect.
The Type 45 destroyer has been in constant problem since its service. It is still in a state of solving the problem. Four of the six ships are in a different "armpit" state because of "not bad or not bad": the first ship "Brave" It is still waiting for the decision to upgrade or return to service. It seems very difficult to make a decision. The ship has not waited until 2017, and there is a time when the air defense destroyer is also used as training. The ship is used; the No. 2 ship "Unyielding" is the most "bright and straight", and is currently undergoing modification and upgrading. It is expected to return to the Navy in 2021; the No. 3 "Diamond" and the No. 5 "Defender" are in progress. Maintenance, the maintenance of the latter has been carried out for more than a year and is expected to be re-commissioned by the end of this year. (Author's signature: Northern Defense)
Https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/74937389
How did the Chinese Xi’an ship “transform” the British warships? How did the Chinese Xi’an ship “transform” the British warships?
Sina military
Sina military
Certified official account
No reliable source of information
In order to avoid misleading you, please be careful
The Chinese Navy 052C Xi'an is currently on a tour of many European countries. After arriving in Toulon, France on July 1 for military exchanges, it was transferred to the port of Rotterdam in the Netherlands on the 15th for replenishment. According to the official micro-signal news of the "China Military Network", on the 14th before arriving in Rotterdam, the Xi'an ship was under surveillance by the British frigate "St. Albans" in the English Channel. However, during the period, the radar of the "Saint Albans" frigate failed, and was reverse locked, and finally had to give up tracking and surveillance. Then why did the radar fail when the British warships were tracking, which reflected the level of electronic warfare of our warships? This issue of "Sheathing" comes to talk about the Xi'an ship electronic war against British warships.
In combination with foreign media reports, when the Xi'an ship approached the English Channel, the British Navy opened the shore-based radar to monitor the trajectory of the Xi'an ship, and then dispatched the 23-type frigate "St. Albans" to follow Xi'an. Ship. But when the Xi'an ship sailed off the English Channel, the radar of St. Albans suddenly failed, and the coordinates of the Xi'an ship disappeared into the screen. So the British ship immediately started the guidance radar, trying to re-search the location of the Xi'an ship, but at this time the guided radar was subjected to strong electromagnetic interference and could not be activated normally.
To the surprise of the British warship crew, the "St. Albans" was also reversed by the Xi'an ship. The reverse locking of the general guided radar means that the ship has been targeted by the Xi'an ship. So "St. Albans" turned around urgently, no longer tracking and monitoring the Xi'an ship, but the guided radar did not return to normal until the return to the strait. On the Xi'an side of the ship, it is reported that after the short replenishment in the port of Rotterdam, the Netherlands, on July 18, it has been transferred to the Karststadt, the resident of the Russian Baltic Fleet, and may participate in the maritime warship style held by the Russian army.
According to media reports, the "St. Albans" was undoubtedly subject to electronic interference from the Xi'an ship during the tracking and monitoring process. People often say that electronic warfare refers to any military action that uses electromagnetic energy and directed energy to control the electromagnetic spectrum to attack the enemy. Electronic warfare is one of the three important aspects that constitute electronic warfare (electronic warfare includes electronic support/electronic reconnaissance ESM, Electronic countermeasures against ECM and electronic opposition to anti-ECCM), that is, the use of their own electronic devices to weaken and destroy the use of enemy electronic devices. Corresponding to this is electronic opposition, that is, using certain technical means to eliminate the harmful effects of enemy electronic countermeasures and to ensure the normal operation of their own electronic equipment.
The electronic countermeasure equipment on general ships can be divided into two categories: passive interference and active interference. The former principle is to use certain technical measures to change the normal propagation conditions of radar electromagnetic waves, change the secondary radiation characteristics of targets, and place reflectors. The interference to the radar can be divided into two categories: suppressed and deceptive according to the method and use of the implementation. Among them, the suppression interference is mainly chaff interference, while the deceptive interference mainly includes chaff jamming, camouflage and radar bait. Due to the simplicity of the technology, passive interference is the first soft interference method used in ship electronic countermeasures. For example, chaff interference has been used during World War II.
The chaff is generally made of aluminum wire or aluminum-coated glass wire with a length of half a wavelength multiple (because the half-wavelength is the strongest for electromagnetic wave resonance reflection, and the effective reflection surface is the largest). When used, it is emitted by the bait emitter and acts in the airflow. The clouds are scattered to form a chaff cloud, which forms a strong noise-like clutter interference waveform on the radar display, thereby shielding the target echo. Chaff jamming is very effective when targeting radar seekers used in early anti-ship missiles. For example, in the Fourth Middle East War, the Israeli Navy successfully launched a Syrian warship through a chaff jamming system equipped on a surface ship. The 52 "Sty River" anti-ship missiles have no target.
The chaff jamming bomb is a deceptive jamming technique. When the radar or radar guided missile tracks the protected ship or aircraft, the chaff jamming bomb can form an interference foil cloud echo that is several times larger than the echo, and Enable radar or radar-guided missiles to track the chaotic cloud, thereby freeing the protected ship or aircraft from tracking. In addition to the chaff jamming, the deceptive jamming technology also has a radar decoy, which is a radar decoy with a strong radar reflecting surface (such as a corner reflector or a Lombor lens reflector) to track the radar to the target. Lead to the tracking radar bait. In general, ships will carry ropes of several kilometers or tens of kilometers at the end of the ship, and the radar bait will be dragged behind the ship, so that the radar tracks the radar bait and loses the target.
However, with the improvement of the anti-interference ability of the ship-borne radar and the anti-ship missile fire control radar seeker, the single-passive passive interference began to be unable to meet the demand. Therefore, the navies of the countries have developed active interference means. Shipborne radar active interference and outboard active interference bait. Radar active interference can be divided into two types: noise interference and deception interference. The former can cover or flood the target radar of the enemy radar by transmitting a high-power noise signal, so that the enemy radar can not work normally; while the latter allows the enemy radar. The target is detected, but the accurate information of the target is not obtained, but the parameters such as the distance, azimuth and speed of the distortion.
Since the application of the shipborne radar active jammer in the 1970s, it has been widely used in all kinds of surface ships, and basically has both noise interference and deception interference. The Western Navy's classic shipborne active jamming electronic warfare system includes the AN/SLQ-32 series and the "Newton-C", while the Chinese navy began to equip the 825-type shipborne electronic countermeasure system on the 051G guided missile destroyer. Active jammed electronic countermeasures systems including the 826 and 726 have been developed, and are heavily equipped on various types of warships such as the 052D destroyer, the 054A frigate and the 071 landing ship.
In addition to the active interference of the shipborne radar, there is a special kind of active interference means - the outboard active interference decoy. It can be simply understood as an active jammer that maintains a certain distance from the ship. Its advantage is that it can counter the threat posed by the “interference source-seeking” model of anti-ship missiles as a disposable consumable bait. At present, the representative outboard active interference is the NULKA system jointly developed by the British "banshee" system and the United States and Australia. The former adopts a relatively simple parachute stagnation mode, while the latter uses a more advanced pulse rocket engine stagnation mode.
The US Navy now attaches great importance to the NULKA system. For example, in the Gulf of Aden in 2016, the US military's DDG-87 "Mason" guided missile destroyer used the NULKA system to cooperate with ESSM and standards when it was attacked by Hussein's anti-ship missile. -2 air defense missiles have effectively intercepted the incoming missiles. In addition, from the configuration of the Burke-class destroyer of the US military, it can be seen that the US Navy attaches importance to this outboard active jamming system, because there are nearly half of the SLQ-32(V)2 on the Burke-class destroyer. The electronic warfare system does not have active interference capability. Generally, the shipboard active interference of these ships mainly relies on the NULKA system.
The earliest result of our military in the shipborne active jamming system was the 825 series electronic countermeasure system developed in the early 1980s. It was not only equipped with the early 053 frigate and some 051G destroyers, but also exported as an accessory equipment for the 053HT frigate. Thailand. Afterwards, based on the "Newton-C" system, China has developed the 827 series electronic countermeasure system for the combat demand of small and medium-sized surface ships. It has not only been equipped with 053H2/H3 frigates, but also in the modern modification of the 051 destroyer. application. At present, in our small and medium-sized surface ships, the 827 series has been replaced by the 727 series electronic countermeasure system. For example, the 054/054A frigate is equipped with the 727 series, and the latest 547A escort 727 system has also been modified with a new phase control. An active jammer of the array system.
In terms of the large-scale surface warship electronic countermeasure system, China has also developed the 826 series electronic countermeasure system based on the "curved knife" system and installed it on the 052 destroyer. However, there is a problem with the 826 series electronic countermeasures system, that is, the development cycle is too long, and the existing ship can be modified with a small room, so the follow-up is quickly replaced by the 726 series electronic countermeasure system. This system is mainly equipped with the 052C/D destroyer. Its improved model is equipped with the Liaoning aircraft carrier and the first domestic aircraft carrier. Its advantage is that it has a very perfect radar warning frequency/direction finding function, and has radar signals for each frequency band. The multi-mode active interference capability, and can work with the 726-4 series of jamming launchers, can achieve a combined interference effect on multi-batch, multi-mode attacks.
In terms of passive interference, China has developed 945 series passive/optical countermeasures system, 946 series interference bomb launcher, 947 series jammer launcher, 726-4 series jammer launcher and 728 series jammer Launcher, etc. The 945 series of rotating foil/infrared launchers and smoke bomb launchers were equipped with the 053H3 frigate, while the 945 series of fixed chaff/infrared launchers were equipped with the 053H2G frigate; the 946 series of 15 tube jams The launcher was once equipped with the Type 051 destroyer; the 10 tube jamming launcher of the 947 series was equipped with the 051B/C destroyer, and the 16-tube jam launcher was equipped with the current Liaoning carrier.
The 726-4 series jamming launcher is the passive interference equipment of the main equipment of our warships. The series mainly includes 3 types, of which the basic type has a total of 18 launch tubes in three rows. It is now equipped with 052B/C. /D destroyer, type 054 frigate and type 071 dock
- Joined
- Nov 29, 2016
- Messages
- 5,674
- Points
- 63
B-2B F-22 etc Top USAF Ace already surpass by New Chinese Jets. PLA way more advanced than bankrupted beggars Chow Ang Mohs.
https://mil.news.sina.com.cn/jssd/2019-08-08/doc-ihytcitm7779837.shtml
中国研发隐身轰炸机已突破7项核心技术 性能比肩B2
中国研发隐身轰炸机已突破7项核心技术 性能比肩B2
347
直到今天,B2洲际隐形轰炸机仍然是全球独一无二的、超级大国独有的战略利器,毕竟其他大国,还从来没有公布过和B2一样级别的武器。

超级大国新一代的B21轰炸机,一看就可知是B2的降配版。因此今后全球出现其他和B2一个级别的洲际隐轰,也基本摆脱不了B2的技术路线,也就是巨型隐身飞翼布局的设计。

中国的洲际战略隐轰已经传说了多年,至今不见露面。要实际出现某种全新型号的战略武器,就必须提前多年突破相关的技术。而B2类型的特殊飞机,比其他常规大飞机需要突破的体系要多的多。现在终于知道了:中国早在201X年以前,相关的7大类技术就已经全部突破。

设计和生产团队先后攻克了:
1、巨型飞翼飞机总体布局和结构设计。
看看B2的外形就知道,这种飞机就像一个没有任何多余翼面的三角风筝。这么一个大风筝还能环球飞行,整体布局和内部结构必然相当不简单。
中方的团队不但分析透彻了B2的整体设计,而且进行了相当多的优化。因此新洲际隐轰的外形和结构应该整体优于已经出现多年的B2。比如超音速飞行能力就是B2系列完全不具备的。

2、攻克了巨型飞翼飞机超临界机翼设计。
B2本身其实是很难区分具体的机翼和机体,机体也是升力体飞翼的一部分。在亚音速和超音速状况下如何确保气流不分散,新飞机的翼尖不失速,就需要深厚的气动理论和实践功底。在这方面也完全突破。

3、攻克了巨型飞翼飞机的电传飞控和控制率算法。
虽然B2的外形像三角大风筝,但实际上B2类飞机的气动控制比三角风筝要复杂得多。三角风筝可以飞上天,实际上是立体气动控制,也就是三角风筝的本体,和腹部风筝拉线之间,有一个立体的迎风体气动面。如果三角风筝突然断线,导致立体的气动格局崩溃,那么任何三角风筝本身都不能在空中稳定的飞行。
而B2作为巨型战机不可能有腹部一条线拉着他升空和飞行。B2和其他大型飞机一样都是采取通过尾部喷气来获得稳定的升力飞行。在严重的不稳定状态下,一个既无平尾,又没有垂尾的巨大的飞翼体,是很难纯人工稳定控制的。

因此任何巨型飞翼体飞行物,不论是有人的B2还是无人的X47B,还是此后大量出现的这类飞翼无人机,都需要电脑飞控软件参与飞翼体的复杂气动控制。
而且编写这类飞控软件最重要的控制率算法,难度要远远大于其他常规的大型飞机,不过这类巨型飞翼的飞控和控制率已经被彻底突破,多种无人飞翼机先于有人洲际隐轰亮相,就是飞控突破的直接体现。

4、攻克了巨型飞翼飞机的全隐身涂层。
洲际隐轰的隐身能力是其作为战略杀手锏的重要体现,而这类大型飞机的隐身涂层,和隐身战斗机的隐身涂层材料并不完全一致,不过也被彻底攻克。
5、攻克了全三维数字化设计及电子协调样机。
过去设计生产飞机,都是先制作全金属样机,气动和结构没有问题,才会进行第一批实体机的试验性生产。

不过现在国际上最先进的飞机设计,已经可以实现全三维数字化设计及电子协调样机。比如某些型号的大型民航客机,就率先实现了从三维数字化原型机,直接过渡到试飞实体机的无缝衔接。而洲际巨型隐轰也突破了这种技术,可以节省大量的初期研发消耗。
6、攻克了多乘员多任务系统驾驶舱综合设计。
在这方面过去是空白,毕竟洲际轰炸任务的复杂性远远大于常规中型轰炸机。

7、攻克了背负式锯齿型并列双发大S弯进气道的关键技术。
这方面也是过去没有涉及的领域,突破意义同样巨大。
笔者认为:
从以上7点来看,中国已经包揽了发动机以外的洲际隐轰的所有关键技术。从7大技术突破的时间来看,到目前恐怕不仅仅是完成首飞而已;很可能已经进入了多机模拟实战试飞阶段。已经过去相当一段时间的某单位的“THE NAXT”,显然不是随随便便发的暗示。(作者署名:军武酷)
China's research and development stealth bomber has broken through 7 core technologies. Performance is comparable to B2
China's research and development stealth bomber has broken through 7 core technologies. Performance is comparable to B2
347
To this day, the B2 Intercontinental Stealth Bomber is still a unique strategic weapon unique to the world, and other major powers have never announced the same level of weapons as B2.
The new generation of B21 bombers in the superpowers, at a glance, can be seen as a drop-off version of B2. Therefore, in the future, there will be other intercontinental concealment at the B2 level in the world, and it will basically be unable to get rid of the technical route of B2, that is, the design of the giant stealth flying wing layout.
China’s intercontinental strategy has been legendary for many years and has not appeared until now. In order to actually launch a new type of strategic weapon, it is necessary to break through the relevant technology for many years. The B2 type of special aircraft is much more than other conventional large aircraft that need to break through. Now I finally know: China as early as 201X years ago, the relevant 7 major types of technology have all broken through.
The design and production team has overcome:
1. The overall layout and structural design of the giant flying wing aircraft.
Looking at the shape of the B2, the aircraft is like a triangular kite without any excess airfoil. Such a big kite can fly around the world, and the overall layout and internal structure are inevitably quite simple.
The Chinese team not only analyzed the overall design of B2, but also carried out quite a lot of optimization. Therefore, the shape and structure of the new intercontinental concealed bomb should be better than the B2 that has been in existence for many years. For example, the supersonic flight capability is completely absent from the B2 series.
2. Conquered the supercritical wing design of the giant flying wing aircraft.
B2 itself is actually difficult to distinguish between specific wings and the body, the body is also part of the lift body wing. How to ensure that the airflow is not dispersed under subsonic and supersonic conditions, and the wing tip of the new aircraft does not stall, which requires deep aerodynamic theory and practical knowledge. In this regard, it also completely broke through.
3. Conquered the fly-by-wire flight control and control rate algorithm of the giant flying-wing aircraft.
Although the shape of the B2 is like a large kite, the pneumatic control of the B2 is actually much more complicated than the triangular kite. The triangular kite can fly to the sky, in fact, it is a three-dimensional pneumatic control, that is, the body of the triangular kite, and the belly kite pull line, there is a three-dimensional windward body aerodynamic surface. If the triangle kite suddenly breaks, causing the three-dimensional aerodynamic pattern to collapse, then any triangle kite itself cannot fly stably in the air.
And B2 as a giant fighter can not have a line of abdomen pulling him off and flying. Like other large aircraft, the B2 uses a tail jet to achieve a stable lift flight. In a severely unstable state, a huge flying wing body with neither a flat tail nor a vertical tail is difficult to control by artificial stability.
Therefore, any giant flying wing body flying object, whether it is a human B2 or an unmanned X47B, or a large number of such flying wing drones, will require computer flight control software to participate in the complex pneumatic control of the flying wing body.
Moreover, the most important control rate algorithm for writing such flight control software is much more difficult than other conventional large aircrafts. However, the flight control and control rate of such giant flying wings has been completely broken, and various unmanned flying wings are first. Appearing in the intercontinental concealment is a direct manifestation of the flight control breakthrough.
4. Conquered the full stealth coating of the giant flying wing aircraft.
The stealth ability of intercontinental stealth is an important manifestation of its strategic killer, and the stealth coating of such large aircraft is not exactly the same as the stealth coating material of the stealth fighter, but it has also been completely overcome.
5. Conquered the full 3D digital design and electronic coordination prototype.
In the past, the design and production of aircraft were first made of all-metal prototypes, and the pneumatic and structural problems were no problem before the experimental production of the first batch of physical machines was carried out.
However, the most advanced aircraft design in the world can already realize full 3D digital design and electronic coordination prototype. For example, some large-scale civil airliners are the first to realize the seamless transition from a three-dimensional digital prototype to a flight test physical machine. The intercontinental giant stealth has also broken through this technology, which can save a lot of initial research and development consumption.
6. Conquered the comprehensive design of the cockpit of the multi-occupant multi-tasking system.
In the past, the past was a blank. After all, the complexity of intercontinental bombing missions is far greater than that of conventional medium bombers.
7. Conquered the key technology of the piggyback type parallel-type double-shot S-bend inlet.
This aspect is also an area that has not been covered in the past, and the breakthrough significance is equally huge.
the author thinks:
From the above 7 points, China has already taken all the key technologies of intercontinental concealment outside the engine. Judging from the time of the 7 major technological breakthroughs, it is probably not only the completion of the first flight until now; it is likely that it has entered the multi-machine simulation actual combat flight test phase. The "THE NAXT" of a certain unit that has passed for quite some time is obviously not a hint of casually. (Author's signature: Junwu Cool)
https://mil.news.sina.com.cn/jssd/2019-08-08/doc-ihytcitm7779837.shtml
中国研发隐身轰炸机已突破7项核心技术 性能比肩B2
中国研发隐身轰炸机已突破7项核心技术 性能比肩B2
347
直到今天,B2洲际隐形轰炸机仍然是全球独一无二的、超级大国独有的战略利器,毕竟其他大国,还从来没有公布过和B2一样级别的武器。

超级大国新一代的B21轰炸机,一看就可知是B2的降配版。因此今后全球出现其他和B2一个级别的洲际隐轰,也基本摆脱不了B2的技术路线,也就是巨型隐身飞翼布局的设计。

中国的洲际战略隐轰已经传说了多年,至今不见露面。要实际出现某种全新型号的战略武器,就必须提前多年突破相关的技术。而B2类型的特殊飞机,比其他常规大飞机需要突破的体系要多的多。现在终于知道了:中国早在201X年以前,相关的7大类技术就已经全部突破。

设计和生产团队先后攻克了:
1、巨型飞翼飞机总体布局和结构设计。
看看B2的外形就知道,这种飞机就像一个没有任何多余翼面的三角风筝。这么一个大风筝还能环球飞行,整体布局和内部结构必然相当不简单。
中方的团队不但分析透彻了B2的整体设计,而且进行了相当多的优化。因此新洲际隐轰的外形和结构应该整体优于已经出现多年的B2。比如超音速飞行能力就是B2系列完全不具备的。

2、攻克了巨型飞翼飞机超临界机翼设计。
B2本身其实是很难区分具体的机翼和机体,机体也是升力体飞翼的一部分。在亚音速和超音速状况下如何确保气流不分散,新飞机的翼尖不失速,就需要深厚的气动理论和实践功底。在这方面也完全突破。

3、攻克了巨型飞翼飞机的电传飞控和控制率算法。
虽然B2的外形像三角大风筝,但实际上B2类飞机的气动控制比三角风筝要复杂得多。三角风筝可以飞上天,实际上是立体气动控制,也就是三角风筝的本体,和腹部风筝拉线之间,有一个立体的迎风体气动面。如果三角风筝突然断线,导致立体的气动格局崩溃,那么任何三角风筝本身都不能在空中稳定的飞行。
而B2作为巨型战机不可能有腹部一条线拉着他升空和飞行。B2和其他大型飞机一样都是采取通过尾部喷气来获得稳定的升力飞行。在严重的不稳定状态下,一个既无平尾,又没有垂尾的巨大的飞翼体,是很难纯人工稳定控制的。

因此任何巨型飞翼体飞行物,不论是有人的B2还是无人的X47B,还是此后大量出现的这类飞翼无人机,都需要电脑飞控软件参与飞翼体的复杂气动控制。
而且编写这类飞控软件最重要的控制率算法,难度要远远大于其他常规的大型飞机,不过这类巨型飞翼的飞控和控制率已经被彻底突破,多种无人飞翼机先于有人洲际隐轰亮相,就是飞控突破的直接体现。

4、攻克了巨型飞翼飞机的全隐身涂层。
洲际隐轰的隐身能力是其作为战略杀手锏的重要体现,而这类大型飞机的隐身涂层,和隐身战斗机的隐身涂层材料并不完全一致,不过也被彻底攻克。
5、攻克了全三维数字化设计及电子协调样机。
过去设计生产飞机,都是先制作全金属样机,气动和结构没有问题,才会进行第一批实体机的试验性生产。

不过现在国际上最先进的飞机设计,已经可以实现全三维数字化设计及电子协调样机。比如某些型号的大型民航客机,就率先实现了从三维数字化原型机,直接过渡到试飞实体机的无缝衔接。而洲际巨型隐轰也突破了这种技术,可以节省大量的初期研发消耗。
6、攻克了多乘员多任务系统驾驶舱综合设计。
在这方面过去是空白,毕竟洲际轰炸任务的复杂性远远大于常规中型轰炸机。

7、攻克了背负式锯齿型并列双发大S弯进气道的关键技术。
这方面也是过去没有涉及的领域,突破意义同样巨大。
笔者认为:
从以上7点来看,中国已经包揽了发动机以外的洲际隐轰的所有关键技术。从7大技术突破的时间来看,到目前恐怕不仅仅是完成首飞而已;很可能已经进入了多机模拟实战试飞阶段。已经过去相当一段时间的某单位的“THE NAXT”,显然不是随随便便发的暗示。(作者署名:军武酷)
China's research and development stealth bomber has broken through 7 core technologies. Performance is comparable to B2
China's research and development stealth bomber has broken through 7 core technologies. Performance is comparable to B2
347
To this day, the B2 Intercontinental Stealth Bomber is still a unique strategic weapon unique to the world, and other major powers have never announced the same level of weapons as B2.
The new generation of B21 bombers in the superpowers, at a glance, can be seen as a drop-off version of B2. Therefore, in the future, there will be other intercontinental concealment at the B2 level in the world, and it will basically be unable to get rid of the technical route of B2, that is, the design of the giant stealth flying wing layout.
China’s intercontinental strategy has been legendary for many years and has not appeared until now. In order to actually launch a new type of strategic weapon, it is necessary to break through the relevant technology for many years. The B2 type of special aircraft is much more than other conventional large aircraft that need to break through. Now I finally know: China as early as 201X years ago, the relevant 7 major types of technology have all broken through.
The design and production team has overcome:
1. The overall layout and structural design of the giant flying wing aircraft.
Looking at the shape of the B2, the aircraft is like a triangular kite without any excess airfoil. Such a big kite can fly around the world, and the overall layout and internal structure are inevitably quite simple.
The Chinese team not only analyzed the overall design of B2, but also carried out quite a lot of optimization. Therefore, the shape and structure of the new intercontinental concealed bomb should be better than the B2 that has been in existence for many years. For example, the supersonic flight capability is completely absent from the B2 series.
2. Conquered the supercritical wing design of the giant flying wing aircraft.
B2 itself is actually difficult to distinguish between specific wings and the body, the body is also part of the lift body wing. How to ensure that the airflow is not dispersed under subsonic and supersonic conditions, and the wing tip of the new aircraft does not stall, which requires deep aerodynamic theory and practical knowledge. In this regard, it also completely broke through.
3. Conquered the fly-by-wire flight control and control rate algorithm of the giant flying-wing aircraft.
Although the shape of the B2 is like a large kite, the pneumatic control of the B2 is actually much more complicated than the triangular kite. The triangular kite can fly to the sky, in fact, it is a three-dimensional pneumatic control, that is, the body of the triangular kite, and the belly kite pull line, there is a three-dimensional windward body aerodynamic surface. If the triangle kite suddenly breaks, causing the three-dimensional aerodynamic pattern to collapse, then any triangle kite itself cannot fly stably in the air.
And B2 as a giant fighter can not have a line of abdomen pulling him off and flying. Like other large aircraft, the B2 uses a tail jet to achieve a stable lift flight. In a severely unstable state, a huge flying wing body with neither a flat tail nor a vertical tail is difficult to control by artificial stability.
Therefore, any giant flying wing body flying object, whether it is a human B2 or an unmanned X47B, or a large number of such flying wing drones, will require computer flight control software to participate in the complex pneumatic control of the flying wing body.
Moreover, the most important control rate algorithm for writing such flight control software is much more difficult than other conventional large aircrafts. However, the flight control and control rate of such giant flying wings has been completely broken, and various unmanned flying wings are first. Appearing in the intercontinental concealment is a direct manifestation of the flight control breakthrough.
4. Conquered the full stealth coating of the giant flying wing aircraft.
The stealth ability of intercontinental stealth is an important manifestation of its strategic killer, and the stealth coating of such large aircraft is not exactly the same as the stealth coating material of the stealth fighter, but it has also been completely overcome.
5. Conquered the full 3D digital design and electronic coordination prototype.
In the past, the design and production of aircraft were first made of all-metal prototypes, and the pneumatic and structural problems were no problem before the experimental production of the first batch of physical machines was carried out.
However, the most advanced aircraft design in the world can already realize full 3D digital design and electronic coordination prototype. For example, some large-scale civil airliners are the first to realize the seamless transition from a three-dimensional digital prototype to a flight test physical machine. The intercontinental giant stealth has also broken through this technology, which can save a lot of initial research and development consumption.
6. Conquered the comprehensive design of the cockpit of the multi-occupant multi-tasking system.
In the past, the past was a blank. After all, the complexity of intercontinental bombing missions is far greater than that of conventional medium bombers.
7. Conquered the key technology of the piggyback type parallel-type double-shot S-bend inlet.
This aspect is also an area that has not been covered in the past, and the breakthrough significance is equally huge.
the author thinks:
From the above 7 points, China has already taken all the key technologies of intercontinental concealment outside the engine. Judging from the time of the 7 major technological breakthroughs, it is probably not only the completion of the first flight until now; it is likely that it has entered the multi-machine simulation actual combat flight test phase. The "THE NAXT" of a certain unit that has passed for quite some time is obviously not a hint of casually. (Author's signature: Junwu Cool)
- Joined
- Aug 8, 2008
- Messages
- 6,070
- Points
- 83
https://mil.news.sina.com.cn/china/2019-08-08/doc-ihytcitm7845756.shtml
我军中将:谁部署美国导弹对付中国 将来就打谁
我军中将:谁部署美国导弹对付中国 将来就打谁
7

多行不义必自毙:美国能否在亚太地区实现“中导霸权”1/15
查看原图图集模式
7月31日,美国政界著名鹰派人物,总统国安顾问博尔顿重申,美俄《中导条约》将于8月2日终止,美国届时将单方面退出。至当地时间8月2日,《中导条约》这一签署了32年的双边核军控条约彻底失效,成为一纸空文。在正式退约前的一星期,美国务卿蓬佩奥7月26日在接受福克斯新闻采访时表示,他不排除这样一种可能性,即美国会在亚太地区部署新型中程导弹。而在退约后的第二天,美国新任防长马克·埃斯珀对蓬佩奥这一说法表达了支持意愿。那么美国能否顺利如愿在亚洲部署中导?本期《出鞘》为您解读。















美国8月2日宣布正式退出1987年与苏联签定的《中导条约》。
一天后的8月3日,美国新任国防部长埃斯珀即宣称,要把新研发(鬼才相信新研发)的陆基中近程导弹,部署在亚洲地区。

中近程导弹射程500公里-5500公里。在这个距离上,西太方向大致包括第二岛链之内(含澳大利亚北部),印度洋方向戈迪加西亚群岛,中亚西亚方向美国各盟国,北美方向美国阿拉斯加的阿留申群岛。
可以这么说,中程导弹之弧,就沿着军事战略专家戴旭前些年指出的C形包围圈部署。
其重点在亚洲,即第一第二岛链,近程导弹重在第一岛链。
第一岛链已残破不全,需要修补。近几年随着我海空军常态化出入第一岛链,进行例行训练,视第一岛链如无人之境。美国苦无相应的战力应对,日本也只能派出机舰监视。
为此,日本在宫古岛部署少量陆基反舰导弹,换装了少量两栖部队。这些举措,相对我战时出击第一岛链之外的强大军力,就是挠痒痒。
美国兰德智库近期论证,我只要80发导弹,就能使美国在亚洲的56个基地瘫痪。这种说法可能扩大了我中近程导弹的威胁,但美国切实感受到我军的威慑,则是无疑的。

因此,美国加强了第二岛链的经营,尤其是关岛和南太的基地建设,把部分易受打击、高价值的海空装备回撤到二线上来。这些动作曾让我疑惑,美军真要放弃第一岛链了吗?
现在答案来了,不是放弃,而是以精干的、只需少量人员操控的近程导弹补位,並辅以防空和岸舰导弹加以防卫,求得“性价比”最高的资源配置,仍在第一岛链与我争夺战场主动权。
对我战略纵深威胁和打击,破坏我战争潜力。射程5000公里的中程导弹部署在关岛,可对我乌鲁木齐以东的几乎全境产生直接威胁;
印度洋戈迪加西亚美军基地可对云贵川战略腹地产生威胁;
部署在中亚西亚盟国的中程导弹,可对我西宁以西的新疆、西藏、青海西半个中国产生威胁,当然也威胁俄罗斯欧洲部分全境;
部署在美阿留申群岛,则可对我首都北京和东北地区产生威胁,同时也威胁俄罗斯远东地区。
由此,我国全境将受到来自C形包围圈美国中程导弹的威胁,有的地幅甚至是重叠威胁。

技术储备雄厚,很快能形成战斗力。废导条约的第二天,美国国防部长就谈到主要部署方向和时间,即亚太方向,争取今年年底完成。
美国让中近程导弹尽快完成部署、形成战斗力,是有底气的。《中导条约》之前,美军装备了大量陆基中近程导弹,如潘兴地对地导弹,射程1600公里,命中精度40米。既使销毁或退役了,但技术储备还在。最新的洲际导弹和巡航导弹技术,迁移到中近程导弹上也不是什么难事。
其实美国已经这么干了。《中导条约》签定之后,美国借开发战区反导系统,研制的拦截弹与中程导弹极其相似,换上弹头,拦截器即变导弹。美国还借口反击伊朗、朝鲜导弹,研制模拟靶弹,能打三四千公里,其实就是中程导弹。说美国遵守《中导条约》不发展中近程导弹,美国人自己都不相信,也不在乎。其国防部长在废约的紧后发声,没脸没皮,近乎无耻。
面对即将到来的美国中近程导弹威胁,该如何应对?
一是事先警告可能部署美国导弹的国家,如果接受美国导弹部署,就是站在美国一边,表示对我不友好。那么经济贸易和各方面交往,我将重新考虑。
二是警告有关国家,战时美国如果发射导弹打击我国,我将视该国为敌国,该国所有目标都在我考虑反击之内,而不仅仅是导弹阵地。
三是如果打击我纵深内核设施(战时核设施美国也难以分辨),我必予以核反击。四是只要美国部署导弹,其发射系统都将被我编入打击目标目录,相关诸元储存于计算机。一旦开战,先敌开火,作为第一批目标予以摧毁。
作者是原南京军区副司令员
Lieutenant General of the Army: Who will deploy the US missile to deal with China? Who will fight in the future?
Lieutenant General of the Army: Who will deploy the US missile to deal with China? Who will fight in the future?
7
Many lines of injustice will be self-defeating: Can the United States achieve "middle-hegemony" in the Asia-Pacific region?
View original image gallery mode
On July 31, the famous hawks in the US political circles and Presidential Security Advisor Bolton reiterated that the US-Russian "Guidelines on the Treaty" will be terminated on August 2, and the United States will unilaterally withdraw. By August 2 local time, the "Guide to the Treaty", a 32-year bilateral nuclear arms control treaty, had completely failed and became a dead letter. One week before the official withdrawal, US Secretary of State Pompeo said in an interview with Fox News on July 26 that he did not rule out the possibility that the United States would deploy new medium-range missiles in the Asia-Pacific region. On the second day after the withdrawal, the new US Defense Secretary Mark Esper expressed his willingness to support Pompeo. So can the United States succeed in deploying a guide in Asia? This issue of "Sheathing" is for you to interpret.
The United States announced on August 2 that it officially withdrew from the "Guidelines on the Treaty" signed in 1987 with the Soviet Union.
One day later, on August 3, the new US Secretary of Defense Espoo announced that it would deploy the land-based medium-range and short-range missiles of the new R&D (the new development of the ghosts) in the Asian region.
The medium-range and short-range missiles range from 500 kilometers to 5,500 kilometers. At this distance, the West Pacific direction generally includes the second island chain (including northern Australia), the Indian Ocean direction of the Gordigas, the Central Asian countries to the United States allies, and the North American direction to the Aleutian Islands of Alaska.
It can be said that the arc of the medium-range missile is deployed along the C-shaped encirclement circle pointed out by the military strategy expert Dai Xu in previous years.
Its focus is on Asia, the first and second island chains, and the short-range missiles are on the first island chain.
The first island chain has been broken and needs to be repaired. In recent years, as the Navy and Air Force normalized into the first island chain, routine training was carried out, depending on the first island chain. The United States has no corresponding response to the war, and Japan can only dispatch aircraft surveillance.
To this end, Japan deployed a small number of land-based anti-ship missiles on Miyako Island and replaced a small number of amphibious units. These measures, compared to the strong military force outside the first island chain in my war, is tickling.
The US RAND think tank recently demonstrated that with only 80 missiles, I can make the United States 56 bases in Asia. This statement may expand the threat of my medium- and short-range missiles, but the United States really feels the deterrent of our army, and it is undoubted.
Therefore, the United States has strengthened the operation of the second island chain, especially the base construction of Guam and Nantai, and has withdrawn some of the vulnerable and high-value air and sea equipment to the second line. These actions have puzzled me. Is the US military really going to give up the first island chain?
Now the answer is coming, not giving up, but using a lean, short-range missile that is controlled by a small number of people, supplemented by air defense and shore-to-ship missiles, and the most cost-effective resource allocation is still in the first place. An island chain competes with me for the initiative on the battlefield.
Threatening and attacking my strategy deeply, destroying the potential of my war. The medium-range missile with a range of 5,000 kilometers is deployed in Guam, which poses a direct threat to almost the entire territory east of Urumqi;
The Indian Ocean Gordi Garcia US military base can pose a threat to the strategic hinterland of Yunnan and Guizhou;
The medium-range missiles deployed in the Central Asian West allies can threaten Xinjiang, Tibet, and the western half of China in the west of Xining, and of course threaten the entire European part of Russia;
Deployment in the US Aleutian Islands can threaten my capital Beijing and the Northeast, as well as the Russian Far East.
As a result, the entire territory of China will be threatened by the US medium-range missiles from the C-shaped encirclement, and some land areas may even overlap threats.
Strong technical reserves, and soon can form combat effectiveness. On the second day of the ADR, the US Secretary of Defense talked about the main deployment direction and time, that is, the Asia-Pacific direction, and strive to complete it by the end of this year.
The United States has made it possible to let the medium- and short-range missiles complete their deployment and form combat effectiveness as soon as possible. Prior to the "Guide to the Treaty", the US military was equipped with a large number of land-based medium-range missiles, such as the Pershing ground-to-ground missile, with a range of 1,600 kilometers and a hit accuracy of 40 meters. Even if it is destroyed or decommissioned, the technical reserve is still there. The latest intercontinental missiles and cruise missile technology are not difficult to move to medium- and short-range missiles.
In fact, the United States has done this. After the signing of the "Guidelines on the Treaty", the United States developed the theater anti-missile system and developed interceptor missiles that are very similar to medium-range missiles. They are replaced by warheads, and the interceptor becomes a missile. The United States has also used the pretext of countering Iranian and North Korean missiles to develop a simulated target projectile that can hit three or four thousand kilometers. It is actually a medium-range missile. When the United States abides by the "Guidelines on the Treaty" and does not develop medium- and short-range missiles, the Americans do not believe it or care. The Minister of National Defense made a sound after the abolition of the contract, and there was no face and no skin, almost shameless.
How to deal with the upcoming US mid-range missile threat?
First, the country that warned against the deployment of US missiles in advance will stand on the side of the United States if it accepts the deployment of US missiles, indicating that it is not friendly to me. Then I will reconsider economic trade and various contacts.
The second is to warn the countries concerned. If the United States launches missiles against the country in wartime, I will regard the country as an enemy. All the goals of the country are within my consideration of counterattacks, not just missile positions.
Third, if I strike against my deep core facilities (the wartime nuclear facilities are difficult for the United States to distinguish), I will counterattack. Fourth, as long as the United States deploys missiles, its launch system will be compiled into the target directory, and the relevant elements will be stored in computers. Once the war begins, the enemy first fires and is destroyed as the first target.
The author is the former deputy commander of the Nanjing Military Region.
我军中将:谁部署美国导弹对付中国 将来就打谁
我军中将:谁部署美国导弹对付中国 将来就打谁
7

多行不义必自毙:美国能否在亚太地区实现“中导霸权”1/15
查看原图图集模式
7月31日,美国政界著名鹰派人物,总统国安顾问博尔顿重申,美俄《中导条约》将于8月2日终止,美国届时将单方面退出。至当地时间8月2日,《中导条约》这一签署了32年的双边核军控条约彻底失效,成为一纸空文。在正式退约前的一星期,美国务卿蓬佩奥7月26日在接受福克斯新闻采访时表示,他不排除这样一种可能性,即美国会在亚太地区部署新型中程导弹。而在退约后的第二天,美国新任防长马克·埃斯珀对蓬佩奥这一说法表达了支持意愿。那么美国能否顺利如愿在亚洲部署中导?本期《出鞘》为您解读。















美国8月2日宣布正式退出1987年与苏联签定的《中导条约》。
一天后的8月3日,美国新任国防部长埃斯珀即宣称,要把新研发(鬼才相信新研发)的陆基中近程导弹,部署在亚洲地区。

中近程导弹射程500公里-5500公里。在这个距离上,西太方向大致包括第二岛链之内(含澳大利亚北部),印度洋方向戈迪加西亚群岛,中亚西亚方向美国各盟国,北美方向美国阿拉斯加的阿留申群岛。
可以这么说,中程导弹之弧,就沿着军事战略专家戴旭前些年指出的C形包围圈部署。
其重点在亚洲,即第一第二岛链,近程导弹重在第一岛链。
第一岛链已残破不全,需要修补。近几年随着我海空军常态化出入第一岛链,进行例行训练,视第一岛链如无人之境。美国苦无相应的战力应对,日本也只能派出机舰监视。
为此,日本在宫古岛部署少量陆基反舰导弹,换装了少量两栖部队。这些举措,相对我战时出击第一岛链之外的强大军力,就是挠痒痒。
美国兰德智库近期论证,我只要80发导弹,就能使美国在亚洲的56个基地瘫痪。这种说法可能扩大了我中近程导弹的威胁,但美国切实感受到我军的威慑,则是无疑的。

因此,美国加强了第二岛链的经营,尤其是关岛和南太的基地建设,把部分易受打击、高价值的海空装备回撤到二线上来。这些动作曾让我疑惑,美军真要放弃第一岛链了吗?
现在答案来了,不是放弃,而是以精干的、只需少量人员操控的近程导弹补位,並辅以防空和岸舰导弹加以防卫,求得“性价比”最高的资源配置,仍在第一岛链与我争夺战场主动权。
对我战略纵深威胁和打击,破坏我战争潜力。射程5000公里的中程导弹部署在关岛,可对我乌鲁木齐以东的几乎全境产生直接威胁;
印度洋戈迪加西亚美军基地可对云贵川战略腹地产生威胁;
部署在中亚西亚盟国的中程导弹,可对我西宁以西的新疆、西藏、青海西半个中国产生威胁,当然也威胁俄罗斯欧洲部分全境;
部署在美阿留申群岛,则可对我首都北京和东北地区产生威胁,同时也威胁俄罗斯远东地区。
由此,我国全境将受到来自C形包围圈美国中程导弹的威胁,有的地幅甚至是重叠威胁。

技术储备雄厚,很快能形成战斗力。废导条约的第二天,美国国防部长就谈到主要部署方向和时间,即亚太方向,争取今年年底完成。
美国让中近程导弹尽快完成部署、形成战斗力,是有底气的。《中导条约》之前,美军装备了大量陆基中近程导弹,如潘兴地对地导弹,射程1600公里,命中精度40米。既使销毁或退役了,但技术储备还在。最新的洲际导弹和巡航导弹技术,迁移到中近程导弹上也不是什么难事。
其实美国已经这么干了。《中导条约》签定之后,美国借开发战区反导系统,研制的拦截弹与中程导弹极其相似,换上弹头,拦截器即变导弹。美国还借口反击伊朗、朝鲜导弹,研制模拟靶弹,能打三四千公里,其实就是中程导弹。说美国遵守《中导条约》不发展中近程导弹,美国人自己都不相信,也不在乎。其国防部长在废约的紧后发声,没脸没皮,近乎无耻。
面对即将到来的美国中近程导弹威胁,该如何应对?
一是事先警告可能部署美国导弹的国家,如果接受美国导弹部署,就是站在美国一边,表示对我不友好。那么经济贸易和各方面交往,我将重新考虑。
二是警告有关国家,战时美国如果发射导弹打击我国,我将视该国为敌国,该国所有目标都在我考虑反击之内,而不仅仅是导弹阵地。
三是如果打击我纵深内核设施(战时核设施美国也难以分辨),我必予以核反击。四是只要美国部署导弹,其发射系统都将被我编入打击目标目录,相关诸元储存于计算机。一旦开战,先敌开火,作为第一批目标予以摧毁。
作者是原南京军区副司令员
Lieutenant General of the Army: Who will deploy the US missile to deal with China? Who will fight in the future?
Lieutenant General of the Army: Who will deploy the US missile to deal with China? Who will fight in the future?
7
Many lines of injustice will be self-defeating: Can the United States achieve "middle-hegemony" in the Asia-Pacific region?
View original image gallery mode
On July 31, the famous hawks in the US political circles and Presidential Security Advisor Bolton reiterated that the US-Russian "Guidelines on the Treaty" will be terminated on August 2, and the United States will unilaterally withdraw. By August 2 local time, the "Guide to the Treaty", a 32-year bilateral nuclear arms control treaty, had completely failed and became a dead letter. One week before the official withdrawal, US Secretary of State Pompeo said in an interview with Fox News on July 26 that he did not rule out the possibility that the United States would deploy new medium-range missiles in the Asia-Pacific region. On the second day after the withdrawal, the new US Defense Secretary Mark Esper expressed his willingness to support Pompeo. So can the United States succeed in deploying a guide in Asia? This issue of "Sheathing" is for you to interpret.
The United States announced on August 2 that it officially withdrew from the "Guidelines on the Treaty" signed in 1987 with the Soviet Union.
One day later, on August 3, the new US Secretary of Defense Espoo announced that it would deploy the land-based medium-range and short-range missiles of the new R&D (the new development of the ghosts) in the Asian region.
The medium-range and short-range missiles range from 500 kilometers to 5,500 kilometers. At this distance, the West Pacific direction generally includes the second island chain (including northern Australia), the Indian Ocean direction of the Gordigas, the Central Asian countries to the United States allies, and the North American direction to the Aleutian Islands of Alaska.
It can be said that the arc of the medium-range missile is deployed along the C-shaped encirclement circle pointed out by the military strategy expert Dai Xu in previous years.
Its focus is on Asia, the first and second island chains, and the short-range missiles are on the first island chain.
The first island chain has been broken and needs to be repaired. In recent years, as the Navy and Air Force normalized into the first island chain, routine training was carried out, depending on the first island chain. The United States has no corresponding response to the war, and Japan can only dispatch aircraft surveillance.
To this end, Japan deployed a small number of land-based anti-ship missiles on Miyako Island and replaced a small number of amphibious units. These measures, compared to the strong military force outside the first island chain in my war, is tickling.
The US RAND think tank recently demonstrated that with only 80 missiles, I can make the United States 56 bases in Asia. This statement may expand the threat of my medium- and short-range missiles, but the United States really feels the deterrent of our army, and it is undoubted.
Therefore, the United States has strengthened the operation of the second island chain, especially the base construction of Guam and Nantai, and has withdrawn some of the vulnerable and high-value air and sea equipment to the second line. These actions have puzzled me. Is the US military really going to give up the first island chain?
Now the answer is coming, not giving up, but using a lean, short-range missile that is controlled by a small number of people, supplemented by air defense and shore-to-ship missiles, and the most cost-effective resource allocation is still in the first place. An island chain competes with me for the initiative on the battlefield.
Threatening and attacking my strategy deeply, destroying the potential of my war. The medium-range missile with a range of 5,000 kilometers is deployed in Guam, which poses a direct threat to almost the entire territory east of Urumqi;
The Indian Ocean Gordi Garcia US military base can pose a threat to the strategic hinterland of Yunnan and Guizhou;
The medium-range missiles deployed in the Central Asian West allies can threaten Xinjiang, Tibet, and the western half of China in the west of Xining, and of course threaten the entire European part of Russia;
Deployment in the US Aleutian Islands can threaten my capital Beijing and the Northeast, as well as the Russian Far East.
As a result, the entire territory of China will be threatened by the US medium-range missiles from the C-shaped encirclement, and some land areas may even overlap threats.
Strong technical reserves, and soon can form combat effectiveness. On the second day of the ADR, the US Secretary of Defense talked about the main deployment direction and time, that is, the Asia-Pacific direction, and strive to complete it by the end of this year.
The United States has made it possible to let the medium- and short-range missiles complete their deployment and form combat effectiveness as soon as possible. Prior to the "Guide to the Treaty", the US military was equipped with a large number of land-based medium-range missiles, such as the Pershing ground-to-ground missile, with a range of 1,600 kilometers and a hit accuracy of 40 meters. Even if it is destroyed or decommissioned, the technical reserve is still there. The latest intercontinental missiles and cruise missile technology are not difficult to move to medium- and short-range missiles.
In fact, the United States has done this. After the signing of the "Guidelines on the Treaty", the United States developed the theater anti-missile system and developed interceptor missiles that are very similar to medium-range missiles. They are replaced by warheads, and the interceptor becomes a missile. The United States has also used the pretext of countering Iranian and North Korean missiles to develop a simulated target projectile that can hit three or four thousand kilometers. It is actually a medium-range missile. When the United States abides by the "Guidelines on the Treaty" and does not develop medium- and short-range missiles, the Americans do not believe it or care. The Minister of National Defense made a sound after the abolition of the contract, and there was no face and no skin, almost shameless.
How to deal with the upcoming US mid-range missile threat?
First, the country that warned against the deployment of US missiles in advance will stand on the side of the United States if it accepts the deployment of US missiles, indicating that it is not friendly to me. Then I will reconsider economic trade and various contacts.
The second is to warn the countries concerned. If the United States launches missiles against the country in wartime, I will regard the country as an enemy. All the goals of the country are within my consideration of counterattacks, not just missile positions.
Third, if I strike against my deep core facilities (the wartime nuclear facilities are difficult for the United States to distinguish), I will counterattack. Fourth, as long as the United States deploys missiles, its launch system will be compiled into the target directory, and the relevant elements will be stored in computers. Once the war begins, the enemy first fires and is destroyed as the first target.
The author is the former deputy commander of the Nanjing Military Region.
- Joined
- Nov 29, 2016
- Messages
- 5,674
- Points
- 63
https://mil.news.sina.com.cn/china/2019-08-09/doc-ihytcerm9659151.shtml
中国如何应对美部署中导 80枚导弹就可打瘫美军基地
中国如何应对美部署中导 80枚导弹就可打瘫美军基地
416

多行不义必自毙:美国能否在亚太地区实现“中导霸权”1/15
查看原图图集模式
7月31日,美国政界著名鹰派人物,总统国安顾问博尔顿重申,美俄《中导条约》将于8月2日终止,美国届时将单方面退出。至当地时间8月2日,《中导条约》这一签署了32年的双边核军控条约彻底失效,成为一纸空文。在正式退约前的一星期,美国务卿蓬佩奥7月26日在接受福克斯新闻采访时表示,他不排除这样一种可能性,即美国会在亚太地区部署新型中程导弹。而在退约后的第二天,美国新任防长马克·埃斯珀对蓬佩奥这一说法表达了支持意愿。那么美国能否顺利如愿在亚洲部署中导?本期《出鞘》为您解读。















[环球网军事报道]美国8月2日正式退出《中导条约》,美国新任防长埃斯珀随即宣称将在亚洲部署陆基中程导弹。中近程导弹射程500公里~5500公里。这个距离的覆盖范围,西太方向大致包括第二岛链之内(含澳大利亚北部),印度洋方向戈迪加西亚群岛,中亚西亚方向美国各盟国,北美方向美国阿拉斯加的阿留申群岛。可以说,美国的中程导弹之弧,就是沿着军事战略专家戴旭前些年指出的“C形包围圈”部署。其重点在亚洲,即第一、第二岛链,近程导弹重在第一岛链。
 美军陆基“战斧”巡航导弹资料图。
美军陆基“战斧”巡航导弹资料图。
美方认为,第一岛链已残破不全,需要修补。近几年我海空军常态化出入第一岛链,进行例行训练,美国苦无相应的战力应对,日本也只能派机舰监视。为此,日本在宫古岛部署少量陆基反舰导弹,换装了少量两栖部队。这些举措,相对我战时出击第一岛链之外的强大军力,就是挠痒痒。美国兰德智库近期论证,我只要80发导弹,就能使美国在亚洲的56个基地瘫痪。这种说法可能夸大了我中近程导弹的威胁,但美国切实感受到我军的威慑,则是无疑的。
因此,美国加强了对第二岛链的经营,尤其是关岛和南太的基地建设,把部分易受打击、高价值的海空装备回撤到二线上来。那么,美军是要放弃第一岛链了吗?现在答案来了,不是放弃,而是以精干、只需少量人员操控的近程导弹补位,并辅以防空和岸舰导弹加以防卫,求得“性价比”最高的资源配置,仍在第一岛链与我争夺战场主动权。
 美军“潘兴”中程弹道导弹资料图。
美军“潘兴”中程弹道导弹资料图。
部署中导,目的在于对我战略纵深进行威胁和打击,破坏我战争潜力。射程5000公里的中程导弹部署在关岛,可对我乌鲁木齐以东的几乎全境产生直接威胁;印度洋戈迪加西亚美军基地可对云贵川战略腹地产生威胁;部署在中亚西亚盟国的中程导弹,可对我西宁以西的新疆、西藏、青海西半个中国产生威胁,当然也威胁俄罗斯欧洲部分全境。部署在美阿留申群岛,则可对我北方地区产生威胁,同时也威胁俄罗斯远东地区。由此,我国全境将受到来自“C形包围圈”美国中程导弹的威胁,有的地幅甚至是重叠威胁。
 美国用C-17空投发射“弹道导弹靶弹”,有关技术可以快速转化为实弹。
美国用C-17空投发射“弹道导弹靶弹”,有关技术可以快速转化为实弹。
美国技术储备雄厚,如果下定决心,或很快就能形成战斗力。废除《中导条约》第二天,美国防长就谈到主要部署方向和时间,即亚太方向。美国让中近程导弹尽快完成部署、形成战斗力,是有底气的。《中导条约》之前,美军装备了大量陆基中近程导弹,如潘兴地对地导弹,射程1600公里,命中精度40米。即使销毁或退役了,但技术储备还在。最新的洲际导弹和巡航导弹技术,迁移到中近程导弹上也不是什么难事。
其实美国已经这么干了。《中导条约》签订后,美国借开发战区反导系统,研制的拦截弹与中程导弹极其相似,换上弹头,拦截器即变导弹。美国还借口反击伊朗、朝鲜导弹,研制模拟靶弹,能打三四千公里,其实就是中程导弹。说美国遵守《中导条约》不发展中近程导弹,美国人自己都不相信,也不在乎。
 火箭军东风-26弹道导弹。对于打击出现在周边中程弹道,东风-16足以。
火箭军东风-26弹道导弹。对于打击出现在周边中程弹道,东风-16足以。
面对未来的美国中近程导弹威胁,该如何应对?
一是事先警告可能部署美国导弹的国家,如果接受美国导弹部署,就是站在美国一边,表示对我不友好。那么经济贸易和各方面交往,我将重新考虑。
二是警告有关国家,战时美国如果发射导弹打击我国,我将视该国为敌国,该国所有目标都在我考虑反击之内,而不仅仅是导弹阵地。
三是如果打击我纵深内核设施(战时核设施美国也难以分辨),我必予以核反击。
四是只要美国部署导弹,其发射系统都将被我编入打击目标目录,相关诸元储存于计算机。一旦开战,先敌开火,作为第一批目标予以摧毁。(作者王洪光,中将,原南京军区副司令员)
点击进入专题:
How can China respond to the US deployment of 80 missiles in the middle of the US military base?
How can China respond to the US deployment of 80 missiles in the middle of the US military base?
416
Many lines of injustice will be self-defeating: Can the United States achieve "middle-hegemony" in the Asia-Pacific region?
View original image gallery mode
On July 31, the famous hawks in the US political circles and Presidential Security Advisor Bolton reiterated that the US-Russian "Guidelines on the Treaty" will be terminated on August 2, and the United States will unilaterally withdraw. By August 2 local time, the "Guide to the Treaty", a 32-year bilateral nuclear arms control treaty, had completely failed and became a dead letter. One week before the official withdrawal, US Secretary of State Pompeo said in an interview with Fox News on July 26 that he did not rule out the possibility that the United States would deploy new medium-range missiles in the Asia-Pacific region. On the second day after the withdrawal, the new US Defense Secretary Mark Esper expressed his willingness to support Pompeo. So can the United States succeed in deploying a guide in Asia? This issue of "Sheathing" is for you to interpret.
[Global Network Military Report] The United States officially withdrew from the "Guidelines on the Treaty" on August 2, and the new US Defense Secretary Espour immediately announced that it would deploy land-based medium-range missiles in Asia. The medium-range and short-range missiles range from 500 kilometers to 5,500 kilometers. The coverage of this distance, the West Pacific direction generally includes the second island chain (including northern Australia), the Indian Ocean direction of the Gordigas, the Central Asian countries to the United States allies, North America to the United States Alaska Aleutian Islands. It can be said that the arc of the medium-range missile of the United States is deployed along the "C-shaped encirclement" pointed out by the military strategy expert Dai Xu in the past few years. Its focus is on Asia, the first and second island chains, and the short-range missiles are on the first island chain.
US Army Land-based "Tomahawk" cruise missile data map. US Army Land-based "Tomahawk" cruise missile data map.
The US believes that the first island chain has been broken and needs to be repaired. In recent years, China's naval air force has normalized its access to the first island chain and conducted routine training. The United States has no corresponding combat power to deal with it. Japan can only send surveillance to ships. To this end, Japan deployed a small number of land-based anti-ship missiles on Miyako Island and replaced a small number of amphibious units. These measures, compared to the strong military force outside the first island chain in my war, is tickling. The US RAND think tank recently demonstrated that with only 80 missiles, I can make the United States 56 bases in Asia. This statement may exaggerate the threat of my medium-range missiles, but the United States really feels the deterrent of our army, it is undoubted.
Therefore, the United States has strengthened its operations on the second island chain, especially the construction of bases in Guam and Nantai, and has withdrawn some of the vulnerable and high-value air and sea equipment to the second line. So, is the US military going to give up the first island chain? Now the answer is coming, not giving up, but using a lean, short-range missile to control the short-range missiles, supplemented by air defense and shore-to-ship missiles to defend, and the most cost-effective resource allocation is still in the first place. The island chain competes with me for the initiative of the battlefield.
US military "Pershing" medium-range ballistic missile data map. US military "Pershing" medium-range ballistic missile data map.
The purpose of the deployment is to threaten and strike against my strategic depth and undermine the potential of my war. The medium-range missile with a range of 5,000 kilometers is deployed in Guam, which can directly threaten the entire territory of the east of Urumqi. The Indian Ocean Gordi Garcia US military base can pose a threat to the strategic hinterland of Yunnan and Guizhou; it is deployed in the middle reaches of the Central Asian Union allies. The missiles can threaten China, Tibet, and the western half of China in the west of Xining, and of course threaten the entire part of Russia and Europe. The deployment in the Aleutian Islands can threaten the northern region of China and threaten the Russian Far East. As a result, the entire territory of China will be threatened by the "C-shaped encirclement" of US medium-range missiles, and some of them even overlap threats.
The United States used the C-17 airdrop to launch a "ballistic missile target", and the technology could be quickly converted into live ammunition. The United States used the C-17 airdrop to launch a "ballistic missile target", and the technology could be quickly converted into live ammunition.
The US has a strong technical reserve, and if it makes up its mind, it will soon be able to form combat power. On the second day of the abolition of the "Guidelines on the Treaty", the US Defense Minister talked about the main direction and time of deployment, that is, the Asia-Pacific direction. The United States has made it possible to let the medium- and short-range missiles complete their deployment and form combat effectiveness as soon as possible. Prior to the "Guide to the Treaty", the US military was equipped with a large number of land-based medium-range missiles, such as the Pershing ground-to-ground missile, with a range of 1,600 kilometers and a hit accuracy of 40 meters. Even if it is destroyed or decommissioned, the technical reserve is still there. The latest intercontinental missiles and cruise missile technology are not difficult to move to medium- and short-range missiles.
In fact, the United States has done this. After the signing of the "Guide to the China-Treaty Treaty", the United States developed a theater anti-missile system, and the interceptor missile developed is very similar to the medium-range missile. The warhead is replaced by a warhead. The United States has also used the pretext of countering Iranian and North Korean missiles to develop a simulated target projectile that can hit three or four thousand kilometers. It is actually a medium-range missile. When the United States abides by the "Guidelines on the Treaty" and does not develop medium- and short-range missiles, the Americans do not believe it or care.
Rocket Army Dongfeng-26 ballistic missile. For the blow to appear in the mid-range trajectory around, the Dongfeng-16 is enough. Rocket Army Dongfeng-26 ballistic missile. For the blow to appear in the mid-range trajectory around, the Dongfeng-16 is enough.
How to deal with the future US mid-range missile threat?
First, the country that warned against the deployment of US missiles in advance will stand on the side of the United States if it accepts the deployment of US missiles, indicating that it is not friendly to me. Then I will reconsider economic trade and various contacts.
The second is to warn the countries concerned. If the United States launches missiles against the country in wartime, I will regard the country as an enemy. All the goals of the country are within my consideration of counterattacks, not just missile positions.
Third, if I strike against my deep core facilities (the wartime nuclear facilities are difficult for the United States to distinguish), I will counterattack.
Fourth, as long as the United States deploys missiles, its launch system will be compiled into the target directory, and the relevant elements will be stored in computers. Once the war begins, the enemy first fires and is destroyed as the first target. (Author Wang Hongguang, Lieutenant General, former commander of the Nanjing Military Region)
Click to enter the topic:
中国如何应对美部署中导 80枚导弹就可打瘫美军基地
中国如何应对美部署中导 80枚导弹就可打瘫美军基地
416

多行不义必自毙:美国能否在亚太地区实现“中导霸权”1/15
查看原图图集模式
7月31日,美国政界著名鹰派人物,总统国安顾问博尔顿重申,美俄《中导条约》将于8月2日终止,美国届时将单方面退出。至当地时间8月2日,《中导条约》这一签署了32年的双边核军控条约彻底失效,成为一纸空文。在正式退约前的一星期,美国务卿蓬佩奥7月26日在接受福克斯新闻采访时表示,他不排除这样一种可能性,即美国会在亚太地区部署新型中程导弹。而在退约后的第二天,美国新任防长马克·埃斯珀对蓬佩奥这一说法表达了支持意愿。那么美国能否顺利如愿在亚洲部署中导?本期《出鞘》为您解读。















[环球网军事报道]美国8月2日正式退出《中导条约》,美国新任防长埃斯珀随即宣称将在亚洲部署陆基中程导弹。中近程导弹射程500公里~5500公里。这个距离的覆盖范围,西太方向大致包括第二岛链之内(含澳大利亚北部),印度洋方向戈迪加西亚群岛,中亚西亚方向美国各盟国,北美方向美国阿拉斯加的阿留申群岛。可以说,美国的中程导弹之弧,就是沿着军事战略专家戴旭前些年指出的“C形包围圈”部署。其重点在亚洲,即第一、第二岛链,近程导弹重在第一岛链。

美方认为,第一岛链已残破不全,需要修补。近几年我海空军常态化出入第一岛链,进行例行训练,美国苦无相应的战力应对,日本也只能派机舰监视。为此,日本在宫古岛部署少量陆基反舰导弹,换装了少量两栖部队。这些举措,相对我战时出击第一岛链之外的强大军力,就是挠痒痒。美国兰德智库近期论证,我只要80发导弹,就能使美国在亚洲的56个基地瘫痪。这种说法可能夸大了我中近程导弹的威胁,但美国切实感受到我军的威慑,则是无疑的。
因此,美国加强了对第二岛链的经营,尤其是关岛和南太的基地建设,把部分易受打击、高价值的海空装备回撤到二线上来。那么,美军是要放弃第一岛链了吗?现在答案来了,不是放弃,而是以精干、只需少量人员操控的近程导弹补位,并辅以防空和岸舰导弹加以防卫,求得“性价比”最高的资源配置,仍在第一岛链与我争夺战场主动权。

部署中导,目的在于对我战略纵深进行威胁和打击,破坏我战争潜力。射程5000公里的中程导弹部署在关岛,可对我乌鲁木齐以东的几乎全境产生直接威胁;印度洋戈迪加西亚美军基地可对云贵川战略腹地产生威胁;部署在中亚西亚盟国的中程导弹,可对我西宁以西的新疆、西藏、青海西半个中国产生威胁,当然也威胁俄罗斯欧洲部分全境。部署在美阿留申群岛,则可对我北方地区产生威胁,同时也威胁俄罗斯远东地区。由此,我国全境将受到来自“C形包围圈”美国中程导弹的威胁,有的地幅甚至是重叠威胁。

美国技术储备雄厚,如果下定决心,或很快就能形成战斗力。废除《中导条约》第二天,美国防长就谈到主要部署方向和时间,即亚太方向。美国让中近程导弹尽快完成部署、形成战斗力,是有底气的。《中导条约》之前,美军装备了大量陆基中近程导弹,如潘兴地对地导弹,射程1600公里,命中精度40米。即使销毁或退役了,但技术储备还在。最新的洲际导弹和巡航导弹技术,迁移到中近程导弹上也不是什么难事。
其实美国已经这么干了。《中导条约》签订后,美国借开发战区反导系统,研制的拦截弹与中程导弹极其相似,换上弹头,拦截器即变导弹。美国还借口反击伊朗、朝鲜导弹,研制模拟靶弹,能打三四千公里,其实就是中程导弹。说美国遵守《中导条约》不发展中近程导弹,美国人自己都不相信,也不在乎。

面对未来的美国中近程导弹威胁,该如何应对?
一是事先警告可能部署美国导弹的国家,如果接受美国导弹部署,就是站在美国一边,表示对我不友好。那么经济贸易和各方面交往,我将重新考虑。
二是警告有关国家,战时美国如果发射导弹打击我国,我将视该国为敌国,该国所有目标都在我考虑反击之内,而不仅仅是导弹阵地。
三是如果打击我纵深内核设施(战时核设施美国也难以分辨),我必予以核反击。
四是只要美国部署导弹,其发射系统都将被我编入打击目标目录,相关诸元储存于计算机。一旦开战,先敌开火,作为第一批目标予以摧毁。(作者王洪光,中将,原南京军区副司令员)
点击进入专题:
How can China respond to the US deployment of 80 missiles in the middle of the US military base?
How can China respond to the US deployment of 80 missiles in the middle of the US military base?
416
Many lines of injustice will be self-defeating: Can the United States achieve "middle-hegemony" in the Asia-Pacific region?
View original image gallery mode
On July 31, the famous hawks in the US political circles and Presidential Security Advisor Bolton reiterated that the US-Russian "Guidelines on the Treaty" will be terminated on August 2, and the United States will unilaterally withdraw. By August 2 local time, the "Guide to the Treaty", a 32-year bilateral nuclear arms control treaty, had completely failed and became a dead letter. One week before the official withdrawal, US Secretary of State Pompeo said in an interview with Fox News on July 26 that he did not rule out the possibility that the United States would deploy new medium-range missiles in the Asia-Pacific region. On the second day after the withdrawal, the new US Defense Secretary Mark Esper expressed his willingness to support Pompeo. So can the United States succeed in deploying a guide in Asia? This issue of "Sheathing" is for you to interpret.
[Global Network Military Report] The United States officially withdrew from the "Guidelines on the Treaty" on August 2, and the new US Defense Secretary Espour immediately announced that it would deploy land-based medium-range missiles in Asia. The medium-range and short-range missiles range from 500 kilometers to 5,500 kilometers. The coverage of this distance, the West Pacific direction generally includes the second island chain (including northern Australia), the Indian Ocean direction of the Gordigas, the Central Asian countries to the United States allies, North America to the United States Alaska Aleutian Islands. It can be said that the arc of the medium-range missile of the United States is deployed along the "C-shaped encirclement" pointed out by the military strategy expert Dai Xu in the past few years. Its focus is on Asia, the first and second island chains, and the short-range missiles are on the first island chain.
US Army Land-based "Tomahawk" cruise missile data map. US Army Land-based "Tomahawk" cruise missile data map.
The US believes that the first island chain has been broken and needs to be repaired. In recent years, China's naval air force has normalized its access to the first island chain and conducted routine training. The United States has no corresponding combat power to deal with it. Japan can only send surveillance to ships. To this end, Japan deployed a small number of land-based anti-ship missiles on Miyako Island and replaced a small number of amphibious units. These measures, compared to the strong military force outside the first island chain in my war, is tickling. The US RAND think tank recently demonstrated that with only 80 missiles, I can make the United States 56 bases in Asia. This statement may exaggerate the threat of my medium-range missiles, but the United States really feels the deterrent of our army, it is undoubted.
Therefore, the United States has strengthened its operations on the second island chain, especially the construction of bases in Guam and Nantai, and has withdrawn some of the vulnerable and high-value air and sea equipment to the second line. So, is the US military going to give up the first island chain? Now the answer is coming, not giving up, but using a lean, short-range missile to control the short-range missiles, supplemented by air defense and shore-to-ship missiles to defend, and the most cost-effective resource allocation is still in the first place. The island chain competes with me for the initiative of the battlefield.
US military "Pershing" medium-range ballistic missile data map. US military "Pershing" medium-range ballistic missile data map.
The purpose of the deployment is to threaten and strike against my strategic depth and undermine the potential of my war. The medium-range missile with a range of 5,000 kilometers is deployed in Guam, which can directly threaten the entire territory of the east of Urumqi. The Indian Ocean Gordi Garcia US military base can pose a threat to the strategic hinterland of Yunnan and Guizhou; it is deployed in the middle reaches of the Central Asian Union allies. The missiles can threaten China, Tibet, and the western half of China in the west of Xining, and of course threaten the entire part of Russia and Europe. The deployment in the Aleutian Islands can threaten the northern region of China and threaten the Russian Far East. As a result, the entire territory of China will be threatened by the "C-shaped encirclement" of US medium-range missiles, and some of them even overlap threats.
The United States used the C-17 airdrop to launch a "ballistic missile target", and the technology could be quickly converted into live ammunition. The United States used the C-17 airdrop to launch a "ballistic missile target", and the technology could be quickly converted into live ammunition.
The US has a strong technical reserve, and if it makes up its mind, it will soon be able to form combat power. On the second day of the abolition of the "Guidelines on the Treaty", the US Defense Minister talked about the main direction and time of deployment, that is, the Asia-Pacific direction. The United States has made it possible to let the medium- and short-range missiles complete their deployment and form combat effectiveness as soon as possible. Prior to the "Guide to the Treaty", the US military was equipped with a large number of land-based medium-range missiles, such as the Pershing ground-to-ground missile, with a range of 1,600 kilometers and a hit accuracy of 40 meters. Even if it is destroyed or decommissioned, the technical reserve is still there. The latest intercontinental missiles and cruise missile technology are not difficult to move to medium- and short-range missiles.
In fact, the United States has done this. After the signing of the "Guide to the China-Treaty Treaty", the United States developed a theater anti-missile system, and the interceptor missile developed is very similar to the medium-range missile. The warhead is replaced by a warhead. The United States has also used the pretext of countering Iranian and North Korean missiles to develop a simulated target projectile that can hit three or four thousand kilometers. It is actually a medium-range missile. When the United States abides by the "Guidelines on the Treaty" and does not develop medium- and short-range missiles, the Americans do not believe it or care.
Rocket Army Dongfeng-26 ballistic missile. For the blow to appear in the mid-range trajectory around, the Dongfeng-16 is enough. Rocket Army Dongfeng-26 ballistic missile. For the blow to appear in the mid-range trajectory around, the Dongfeng-16 is enough.
How to deal with the future US mid-range missile threat?
First, the country that warned against the deployment of US missiles in advance will stand on the side of the United States if it accepts the deployment of US missiles, indicating that it is not friendly to me. Then I will reconsider economic trade and various contacts.
The second is to warn the countries concerned. If the United States launches missiles against the country in wartime, I will regard the country as an enemy. All the goals of the country are within my consideration of counterattacks, not just missile positions.
Third, if I strike against my deep core facilities (the wartime nuclear facilities are difficult for the United States to distinguish), I will counterattack.
Fourth, as long as the United States deploys missiles, its launch system will be compiled into the target directory, and the relevant elements will be stored in computers. Once the war begins, the enemy first fires and is destroyed as the first target. (Author Wang Hongguang, Lieutenant General, former commander of the Nanjing Military Region)
Click to enter the topic:
- Joined
- Nov 29, 2016
- Messages
- 5,674
- Points
- 63
https://mil.news.sina.com.cn/2019-08-09/doc-ihytcerm9651130.shtml
俄媒:中国可用4款导弹反制美军在亚太部署中导
俄媒:中国可用4款导弹反制美军在亚太部署中导
194

多行不义必自毙:美国能否在亚太地区实现“中导霸权”1/15
查看原图图集模式
7月31日,美国政界著名鹰派人物,总统国安顾问博尔顿重申,美俄《中导条约》将于8月2日终止,美国届时将单方面退出。至当地时间8月2日,《中导条约》这一签署了32年的双边核军控条约彻底失效,成为一纸空文。在正式退约前的一星期,美国务卿蓬佩奥7月26日在接受福克斯新闻采访时表示,他不排除这样一种可能性,即美国会在亚太地区部署新型中程导弹。而在退约后的第二天,美国新任防长马克·埃斯珀对蓬佩奥这一说法表达了支持意愿。那么美国能否顺利如愿在亚洲部署中导?本期《出鞘》为您解读。















参考消息网8月9日报道 俄罗斯报纸网8月7日发表了题为《在亚洲部署导弹:中国如何反击美国》的报道,文章编译如下:
中国对美国研制和试验陆基中程导弹的计划表示关切,并指出若华盛顿在亚太地区部署这些导弹将予以反制。
中国外交部军控司司长傅聪在吹风会上呼吁美国方面保持克制,一旦美国采取行动中方将被迫进行反制。不过,这位外交官没有具体说明是哪些反制措施。他表示,中国不会坐视美国在该地区部署陆基中程导弹。
俄罗斯战略和技术分析中心副主任康斯坦丁·马基延科介绍说:“中国人民解放军有不少让美国人忌惮的武器和军事装备。首先是使用东风-21D和东风-26反舰弹道导弹系统。这2种导弹系统用于保护领海及沿海地区。东风-21D和东风-26在中国被称为‘航母杀手’。”
东风-21D系统是机动式中程弹道导弹发射平台。导弹最大射程1450公里、飞行速度10马赫,使用非核弹头。

资料图片:参加2015年中国抗战胜利日阅兵的东风-21D导弹发射车方队。

资料图片:阅兵式上的中国东风-26弹道导弹发射车方队。(图片来源于网络)
新型的东风-26反舰弹道导弹系统也拥有强大战力,这种导弹能对地面目标和大中型舰艇实施精准打击,并参与核反击。
中国军方称,东风-21D和东风-26是用于防御目的,不是为了攻击别国。
马基延科指出:“中国对美国的洲际弹道导弹反击也同样具有威慑力。”中国人民解放军现在装备了东风-31/东风-31A公路机动式洲际导弹系统。
东风-31A是3级固体燃料导弹,射程超过1.1万公里。东风-31A导弹命中精度在100到1000米之间,但多数专家接受的估值是300米,这对洲际弹道导弹来说已经相当高了。
马基延科提醒,中国也能从空中发动“雷霆一击”。中国空军装备了轰-6K战略轰炸机。它能携带6枚长剑-10A远程巡航导弹(射程约3000公里)。
马基延科总结道:“如此看来,中国对美国在亚太地区部署中程导弹的军事反制,可能令华盛顿相当痛苦。”

资料图片:挂载巡航导弹的中国空军轰-6K轰炸机。(图片来源于网络)
Russian media: China can use four missiles to counter the US military's deployment in the Asia-Pacific
Russian media: China can use four missiles to counter the US military's deployment in the Asia-Pacific
194
Many lines of injustice will be self-defeating: Can the United States achieve "middle-hegemony" in the Asia-Pacific region?
View original image gallery mode
On July 31, the famous hawks in the US political circles and Presidential Security Advisor Bolton reiterated that the US-Russian "Guidelines on the Treaty" will be terminated on August 2, and the United States will unilaterally withdraw. By August 2 local time, the "Guide to the Treaty", a 32-year bilateral nuclear arms control treaty, had completely failed and became a dead letter. One week before the official withdrawal, US Secretary of State Pompeo said in an interview with Fox News on July 26 that he did not rule out the possibility that the United States would deploy new medium-range missiles in the Asia-Pacific region. On the second day after the withdrawal, the new US Defense Secretary Mark Esper expressed his willingness to support Pompeo. So can the United States succeed in deploying a guide in Asia? This issue of "Sheathing" is for you to interpret.
Reference News Network reported on August 9 Russian newspaper network published on August 7th entitled "Deploying missiles in Asia: how China counterattacks the United States" report, the article compiled as follows:
China expressed concern about the US plan to develop and test land-based medium-range missiles, and pointed out that if Washington deploys these missiles in the Asia-Pacific region, it will be countered.
Fu Cong, director of the Arms Control Department of the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs, called on the US side to exercise restraint at the briefing. Once the United States takes action, China will be forced to counter it. However, the diplomat did not specify what countermeasures were in place. He said that China will not sit idly by the United States to deploy land-based medium-range missiles in the region.
Konstantin Makiyanko, deputy director of the Russian Center for Strategic and Technical Analysis, said: "The Chinese People's Liberation Army has many weapons and military equipment that make Americans jealous. The first is the use of Dongfeng-21D and Dongfeng-26 anti-ship ballistic missiles. System. These two missile systems are used to protect the territorial sea and coastal areas. Dongfeng-21D and Dongfeng-26 are known as 'aircraft carrier killers' in China."
The Dongfeng-21D system is a mobile medium-range ballistic missile launching platform. The missile has a maximum range of 1,450 kilometers and a speed of 10 Mach, using non-nuclear warheads.
Profile photo: Participated in the Dongfeng-21D missile launch vehicle team of the 2015 China Anti-Japanese War Victory Day parade.
Profile picture: China Dongfeng-26 ballistic missile launch vehicle team on the parade. (Image from the network)
The new Dongfeng-26 anti-ship ballistic missile system also has a powerful combat capability. It can accurately strike ground targets and large and medium-sized ships and participate in nuclear counterattacks.
The Chinese military said that Dongfeng-21D and Dongfeng-26 were used for defensive purposes, not to attack other countries.
Makiyanke pointed out: "China's counter-attacks on intercontinental ballistic missiles against the United States are equally deterrent." The Chinese People's Liberation Army is now equipped with the Dongfeng-31/Dongfeng-31A highway mobile intercontinental missile system.
The Dongfeng-31A is a Class 3 solid fuel missile with a range of more than 11,000 kilometers. The Dongfeng-31A missile hit accuracy is between 100 and 1000 meters, but most experts accept a valuation of 300 meters, which is quite high for intercontinental ballistic missiles.
Makiyanke reminded that China can also launch a "Thunder strike" from the air. The Chinese Air Force is equipped with a H-6K strategic bomber. It can carry 6 long-sword-10A long-range cruise missiles (with a range of about 3,000 kilometers).
Makiyanke concluded: "It seems that China's military counter-measure of the deployment of medium-range missiles by the United States in the Asia-Pacific region may make Washington quite painful."
Profile picture: China Air Force H-6K bomber with cruise missiles mounted. (Image from the network)
俄媒:中国可用4款导弹反制美军在亚太部署中导
俄媒:中国可用4款导弹反制美军在亚太部署中导
194

多行不义必自毙:美国能否在亚太地区实现“中导霸权”1/15
查看原图图集模式
7月31日,美国政界著名鹰派人物,总统国安顾问博尔顿重申,美俄《中导条约》将于8月2日终止,美国届时将单方面退出。至当地时间8月2日,《中导条约》这一签署了32年的双边核军控条约彻底失效,成为一纸空文。在正式退约前的一星期,美国务卿蓬佩奥7月26日在接受福克斯新闻采访时表示,他不排除这样一种可能性,即美国会在亚太地区部署新型中程导弹。而在退约后的第二天,美国新任防长马克·埃斯珀对蓬佩奥这一说法表达了支持意愿。那么美国能否顺利如愿在亚洲部署中导?本期《出鞘》为您解读。















参考消息网8月9日报道 俄罗斯报纸网8月7日发表了题为《在亚洲部署导弹:中国如何反击美国》的报道,文章编译如下:
中国对美国研制和试验陆基中程导弹的计划表示关切,并指出若华盛顿在亚太地区部署这些导弹将予以反制。
中国外交部军控司司长傅聪在吹风会上呼吁美国方面保持克制,一旦美国采取行动中方将被迫进行反制。不过,这位外交官没有具体说明是哪些反制措施。他表示,中国不会坐视美国在该地区部署陆基中程导弹。
俄罗斯战略和技术分析中心副主任康斯坦丁·马基延科介绍说:“中国人民解放军有不少让美国人忌惮的武器和军事装备。首先是使用东风-21D和东风-26反舰弹道导弹系统。这2种导弹系统用于保护领海及沿海地区。东风-21D和东风-26在中国被称为‘航母杀手’。”
东风-21D系统是机动式中程弹道导弹发射平台。导弹最大射程1450公里、飞行速度10马赫,使用非核弹头。

资料图片:参加2015年中国抗战胜利日阅兵的东风-21D导弹发射车方队。

资料图片:阅兵式上的中国东风-26弹道导弹发射车方队。(图片来源于网络)
新型的东风-26反舰弹道导弹系统也拥有强大战力,这种导弹能对地面目标和大中型舰艇实施精准打击,并参与核反击。
中国军方称,东风-21D和东风-26是用于防御目的,不是为了攻击别国。
马基延科指出:“中国对美国的洲际弹道导弹反击也同样具有威慑力。”中国人民解放军现在装备了东风-31/东风-31A公路机动式洲际导弹系统。
东风-31A是3级固体燃料导弹,射程超过1.1万公里。东风-31A导弹命中精度在100到1000米之间,但多数专家接受的估值是300米,这对洲际弹道导弹来说已经相当高了。
马基延科提醒,中国也能从空中发动“雷霆一击”。中国空军装备了轰-6K战略轰炸机。它能携带6枚长剑-10A远程巡航导弹(射程约3000公里)。
马基延科总结道:“如此看来,中国对美国在亚太地区部署中程导弹的军事反制,可能令华盛顿相当痛苦。”

资料图片:挂载巡航导弹的中国空军轰-6K轰炸机。(图片来源于网络)
Russian media: China can use four missiles to counter the US military's deployment in the Asia-Pacific
Russian media: China can use four missiles to counter the US military's deployment in the Asia-Pacific
194
Many lines of injustice will be self-defeating: Can the United States achieve "middle-hegemony" in the Asia-Pacific region?
View original image gallery mode
On July 31, the famous hawks in the US political circles and Presidential Security Advisor Bolton reiterated that the US-Russian "Guidelines on the Treaty" will be terminated on August 2, and the United States will unilaterally withdraw. By August 2 local time, the "Guide to the Treaty", a 32-year bilateral nuclear arms control treaty, had completely failed and became a dead letter. One week before the official withdrawal, US Secretary of State Pompeo said in an interview with Fox News on July 26 that he did not rule out the possibility that the United States would deploy new medium-range missiles in the Asia-Pacific region. On the second day after the withdrawal, the new US Defense Secretary Mark Esper expressed his willingness to support Pompeo. So can the United States succeed in deploying a guide in Asia? This issue of "Sheathing" is for you to interpret.
Reference News Network reported on August 9 Russian newspaper network published on August 7th entitled "Deploying missiles in Asia: how China counterattacks the United States" report, the article compiled as follows:
China expressed concern about the US plan to develop and test land-based medium-range missiles, and pointed out that if Washington deploys these missiles in the Asia-Pacific region, it will be countered.
Fu Cong, director of the Arms Control Department of the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs, called on the US side to exercise restraint at the briefing. Once the United States takes action, China will be forced to counter it. However, the diplomat did not specify what countermeasures were in place. He said that China will not sit idly by the United States to deploy land-based medium-range missiles in the region.
Konstantin Makiyanko, deputy director of the Russian Center for Strategic and Technical Analysis, said: "The Chinese People's Liberation Army has many weapons and military equipment that make Americans jealous. The first is the use of Dongfeng-21D and Dongfeng-26 anti-ship ballistic missiles. System. These two missile systems are used to protect the territorial sea and coastal areas. Dongfeng-21D and Dongfeng-26 are known as 'aircraft carrier killers' in China."
The Dongfeng-21D system is a mobile medium-range ballistic missile launching platform. The missile has a maximum range of 1,450 kilometers and a speed of 10 Mach, using non-nuclear warheads.
Profile photo: Participated in the Dongfeng-21D missile launch vehicle team of the 2015 China Anti-Japanese War Victory Day parade.
Profile picture: China Dongfeng-26 ballistic missile launch vehicle team on the parade. (Image from the network)
The new Dongfeng-26 anti-ship ballistic missile system also has a powerful combat capability. It can accurately strike ground targets and large and medium-sized ships and participate in nuclear counterattacks.
The Chinese military said that Dongfeng-21D and Dongfeng-26 were used for defensive purposes, not to attack other countries.
Makiyanke pointed out: "China's counter-attacks on intercontinental ballistic missiles against the United States are equally deterrent." The Chinese People's Liberation Army is now equipped with the Dongfeng-31/Dongfeng-31A highway mobile intercontinental missile system.
The Dongfeng-31A is a Class 3 solid fuel missile with a range of more than 11,000 kilometers. The Dongfeng-31A missile hit accuracy is between 100 and 1000 meters, but most experts accept a valuation of 300 meters, which is quite high for intercontinental ballistic missiles.
Makiyanke reminded that China can also launch a "Thunder strike" from the air. The Chinese Air Force is equipped with a H-6K strategic bomber. It can carry 6 long-sword-10A long-range cruise missiles (with a range of about 3,000 kilometers).
Makiyanke concluded: "It seems that China's military counter-measure of the deployment of medium-range missiles by the United States in the Asia-Pacific region may make Washington quite painful."
Profile picture: China Air Force H-6K bomber with cruise missiles mounted. (Image from the network)
- Joined
- Nov 29, 2016
- Messages
- 5,674
- Points
- 63
https://mil.news.sina.com.cn/jssd/2019-08-09/doc-ihytcitm8046525.shtml
伊朗参加坦克大赛坦言俄T72不如中国96B 或有意采购
2019年08月09日 16:56 新浪军事
66

坦克两项中国第三车组惜夺第二 将挺进半决赛1/6
查看原图图集模式
8月7日,在俄罗斯阿拉比诺靶场举行2019国际军事比赛“坦克两项”赛事迎来小组赛的第三场,中国代表队的第三车组最终以24分36秒的成绩夺得小组第二名。






 燃起浓烟的伊朗队T-73B3
燃起浓烟的伊朗队T-73B3
近日,据媒体报道,8月3日开幕的“国际军事比赛-2019”正在多个国家火热进行中。诸多项目中,最引人注目的莫过于“坦克两项”比赛。从2014年开始举办至今,一直在俄罗斯阿拉比诺训练场举行的“坦克两项”已经进入了第六个年头。但是,这两天的赛场上却发生一些让人意想不到的危险状况,伊朗队在驾驶T-72B3坦克进行比赛时,车辆燃起浓烟,状况十分危险,导致伊朗队紧急换车,耽误了较多时间。
 俄罗斯T-72B3M
俄罗斯T-72B3M
据赛事官方提供的资料显示,参加“坦克两项”比赛的十余个参赛国,除了中国与俄罗斯,其他队伍均使用俄罗斯提供的T-72B3坦克参加比赛。中国派出的是国产96B型主战坦克,而俄罗斯使用的是T-72B3的进一步改进型T-72B3M(也被称为“终极T-72”)。96B自从2016年参加“坦克两项”以来,表现都非常稳定,无论是动力系统还是火控系统都经受住了考验。
 已多次参加“坦克两项”的96B
已多次参加“坦克两项”的96B
事故发生之后,伊朗代表队有人指出,经过多届的比赛确实可以看出,T-72B3在所有性能上都与解放军的96B有一定差距差距。其实,“坦克两项”比赛的课目设置,其实并不是特别实战化,有点类似于赛车。比赛过程中,车组需要对三个坦克靶进行主炮射击,然后使用高射机枪对直升机靶进行射击,使用并列机枪对RPG射手靶进行射击,除此之外,还需要驾驶员有特别优秀的驾驶技巧,坦克车也需要有优秀的动力系统,毕竟“坦克两项”是个计时赛而不是积分赛。
 2019年参加“坦克两项”的96B
2019年参加“坦克两项”的96B
伊朗方面所言不虚。目前来说,我国的96B坦克已经全面超越了俄罗斯的T-72B3甚至是T-72B3M。动力上来说,目前96B采用的是我国自行研制的“新150”系列V8发动机,动力超过1000马力。尽管仍略低于俄罗斯T-72B3M的1130马力,但是由于96B采用了先进的综合液力自动变速箱,操控性能非常优秀,简单来说,就和开自动挡的汽车一样,使用方向盘操控,脚下只需要踩油门和刹车。而T-72系列都还是传统的老式机械传动,使用操纵杆控制,对驾驶员的体力要求和技术要求都非常高。
 伊朗军队现役的T-72坦克
伊朗军队现役的T-72坦克
从火控和火力系统上来说,两者的差距可谓是更大。尽管96B坦克的125毫米坦克炮从技术来源上来讲,源自于上世纪80年代我国从罗马尼亚获得的一辆T-72上的2A46M坦克炮。但是我国并不是简单的对其进行仿制,而是改进了其一系列的弊端,精度、炮弹初速和威力都大大提高。从火控的角度来说,T-72系列目前使用的是下反稳像式火控系统,落后于目前我军的96B上装备的世界先进水平的上反稳像式火控系统。
 VT-2B外贸主战坦克
VT-2B外贸主战坦克
除此之外,96B在装甲、可维护性等方面也胜过T-72B3。更何况,96B的外观也更符合现在人们对于先进坦克的概念。96B也有其对应的外贸型号,那就是VT-2B。目前,伊朗军队装备的仍然是早期型号的T-72,性能与目前的VT-2B完全不可同日而语。况且,伊朗军队也装备有大量的中国59式和69式坦克,从中国购买相对物美价廉的VT-2B来替换其老旧的坦克阵容也不失为一个方法,从中国采购军备也不会有附加政治条款。(作者:兔子蹬鹰)
Iran participates in the tank competition and admits that the Russian T72 is not as good as China 96B or intends to purchase
August 09, 2019 16:56 Sina Military
66
The two Chinese tanks of the tank won the second place and will advance to the semifinals 1/6.
View original image gallery mode
On August 7th, at the Alabino shooting range in Russia, the 2019 international military competition "Tank Two" event ushered in the third game of the group stage. The third team of the Chinese team finally won the group with 24 minutes and 36 seconds. Second place.
Iranian team T-73B3, which is burning smoke, is burning Iranian T-73B3
Recently, according to media reports, the "International Military Competition - 2019", which opened on August 3, is in full swing in many countries. Among the many projects, the most striking is the "two tanks" competition. Since its inception in 2014, the “Tank Two” that has been held at the Arabino training ground in Russia has entered its sixth year. However, there were some unexpected dangerous situations on the two days of the game. When the Iranian team was driving the T-72B3 tank, the vehicles ignited heavy smoke and the situation was very dangerous, causing the Iranian team to change the car urgently. More time.
Russia T-72B3M Russia T-72B3M
According to the official information provided by the event, more than a dozen participating countries participating in the "Colour Two Tanks" competition, except China and Russia, used the T-72B3 tank provided by Russia to participate in the competition. China sent the domestic 96B main battle tank, while Russia used the T-72B3 further improved T-72B3M (also known as the "ultimate T-72"). Since the 96B participated in the "tank two" in 2016, the performance has been very stable, and both the power system and the fire control system have withstood the test.
96B, who has participated in the "tank two" multiple times, has participated in the "tank two" 96B many times.
After the accident, the Iranian team pointed out that after several sessions, it can be seen that the T-72B3 has a certain gap with the PLA 96B in all performances. In fact, the setting of the "two tanks" competition is not particularly combative, and is somewhat similar to racing. During the competition, the team needs to shoot the main guns of the three tank targets, then use the high-altitude machine guns to shoot the helicopter targets, and use the parallel machine guns to shoot the RPG shooter targets. In addition, the driver needs to be particularly excellent. Driving skills, tanks also need to have an excellent power system, after all, "tank two" is a time trial rather than a points game.
In 2019, participated in the "tank two" 96B2019 to participate in the "tank two" 96B
The Iranian side is full of words. At present, China's 96B tank has completely surpassed Russia's T-72B3 and even T-72B3M. In terms of power, the current 96B adopts the "new 150" series V8 engine developed by China itself, with a power of more than 1000 horsepower. Although still slightly lower than the 1130 hp of the Russian T-72B3M, the 96B uses an advanced integrated hydraulic automatic transmission, which has excellent handling performance. Simply put, like the automatic car, use the steering wheel to control the foot. Just step on the throttle and brakes. The T-72 series is still a traditional old-fashioned mechanical transmission, using the joystick control, the driver's physical requirements and technical requirements are very high.
T-72 tanks in active service of the Iranian army T-72 tanks in active service of the Iranian army
From the perspective of fire control and firepower systems, the gap between the two can be said to be even greater. Although the 125mm tank gun of the 96B tank is derived from the technical source, it originated from the 2A46M tank gun on a T-72 that China obtained from Romania in the 1980s. However, China is not simply imitating it, but has improved its series of drawbacks. The accuracy, the initial velocity and the power of the shells have been greatly improved. From the perspective of fire control, the T-72 series currently uses the lower anti-stabilized fire control system, which is behind the current world-class anti-stabilized image fire control system equipped on our 96B.
VT-2B foreign trade main battle tank VT-2B foreign trade main battle tank
In addition, the 96B outperforms the T-72B3 in terms of armor and maintainability. What's more, the appearance of the 96B is more in line with the current concept of advanced tanks. 96B also has its corresponding foreign trade model, that is VT-2B. At present, the Iranian army is still equipped with the early model T-72, and its performance is completely different from the current VT-2B. Moreover, the Iranian army is also equipped with a large number of Chinese Type 59 and Type 69 tanks. It is also a method to buy a relatively inexpensive VT-2B from China to replace its old tank lineup. There is no additional purchase of armaments from China. Political terms. (Author: rabbit kicking Eagle)
伊朗参加坦克大赛坦言俄T72不如中国96B 或有意采购
2019年08月09日 16:56 新浪军事
66

坦克两项中国第三车组惜夺第二 将挺进半决赛1/6
查看原图图集模式
8月7日,在俄罗斯阿拉比诺靶场举行2019国际军事比赛“坦克两项”赛事迎来小组赛的第三场,中国代表队的第三车组最终以24分36秒的成绩夺得小组第二名。







近日,据媒体报道,8月3日开幕的“国际军事比赛-2019”正在多个国家火热进行中。诸多项目中,最引人注目的莫过于“坦克两项”比赛。从2014年开始举办至今,一直在俄罗斯阿拉比诺训练场举行的“坦克两项”已经进入了第六个年头。但是,这两天的赛场上却发生一些让人意想不到的危险状况,伊朗队在驾驶T-72B3坦克进行比赛时,车辆燃起浓烟,状况十分危险,导致伊朗队紧急换车,耽误了较多时间。

据赛事官方提供的资料显示,参加“坦克两项”比赛的十余个参赛国,除了中国与俄罗斯,其他队伍均使用俄罗斯提供的T-72B3坦克参加比赛。中国派出的是国产96B型主战坦克,而俄罗斯使用的是T-72B3的进一步改进型T-72B3M(也被称为“终极T-72”)。96B自从2016年参加“坦克两项”以来,表现都非常稳定,无论是动力系统还是火控系统都经受住了考验。

事故发生之后,伊朗代表队有人指出,经过多届的比赛确实可以看出,T-72B3在所有性能上都与解放军的96B有一定差距差距。其实,“坦克两项”比赛的课目设置,其实并不是特别实战化,有点类似于赛车。比赛过程中,车组需要对三个坦克靶进行主炮射击,然后使用高射机枪对直升机靶进行射击,使用并列机枪对RPG射手靶进行射击,除此之外,还需要驾驶员有特别优秀的驾驶技巧,坦克车也需要有优秀的动力系统,毕竟“坦克两项”是个计时赛而不是积分赛。

伊朗方面所言不虚。目前来说,我国的96B坦克已经全面超越了俄罗斯的T-72B3甚至是T-72B3M。动力上来说,目前96B采用的是我国自行研制的“新150”系列V8发动机,动力超过1000马力。尽管仍略低于俄罗斯T-72B3M的1130马力,但是由于96B采用了先进的综合液力自动变速箱,操控性能非常优秀,简单来说,就和开自动挡的汽车一样,使用方向盘操控,脚下只需要踩油门和刹车。而T-72系列都还是传统的老式机械传动,使用操纵杆控制,对驾驶员的体力要求和技术要求都非常高。

从火控和火力系统上来说,两者的差距可谓是更大。尽管96B坦克的125毫米坦克炮从技术来源上来讲,源自于上世纪80年代我国从罗马尼亚获得的一辆T-72上的2A46M坦克炮。但是我国并不是简单的对其进行仿制,而是改进了其一系列的弊端,精度、炮弹初速和威力都大大提高。从火控的角度来说,T-72系列目前使用的是下反稳像式火控系统,落后于目前我军的96B上装备的世界先进水平的上反稳像式火控系统。

除此之外,96B在装甲、可维护性等方面也胜过T-72B3。更何况,96B的外观也更符合现在人们对于先进坦克的概念。96B也有其对应的外贸型号,那就是VT-2B。目前,伊朗军队装备的仍然是早期型号的T-72,性能与目前的VT-2B完全不可同日而语。况且,伊朗军队也装备有大量的中国59式和69式坦克,从中国购买相对物美价廉的VT-2B来替换其老旧的坦克阵容也不失为一个方法,从中国采购军备也不会有附加政治条款。(作者:兔子蹬鹰)
Iran participates in the tank competition and admits that the Russian T72 is not as good as China 96B or intends to purchase
August 09, 2019 16:56 Sina Military
66
The two Chinese tanks of the tank won the second place and will advance to the semifinals 1/6.
View original image gallery mode
On August 7th, at the Alabino shooting range in Russia, the 2019 international military competition "Tank Two" event ushered in the third game of the group stage. The third team of the Chinese team finally won the group with 24 minutes and 36 seconds. Second place.
Iranian team T-73B3, which is burning smoke, is burning Iranian T-73B3
Recently, according to media reports, the "International Military Competition - 2019", which opened on August 3, is in full swing in many countries. Among the many projects, the most striking is the "two tanks" competition. Since its inception in 2014, the “Tank Two” that has been held at the Arabino training ground in Russia has entered its sixth year. However, there were some unexpected dangerous situations on the two days of the game. When the Iranian team was driving the T-72B3 tank, the vehicles ignited heavy smoke and the situation was very dangerous, causing the Iranian team to change the car urgently. More time.
Russia T-72B3M Russia T-72B3M
According to the official information provided by the event, more than a dozen participating countries participating in the "Colour Two Tanks" competition, except China and Russia, used the T-72B3 tank provided by Russia to participate in the competition. China sent the domestic 96B main battle tank, while Russia used the T-72B3 further improved T-72B3M (also known as the "ultimate T-72"). Since the 96B participated in the "tank two" in 2016, the performance has been very stable, and both the power system and the fire control system have withstood the test.
96B, who has participated in the "tank two" multiple times, has participated in the "tank two" 96B many times.
After the accident, the Iranian team pointed out that after several sessions, it can be seen that the T-72B3 has a certain gap with the PLA 96B in all performances. In fact, the setting of the "two tanks" competition is not particularly combative, and is somewhat similar to racing. During the competition, the team needs to shoot the main guns of the three tank targets, then use the high-altitude machine guns to shoot the helicopter targets, and use the parallel machine guns to shoot the RPG shooter targets. In addition, the driver needs to be particularly excellent. Driving skills, tanks also need to have an excellent power system, after all, "tank two" is a time trial rather than a points game.
In 2019, participated in the "tank two" 96B2019 to participate in the "tank two" 96B
The Iranian side is full of words. At present, China's 96B tank has completely surpassed Russia's T-72B3 and even T-72B3M. In terms of power, the current 96B adopts the "new 150" series V8 engine developed by China itself, with a power of more than 1000 horsepower. Although still slightly lower than the 1130 hp of the Russian T-72B3M, the 96B uses an advanced integrated hydraulic automatic transmission, which has excellent handling performance. Simply put, like the automatic car, use the steering wheel to control the foot. Just step on the throttle and brakes. The T-72 series is still a traditional old-fashioned mechanical transmission, using the joystick control, the driver's physical requirements and technical requirements are very high.
T-72 tanks in active service of the Iranian army T-72 tanks in active service of the Iranian army
From the perspective of fire control and firepower systems, the gap between the two can be said to be even greater. Although the 125mm tank gun of the 96B tank is derived from the technical source, it originated from the 2A46M tank gun on a T-72 that China obtained from Romania in the 1980s. However, China is not simply imitating it, but has improved its series of drawbacks. The accuracy, the initial velocity and the power of the shells have been greatly improved. From the perspective of fire control, the T-72 series currently uses the lower anti-stabilized fire control system, which is behind the current world-class anti-stabilized image fire control system equipped on our 96B.
VT-2B foreign trade main battle tank VT-2B foreign trade main battle tank
In addition, the 96B outperforms the T-72B3 in terms of armor and maintainability. What's more, the appearance of the 96B is more in line with the current concept of advanced tanks. 96B also has its corresponding foreign trade model, that is VT-2B. At present, the Iranian army is still equipped with the early model T-72, and its performance is completely different from the current VT-2B. Moreover, the Iranian army is also equipped with a large number of Chinese Type 59 and Type 69 tanks. It is also a method to buy a relatively inexpensive VT-2B from China to replace its old tank lineup. There is no additional purchase of armaments from China. Political terms. (Author: rabbit kicking Eagle)
- Joined
- Jul 25, 2018
- Messages
- 4,593
- Points
- 113
https://www.quora.com/Does-China-al...atively-or-quantitatively/answer/Husuo-Batao?
China budget for military spending is 1.5% , or 175 billion USD. Not even at 2% as wanted by USA for her puppet countries like UK, France , Germany , Australia , Japan etc. USA budget for military spending is 686 billion USD or 3.5%
Just imagine if China military budget is at 2%, or like USA, at 3.5%
Further more, this is not like in the case of Germany during Hitler time. Werhmact had the Tigers tanks, a much better tank than Russia or USA or UK.
BUT
Germany manufactured only 5,966 tanks, as compared to 29,497 for the US, 7,476 for Britain, and an estimated 20,000 for the Soviet Union. And the results shown many many more will take out the best and the few.
In China now, not only the key assets got better reach and more bang then USA, China got more of them than USA.
Report: China has some of world’s most advanced weapons, remains ‘long way’ from US military
China’s been showing off a lot of new powerful weapons, and experts think they’re sending a message
Some Chinese military tech surpasses US, Pentagon admits
**Let us start with MRLS.**
Now China is as good if not better than Russians in rocket artillery.
Top 10 Multiple Launch Rocket Systems (Top 10 Multiple Launch Rocket Systems)
The PHL 03 is a Chinese artillery rocket system. It is a copy of the Soviet
Smerch (Smerch Multiple Launch Rocket System)
. It reportedly entered service with the Chinese army in 2004-2005. The PHL 03 is also being proposed for the export customers as the AR2. It has been exported to Morocco (one battalion with 36 units).
The PHL 03 has 12 tubes for 300 mm rockets. A standard rocket weights around 800 kg and has a 280 kg warhead. Maximum range of fire is 70-130 km depending on the warhead type. Though some sources report that rockets of this system has a maximum range of 150 km. Rockets are available with High Explosive Fragmentation (HE-FRAG), fuel-air explosive, and cluster warheads with anti-armor and anti-personnel submunitions. Cluster warheads may also carry self-targeting anti-tank munitions. A full salvo of this system could potentially cover an area of up to 67 hectares.
**Even though the PHL 03 is a Chinese version of the Smerch, it appears that Chinese overtook Russians in terms of rockets, as rockets of the PHL 03 have longer range than those of the Smerch. Manufacturers claim, that Chinese 300 mm rockets are not compatible with the Russian Smerch rockets as these use different propellant motors and components.**
USA is a distant third to Russia and China. Be that in rocket artillery or tube artillery.
China's PHL03, advanced Multiple Launch Rocket System (China's PHL03, advanced Multiple Launch Rocket System)
Various types of the 300 mm caliber rocket shells fired by the PHL03 are equipped with simple automatic correction system which allows more dense impact points. The impact point intensity doubles and the accuracy triples. In this way, a high kill probability with fewer rocket shells is possible.
Comparison with its peers

From the table above, it can be concluded that in terms of overall design, or in particular, the range, intensity, power, survivability and maneuverability, the PHL03 MLRS has a series of major breakthroughs compared with traditional rockets. Some of its aspects meet or even exceed the world's advanced level.
The service of the PHL03 Multiple Launch Rocket System has greatly enhanced the capability of remote fire support of the Chinese military. The operational performance of the system will continue to improve with the development of China's rocket shell technology. And it will become an indispensable remote firepower for the Chinese military.
**Chinese tube artillery**
Saudi Arabia uses Chinese NORINCO PLZ-45 self propelled howitzer for the clear advantage over that of the best of USA artillery. More accurate and longer reach than the best of USA artillery. And Saudi Arabia is USA captive country and yet refused to use USA artillery as that so inferior to China.
Saudis Use Chinese-made Cannons in Yemen (Saudis Use Chinese-made Cannons in Yemen)






Chinese designed and made their own GL5 APS for their battle tanks.
China unveils GL5 active protection system for main battle tanks
You will see photos of the missile warhead being taken out by the APS meters before the missile hit the tank .




USA got no equivalent despite their vast spendings , and had to go cap in hand to Israel to buy their Trophy system and mount it on their Abrahms.
**Explosives**
China also got the most powerful non-nuclear explosive. So a Chinese AShM carrying 500 kg semi armour piercing warhead might well be the equivalent of a 1,500 kg warhead of USA equivalent. And same for Chinese propellant.
Other than nuclear explosives, the most powerful are Semtex, HMX, or even the holy grail Octanitrocubane sought by the West in vain.
China leapt pass that into the N15 kind of explosive 10 to 100 times more powerful than TNT. N15 in propellent form is also used by China in her missiles .
In Chinese
军事深度_新浪军事_新浪网... (中国竟先于美推出高含能材料:重要程度堪比055下水)
**中国竟先于美推出高含能材料:重要程度堪比055下水**
2017年11月18日
Partial extract via
Google Translate (Google Translate)
In January 2017, China announced a new research result. The world's first all-anion anion salt was successfully synthesized. The related research papers have become China's first research paper in the field of energetic materials published in the international top science "science" , But also allow China to occupy a new generation of ultra-high-energy energetic materials to study the international high ground.
As all-nitrogen ultra-high energy material energy up to 10 to 100 times the TNT above, the power comparable to small nuclear bombs, with high density, high energy, clean and detonated pollution-free, nitrogen explosion products, stable and safe. Therefore, the main object of development.
More than 200 years ago, people isolated nitrogen from the air and later discovered nitrogen ions. Various theoretical calculations were made on all-nitrogen derivatives. However, the earliest synthesis was recorded in 1956. Before this century, It is considered a breakthrough and is currently under exploration. Its prospects have attracted the positive research from all countries.

**Shooting war in the sea will also have shooting war in the air and AWACs important to that air war.**
Husuo Batao's answer to Is it true that Chinese AWACS aircraft are 50 percent more efficient than those used by the USA? (Quora User's answer to Is it true that Chinese AWACS aircraft are 50 percent more efficient than those used by the USA?)
extract of above


Meet KJ-600, the aircraft that could help China's navy rival America's
And from Wuming Chan answer.
How China's Clever New Missile Could Cripple American Air Power
China's Mach 6 Monster Air-to-Air Missile Could Make the U.S. Air Force Come in for a ‘Crash Landing’
This is what USA Airforce Secretary got to say in 2018
Air Force secretary: China, Russia could shoot down new JSTARS on day one of a war
There will be no usable bases for USA airforce in Japan or Guam within the first 10 minutes of the war.
First Strike: China's Missile Threat to U.S. Bases in Asia
A Missile 'Pearl Harbor': How China Could Win a War Against America?
Missile Strikes on U.S. Bases in Asia: Is This China's Real Threat to America?
Those bases will all be hit and cratered by DFs with conventional warheads so planes cannot take off.
Go into above to see photos of strikes made by Chinese on model setups in the Western desert of China that represent hardened bunkers for planes and runways and dock settings with models of Burkes and Ticos and the bases HQs to see the pin point targetting of the DFs.






Naval assets and head quarters will all be hit and sunk and taken out of play.
Then Chinese cruise missiles will fly by the thousands to take out planes still stuck in those bases.
As for shooting war at the sea. And forgetting for time being the DF-21Ds and DF-26Bs and CM-401s that China have and figment of imagination in heads of USA Admirals.
Just on AShMs.
Xi Jinping's Rocket Force is nullifying U.S. military primacy in Asia





The whole world will be watching Muricans kids lead by a Dotard and his demented side kicks Bolton and Pompeo carrying knives to indulge in their blood letting fantasies in a fucking gun fight with China, when China got the guns against the knives of Murican kids.





"Illustration of U.S. and threat anti-ship missile ranges from Bryan Clark's CSBA monograph 'Commanding the Seas: A Plan to Reinvigorate U.S. Navy Surface Warfare' https://csbaonline.org/uploads/d...
And do not forget the DF-21Ds and DF-26Bs and the CM-401s


The U.S. Navy Won't Like China's New Ship-Killer Hypersonic Missile
China Reveals Short-Range Anti-Ship Ballistic Missile Designed To Dodge Enemy Defenses
Graphics associated with the CM-401 suggest it has a “porpoising” or “skip-glide” trajectory that involves the warhead abruptly pulling up at least once as it begins the terminal stage of its flight. This maneuver could extend the range of a ballistic weapon, but has only ever been used to give the warhead a much more irregular flight path and allow it to adjust its course.

CHINESE INTERNET
A Chinese graphic showing a ballistic missile with a skip-glide trajectory associated with the CM-401.
This, in turn, makes it harder for an opponent to try and intercept the warhead. The CM-401’s terminal speed, which CASIC says is between Mach 4 and 6, would also help it break through enemy defenses to reach its target. The launch platform reportedly has the ability to fire its two missiles on different trajectories against either one or two targets at once, again increasing the difficulty for the defender to respond to the incoming threat.
I cannot imagine the big brothers of CM-401 do not have that capability. Especially as the CM-401 build for the export market.
And what about hypersonic weapons?
The Chinese military in 2014 said it had conducted a hypersonic test flight. By early 2016, it had conducted six successful tests, according to U.S. military officials. How many more since then is anyone guess.






Starry Sky 2
More likely than not, Chinese hypersonic weapon systems already operational and deployed . USA equivalent still in the dreaming stages and going out to tender.
China leads U.S. on potent super-fast missiles
As for the really serious business that I hope never ever be used,
DF-41 - Wikipedia
The Dong Feng 41 (CSS-X-10) is a road- and rail-mobile intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). The DF-41 is currently in its final testing stages and will be the next land-based ballistic missile to be deployed in the People’s Republic of China (PRC). It is estimated to have an operational range of 12,000 to 15,000 km, which would make it the longest range missile in operation. It will likely have a top speed of Mach 25 and will be capable of delivering up to 10 MIRVed warheads.
The DF-41 is a three-stage solid-fueled intercontinental ballistic missile reported to have a maximum range of up to 15,000 kilometers (more than 9320 miles) and a top speed of Mach 25 (19,030 mph). It is said to be capable of carrying up to 10 multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRVs). Its launch preparation time is estimated to be between 3 to 5 minutes.
This would make the DF-41 the world's longest range missile, surpassing the range of the US LGM-30 Minuteman which has a reported range of 13,000 km.
As by Jan 2017, Chinese media have reported the deployment of three brigades of DF-41 ICBMs. There is photographic evidence of a possible fourth brigade of DF-41 ICBMs on the Tibetan plateau. However, we have only counted the number of DF-41 ICBM TELs (ie. Transporter Erector Launcher), or 4 X 12 TELs
It is inefficient to fire only one ballistic missile per launcher. It is more logical to fire two ballistic missiles per launcher. This process is called re-loading. A DF-41 TEL can either be re-loaded with another DF-41 ICBM missile nearby or the DF-41 TEL can drive to a hidden re-supply location for another DF-41 ICBM.
If you accept that China has one re-load missile for each DF-41 TEL then the total number of Chinese DF-41 ICBMs has to be doubled.
Four brigades of DF-41 ICBMs (Heilongjiang, Henan, Xinjiang, and Tibet Provinces) with one re-load per DF-41 TEL yields 96 total DF-41 ICBMs.

Reported DF-41 Deployment: China 'Responding to US Missile Defense in Asia'
Expert: DF-41 among most advanced missiles in the world
If China got only 260 thermonukes like what everyone is saying and hoping, the surplus warheads will be delivering dim sum and tea bags and cleaned pressed laundry from Chinese laundrymen.
Please remember DF-41 got a very big brother coming up as well in case you think DF-41 not worthy enough to deliver dim sum and tea bags and cleaned laundry.
Russia’s RS-28 “Sarmat” ten-ton payload, rated as the most dangerous ICBM . Reportedly it may carry up to fifteen 350 kiloton warheads, or up to twenty-four of the new “Avangard” nuclear-armed Hypersonic Glide Vehicle (HGV) warheads. Sarmat will be dwarfed by Chinese new missile with even larger twenty-ton payload. That will be solid-fuel space-launch vehicle (SLV), and could form the basis for what might become the world’s largest “mobile” ICBM.
The Next China Military Threat: The World's Biggest Mobile ICBM?
So please be peaceful and respectful and more courtesy, and no more phony FONOPs and playing games of who will blink with China with phony FONOPs. Do not play with fire regarding Taiwan.
China budget for military spending is 1.5% , or 175 billion USD. Not even at 2% as wanted by USA for her puppet countries like UK, France , Germany , Australia , Japan etc. USA budget for military spending is 686 billion USD or 3.5%
Just imagine if China military budget is at 2%, or like USA, at 3.5%
Further more, this is not like in the case of Germany during Hitler time. Werhmact had the Tigers tanks, a much better tank than Russia or USA or UK.
BUT
Germany manufactured only 5,966 tanks, as compared to 29,497 for the US, 7,476 for Britain, and an estimated 20,000 for the Soviet Union. And the results shown many many more will take out the best and the few.
In China now, not only the key assets got better reach and more bang then USA, China got more of them than USA.
Report: China has some of world’s most advanced weapons, remains ‘long way’ from US military
China’s been showing off a lot of new powerful weapons, and experts think they’re sending a message
Some Chinese military tech surpasses US, Pentagon admits
**Let us start with MRLS.**
Now China is as good if not better than Russians in rocket artillery.
Top 10 Multiple Launch Rocket Systems (Top 10 Multiple Launch Rocket Systems)
The PHL 03 is a Chinese artillery rocket system. It is a copy of the Soviet
Smerch (Smerch Multiple Launch Rocket System)
. It reportedly entered service with the Chinese army in 2004-2005. The PHL 03 is also being proposed for the export customers as the AR2. It has been exported to Morocco (one battalion with 36 units).
The PHL 03 has 12 tubes for 300 mm rockets. A standard rocket weights around 800 kg and has a 280 kg warhead. Maximum range of fire is 70-130 km depending on the warhead type. Though some sources report that rockets of this system has a maximum range of 150 km. Rockets are available with High Explosive Fragmentation (HE-FRAG), fuel-air explosive, and cluster warheads with anti-armor and anti-personnel submunitions. Cluster warheads may also carry self-targeting anti-tank munitions. A full salvo of this system could potentially cover an area of up to 67 hectares.
**Even though the PHL 03 is a Chinese version of the Smerch, it appears that Chinese overtook Russians in terms of rockets, as rockets of the PHL 03 have longer range than those of the Smerch. Manufacturers claim, that Chinese 300 mm rockets are not compatible with the Russian Smerch rockets as these use different propellant motors and components.**
USA is a distant third to Russia and China. Be that in rocket artillery or tube artillery.
China's PHL03, advanced Multiple Launch Rocket System (China's PHL03, advanced Multiple Launch Rocket System)
Various types of the 300 mm caliber rocket shells fired by the PHL03 are equipped with simple automatic correction system which allows more dense impact points. The impact point intensity doubles and the accuracy triples. In this way, a high kill probability with fewer rocket shells is possible.
Comparison with its peers
From the table above, it can be concluded that in terms of overall design, or in particular, the range, intensity, power, survivability and maneuverability, the PHL03 MLRS has a series of major breakthroughs compared with traditional rockets. Some of its aspects meet or even exceed the world's advanced level.
The service of the PHL03 Multiple Launch Rocket System has greatly enhanced the capability of remote fire support of the Chinese military. The operational performance of the system will continue to improve with the development of China's rocket shell technology. And it will become an indispensable remote firepower for the Chinese military.
**Chinese tube artillery**
Saudi Arabia uses Chinese NORINCO PLZ-45 self propelled howitzer for the clear advantage over that of the best of USA artillery. More accurate and longer reach than the best of USA artillery. And Saudi Arabia is USA captive country and yet refused to use USA artillery as that so inferior to China.
Saudis Use Chinese-made Cannons in Yemen (Saudis Use Chinese-made Cannons in Yemen)
Chinese designed and made their own GL5 APS for their battle tanks.
China unveils GL5 active protection system for main battle tanks
You will see photos of the missile warhead being taken out by the APS meters before the missile hit the tank .




USA got no equivalent despite their vast spendings , and had to go cap in hand to Israel to buy their Trophy system and mount it on their Abrahms.
**Explosives**
China also got the most powerful non-nuclear explosive. So a Chinese AShM carrying 500 kg semi armour piercing warhead might well be the equivalent of a 1,500 kg warhead of USA equivalent. And same for Chinese propellant.
Other than nuclear explosives, the most powerful are Semtex, HMX, or even the holy grail Octanitrocubane sought by the West in vain.
China leapt pass that into the N15 kind of explosive 10 to 100 times more powerful than TNT. N15 in propellent form is also used by China in her missiles .
In Chinese
军事深度_新浪军事_新浪网... (中国竟先于美推出高含能材料:重要程度堪比055下水)
**中国竟先于美推出高含能材料:重要程度堪比055下水**
2017年11月18日
Partial extract via
Google Translate (Google Translate)
In January 2017, China announced a new research result. The world's first all-anion anion salt was successfully synthesized. The related research papers have become China's first research paper in the field of energetic materials published in the international top science "science" , But also allow China to occupy a new generation of ultra-high-energy energetic materials to study the international high ground.
As all-nitrogen ultra-high energy material energy up to 10 to 100 times the TNT above, the power comparable to small nuclear bombs, with high density, high energy, clean and detonated pollution-free, nitrogen explosion products, stable and safe. Therefore, the main object of development.
More than 200 years ago, people isolated nitrogen from the air and later discovered nitrogen ions. Various theoretical calculations were made on all-nitrogen derivatives. However, the earliest synthesis was recorded in 1956. Before this century, It is considered a breakthrough and is currently under exploration. Its prospects have attracted the positive research from all countries.

**Shooting war in the sea will also have shooting war in the air and AWACs important to that air war.**
Husuo Batao's answer to Is it true that Chinese AWACS aircraft are 50 percent more efficient than those used by the USA? (Quora User's answer to Is it true that Chinese AWACS aircraft are 50 percent more efficient than those used by the USA?)
extract of above
Thanks a lot to all those that feared China and took steps to block her from the Israeli deal.
Thereby forcing China to do it by herself and thereby making even far better AWACs then those possessed by USA or Israel instead of merely being on par with USA /Israel.
Just like the fear that China supercomputers be better than USA and USA blocking sales of chips to be used on China supercomputer. China went on to design and made their own chips and China Supercomputers fastest in the world. Please do not tell me USA now hold the title for fastest supercomputer.
China decided not to enter her latest supercomputer in that Top500 to avoid yet more kneejerks from Dotard.
As for Chinese AWACs, I am reposting Lin Xieyi from his July 2017 answer on How capable is Chinese AWACS system as compared to US or Israeli systems?
It was the successful efforts by the US in 2000 in pressurizing Israel and Russia not to export AWACs technology to China that prompted Beijing to embark on an intensive effort to develop advanced home-grown radar technology. Only when the KJ-2000 entered service in 2005 did China possess the capability to coordinate its air force in large-scale air battles while simultaneously tracking many enemy aircraft and ships. The speed of Chinese AWACS development overtook the speed of acquisition of AWACS by other countries - China completed the path of catching up and overtaking the West on AWACS research and by 2012, China became the world leader in AWACS aircraft in terms of stealth detection range and fixed rotodome design.
- Stealth detection Range : Although the US E-3 Sentry AWACS can detect/track 3rd-Gen military aircraft out to 400 km in range, it can only detect 4th and 5th Gen stealth aircraft out to 150 Km. On the other hand the Chinese KJ-500 (or KJ-2000) can detect 4th & 5th Gen stealth aircraft at 250 km range, giving it a heads-up in transmitting enemy aircraft info to escorting fighters.
- Fixed Rotodome design : The PLAAF’s current top-of-the-line AEWC&C system, the KJ-2000, is believed to be one full generation ahead of U.S. E-3 AWACS and E-2 Hawkeye aircraft. While the US AWACS are still using rotating rotodomes, the Chinese AWACS are using fixed rotodome which reduce wear and tear due to less moving mechanical parts.
[1] China’s Emerging C4ISR Revolution

Footnotes
Since then, China came up with even more powerful AWACS, aka KJ-600 Carrier Based AWACS .Meet KJ-600, the aircraft that could help China's navy rival America's
And from Wuming Chan answer.
How much can one truly know how capable the Chinese AWACS systems can be?
Much of that might be secret until the time when that is being used to deliver good news to KC-135s and carriers and AWECs and other assets which is likely to be a lot less stealth than hoped for.
How difficult is it to detect stealth planes and to target them when the quality of radar Chinese are dealing with can be set to detect not just mosquitoes a few kilometers away.
Whether the mosquito is female or male will also be known.
Your stealth F35s or B1s B2s got smaller radar profile than a mosquito?
USA or Israeli got any systems able to do that?
Thank you USA for enforcing ban on China in purchasing that from Israel or other countries.
Forcing China to do it all on its own and leaving you either far behind or far far behind.
**And Chinese air weaponary. To splash the air tankers and AWACs and JSTAR USA rely on to direct the fight in the air. And the Stealth planes of USA.**How China's Clever New Missile Could Cripple American Air Power
China's Mach 6 Monster Air-to-Air Missile Could Make the U.S. Air Force Come in for a ‘Crash Landing’
This is what USA Airforce Secretary got to say in 2018
Air Force secretary: China, Russia could shoot down new JSTARS on day one of a war
There will be no usable bases for USA airforce in Japan or Guam within the first 10 minutes of the war.
First Strike: China's Missile Threat to U.S. Bases in Asia
A Missile 'Pearl Harbor': How China Could Win a War Against America?
Missile Strikes on U.S. Bases in Asia: Is This China's Real Threat to America?
Those bases will all be hit and cratered by DFs with conventional warheads so planes cannot take off.
Go into above to see photos of strikes made by Chinese on model setups in the Western desert of China that represent hardened bunkers for planes and runways and dock settings with models of Burkes and Ticos and the bases HQs to see the pin point targetting of the DFs.
Naval assets and head quarters will all be hit and sunk and taken out of play.
Then Chinese cruise missiles will fly by the thousands to take out planes still stuck in those bases.
As for shooting war at the sea. And forgetting for time being the DF-21Ds and DF-26Bs and CM-401s that China have and figment of imagination in heads of USA Admirals.
Just on AShMs.
Xi Jinping's Rocket Force is nullifying U.S. military primacy in Asia
Apart from weapons covered by the INF Treaty where China has a monopoly, the PLA has other missiles in its arsenal that outperform their U.S. counterparts. These include two supersonic anti-ship cruise missiles, the YJ-12, with a range of 400 km, and the YJ-18, which can hit targets up to 540 km away.
To counter these missiles, the United States relies on its subsonic, Harpoon anti-ship missile which has been modified to give it a maximum range of about 240 km. “That is a very big gap,” said Haddick, who is also an adviser to the U.S. Special Operations Command. “China’s anti-ship missile capability exceeds those of the United States in terms of range, speed and sensor performance.”
The whole world will be watching Muricans kids lead by a Dotard and his demented side kicks Bolton and Pompeo carrying knives to indulge in their blood letting fantasies in a fucking gun fight with China, when China got the guns against the knives of Murican kids.
China has thousands of supersonic Mach 3 AShMs and thousands of subsonic stealth AShMs that then can sprint to Mach 3 within 40 km of the target.
And eyes above in satellite and high flying drones above and sonar devices on sea bed that will know every second where the carriers are and where they are heading to tell the AShMs where to hit.
Truly god view, Jilin-1 video satellite shot @OneSpace01 OS-X1 suborbital rocket's launch at JSLC this noon.
1,323 people are talking about thisChina got 3000++ of Mach 3s YJ-12 and YJ18 to throw against the 11 carriers USA want to bring to their self declared FONOP.
Or at least 300++ Mach 3s on each carrier group.
Assuming only 20 % of those will hit. So be assured that at least 10 missiles will hit the carrier and not just 1 missile.
And not just the warhead, there will be 2–3 tons of missiles coming behind the warhead at Mach 3 tearing into the bulkheads and ordnance and aviation fuel and the poor men and women in the carrier. Those 2–3 tons of missile body will be tearing in the bulkheads faster and more deadly then APFSDS. Andf carrying its own unburned fuel to add to the fun.
Even steel will burn when hit with hell fire and tons of steel and debris coming in at Mach 3. The aviation fuel, and paint on walls, the bombs and ordnance will all cook off and add to the huge huge fire inside the carrier. Regardless if carrier under Condition Zebra or Donkey or Jackass.
The brave sailors in those carriers will not care or worry and be happy that their carrier not sinking. And only burning and burning from one end to the other end.
"Illustration of U.S. and threat anti-ship missile ranges from Bryan Clark's CSBA monograph 'Commanding the Seas: A Plan to Reinvigorate U.S. Navy Surface Warfare' https://csbaonline.org/uploads/d...
And do not forget the DF-21Ds and DF-26Bs and the CM-401s
The U.S. Navy Won't Like China's New Ship-Killer Hypersonic Missile
China Reveals Short-Range Anti-Ship Ballistic Missile Designed To Dodge Enemy Defenses
Graphics associated with the CM-401 suggest it has a “porpoising” or “skip-glide” trajectory that involves the warhead abruptly pulling up at least once as it begins the terminal stage of its flight. This maneuver could extend the range of a ballistic weapon, but has only ever been used to give the warhead a much more irregular flight path and allow it to adjust its course.
CHINESE INTERNET
A Chinese graphic showing a ballistic missile with a skip-glide trajectory associated with the CM-401.
This, in turn, makes it harder for an opponent to try and intercept the warhead. The CM-401’s terminal speed, which CASIC says is between Mach 4 and 6, would also help it break through enemy defenses to reach its target. The launch platform reportedly has the ability to fire its two missiles on different trajectories against either one or two targets at once, again increasing the difficulty for the defender to respond to the incoming threat.
I cannot imagine the big brothers of CM-401 do not have that capability. Especially as the CM-401 build for the export market.
And what about hypersonic weapons?
The Chinese military in 2014 said it had conducted a hypersonic test flight. By early 2016, it had conducted six successful tests, according to U.S. military officials. How many more since then is anyone guess.
中国の地上配備中間段階弾道ミサイル防衛試験の動画
80
59 people are talking about thisStarry Sky 2
More likely than not, Chinese hypersonic weapon systems already operational and deployed . USA equivalent still in the dreaming stages and going out to tender.
China leads U.S. on potent super-fast missiles
As for the really serious business that I hope never ever be used,
DF-41 - Wikipedia
The Dong Feng 41 (CSS-X-10) is a road- and rail-mobile intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). The DF-41 is currently in its final testing stages and will be the next land-based ballistic missile to be deployed in the People’s Republic of China (PRC). It is estimated to have an operational range of 12,000 to 15,000 km, which would make it the longest range missile in operation. It will likely have a top speed of Mach 25 and will be capable of delivering up to 10 MIRVed warheads.
The DF-41 is a three-stage solid-fueled intercontinental ballistic missile reported to have a maximum range of up to 15,000 kilometers (more than 9320 miles) and a top speed of Mach 25 (19,030 mph). It is said to be capable of carrying up to 10 multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRVs). Its launch preparation time is estimated to be between 3 to 5 minutes.
This would make the DF-41 the world's longest range missile, surpassing the range of the US LGM-30 Minuteman which has a reported range of 13,000 km.
As by Jan 2017, Chinese media have reported the deployment of three brigades of DF-41 ICBMs. There is photographic evidence of a possible fourth brigade of DF-41 ICBMs on the Tibetan plateau. However, we have only counted the number of DF-41 ICBM TELs (ie. Transporter Erector Launcher), or 4 X 12 TELs
It is inefficient to fire only one ballistic missile per launcher. It is more logical to fire two ballistic missiles per launcher. This process is called re-loading. A DF-41 TEL can either be re-loaded with another DF-41 ICBM missile nearby or the DF-41 TEL can drive to a hidden re-supply location for another DF-41 ICBM.
If you accept that China has one re-load missile for each DF-41 TEL then the total number of Chinese DF-41 ICBMs has to be doubled.
Four brigades of DF-41 ICBMs (Heilongjiang, Henan, Xinjiang, and Tibet Provinces) with one re-load per DF-41 TEL yields 96 total DF-41 ICBMs.
Reported DF-41 Deployment: China 'Responding to US Missile Defense in Asia'
Expert: DF-41 among most advanced missiles in the world
If China got only 260 thermonukes like what everyone is saying and hoping, the surplus warheads will be delivering dim sum and tea bags and cleaned pressed laundry from Chinese laundrymen.
Please remember DF-41 got a very big brother coming up as well in case you think DF-41 not worthy enough to deliver dim sum and tea bags and cleaned laundry.
Russia’s RS-28 “Sarmat” ten-ton payload, rated as the most dangerous ICBM . Reportedly it may carry up to fifteen 350 kiloton warheads, or up to twenty-four of the new “Avangard” nuclear-armed Hypersonic Glide Vehicle (HGV) warheads. Sarmat will be dwarfed by Chinese new missile with even larger twenty-ton payload. That will be solid-fuel space-launch vehicle (SLV), and could form the basis for what might become the world’s largest “mobile” ICBM.
The Next China Military Threat: The World's Biggest Mobile ICBM?
So please be peaceful and respectful and more courtesy, and no more phony FONOPs and playing games of who will blink with China with phony FONOPs. Do not play with fire regarding Taiwan.
- Joined
- Jul 25, 2018
- Messages
- 4,593
- Points
- 113
https://www.quora.com/What-would-it-take-to-destroy-Chinas-artificial-islands
Extracted below
It will take a war to destroy China islands in China waters.
Dont talk about that kangaroo court helped in a room rented in Hague as Hague arbitration as that was a total sham.
If you want war with China, then go and do that.
If war is not going to be nuclear and just naval battle, this will be the shape of that war.
Quora User's answer to What would a naval war between China and the U.S. look like?
Which in all likelihood, lead to a nuclear war.
And if you think China got 260 nukes, think again.
Read below as to the nukes China is likely to have.
Wuming Chan's answer to Could China's 200 nukes realistically kill more than 50% of the US population in a nuclear war?
Wuming Chan's answer to Given that China has thousands of kilometres of "underground nuclear wall", is it credible that it has only 270 warheads?
China already got the world most deadly ICBM the DF-41 . Wuming Chan's answer to Which missile can be considered as the world's most dangerous Intercontinental Ballistic missile (ICBM) ?
The DF-41 is a three-stage solid-fueled intercontinental ballistic missile reported to have a maximum range of up to 15,000 kilometers (more than 9320 miles) and a top speed of Mach 25 (19,030 mph). It is said to be capable of carrying up to 10 multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRVs). Its launch preparation time is estimated to be between 3 to 5 minutes.
China has at least 100 DF-41s, operational and organised in 4 Brigades.
As by Jan 2017, Chinese media have reported the deployment of three brigades of DF-41 ICBMs. There is photographic evidence of a possible fourth brigade of DF-41 ICBMs on the Tibetan plateau. However, we have only counted the number of DF-41 ICBM TELs (ie. Transporter Erector Launcher).
It is inefficient to fire only one ballistic missile per launcher. It is more logical to fire two ballistic missiles per launcher. This process is called re-loading. A DF-41 TEL can either be re-loaded with another DF-41 ICBM missile nearby or the DF-41 TEL can drive to a hidden re-supply location for another DF-41 ICBM.
If you accept that China has one re-load missile for each DF-41 TEL then the total number of Chinese DF-41 ICBMs has to be doubled.
Four brigades of DF-41 ICBMs (Heilongjiang, Henan, Xinjiang, and Tibet Provinces) with one re-load per DF-41 TEL yields 96 total DF-41 ICBMs.
4 DF-41 ICBM brigades x 12 DF-41 ICBM ballistic missiles per brigade x 2 (for the re-load) = 96 total DF-41 ICBMs
Which can send 10 MIRV thermonuclear warheads at Mach 25 15,000 km away.
JL-3 is the navalised version of the DF-41.
China Conducts First Test of New JL-3 Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile
The first test of JL-3 successfully done in Dec 2018.
Currently, 6 numbers of 096 SSBNs are being build simultaneously.
Carrying 24 JL-3 missiles , each mirving 5–7 warheads.
Type 096 Tang Class SSBN
This is similar to Ohio Class

China is going to have a even Bigger Big Brother to stand beside DF-41. And even more deadly ICBM should ‘Muricans want to be funny.
The Next China Military Threat: The World's Biggest Mobile ICBM?
In addition to many Chinese satellites above, togther with 25,000 meters high flying drones Divine Eagles and Soar Dragons, and acoustic sonars on sea beds, there is this too.
News of advanced Over-the-Horizon programme for carrier fleet emerges as senior research receives China’s top science award
China’s new ‘compact’ radar will cover an area the size of India
This will be on Chinese Navy ships that will see and can see ‘Muricans carriers and Burkes and Ticos over the horizon way way before ‘Muricans can see the Chinese ships.
And if ‘Muricans chose to attack China and have war with China, this will be the way that war will take place.
Wuming Chan's answer to How long would actual intense combat last in a full scale conflict between the US armed forces and the People's Liberation Army waged in Asia?
China will never attack USA and start the war.
So how likely will it be that ‘Muricans decide to attack China and have that war?
Then you will get a war that is likely to lead to WW3.
You still looking forward to that WW3?
Still happy at steaming carriers in South China Sea that likely will escalate into WW3?
Still want to provoke wars with major countries that likely to escalate into WW3?
Will the quarrels and disagreements that lead to this war be relevant or even remembered once the war started?
Can this kind of war ever come to an end once started?
Isnt it so fucking stupid to even let the war start in the first place?
Isnt that other alternative a lot better?
Young men and women of both countries and all countries should smell roses, make love and drink and dine and laugh and go enjoy sunrises and sunsets and play with their kids and children.
How about remaining Be Nice Be Respectful and work together for a better world?
And let all those lethality toys remain toys to be admired like Hydrogen bombs . Seen and known, and never ever to be used in anger or sorrow.
Young men and women of both countries and all countries should smell roses, make love and drink and dine and laugh and go enjoy sunrises and sunsets and play with their kids and children.
China promised never be the first to use nuke
But if even one nuke land on China or Chinese forces, USA and all of USA bases around the world from Guam to Okinawa and Japan and Diego Garcia and Singapore and UK and Europe will become lakes and seas of molten glowing green and multicolored glass.
The irony is that more likely than not, China might well be the only country to have the thermonuclear bomb. China thermonuclear bombs are build to the Yu Min configuration . Which required very little maintenance. USA and Russia uses the Ulam Teller configuration requiring a lot of maintenance.
Each warhead needs to have about 200 milligrams of fresh tritium added every year. Here’s a pic showing W80s having their gas changed.

So how many of USA thermonukes are actually working in between the bouts of maintenance? Not likely you get the answer.
Extracted below
It will take a war to destroy China islands in China waters.
Dont talk about that kangaroo court helped in a room rented in Hague as Hague arbitration as that was a total sham.
If you want war with China, then go and do that.
If war is not going to be nuclear and just naval battle, this will be the shape of that war.
Quora User's answer to What would a naval war between China and the U.S. look like?
Which in all likelihood, lead to a nuclear war.
And if you think China got 260 nukes, think again.
Read below as to the nukes China is likely to have.
Wuming Chan's answer to Could China's 200 nukes realistically kill more than 50% of the US population in a nuclear war?
Wuming Chan's answer to Given that China has thousands of kilometres of "underground nuclear wall", is it credible that it has only 270 warheads?
China already got the world most deadly ICBM the DF-41 . Wuming Chan's answer to Which missile can be considered as the world's most dangerous Intercontinental Ballistic missile (ICBM) ?
The DF-41 is a three-stage solid-fueled intercontinental ballistic missile reported to have a maximum range of up to 15,000 kilometers (more than 9320 miles) and a top speed of Mach 25 (19,030 mph). It is said to be capable of carrying up to 10 multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRVs). Its launch preparation time is estimated to be between 3 to 5 minutes.
China has at least 100 DF-41s, operational and organised in 4 Brigades.
As by Jan 2017, Chinese media have reported the deployment of three brigades of DF-41 ICBMs. There is photographic evidence of a possible fourth brigade of DF-41 ICBMs on the Tibetan plateau. However, we have only counted the number of DF-41 ICBM TELs (ie. Transporter Erector Launcher).
It is inefficient to fire only one ballistic missile per launcher. It is more logical to fire two ballistic missiles per launcher. This process is called re-loading. A DF-41 TEL can either be re-loaded with another DF-41 ICBM missile nearby or the DF-41 TEL can drive to a hidden re-supply location for another DF-41 ICBM.
If you accept that China has one re-load missile for each DF-41 TEL then the total number of Chinese DF-41 ICBMs has to be doubled.
Four brigades of DF-41 ICBMs (Heilongjiang, Henan, Xinjiang, and Tibet Provinces) with one re-load per DF-41 TEL yields 96 total DF-41 ICBMs.
4 DF-41 ICBM brigades x 12 DF-41 ICBM ballistic missiles per brigade x 2 (for the re-load) = 96 total DF-41 ICBMs
Which can send 10 MIRV thermonuclear warheads at Mach 25 15,000 km away.
JL-3 is the navalised version of the DF-41.
China Conducts First Test of New JL-3 Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile
The first test of JL-3 successfully done in Dec 2018.
Currently, 6 numbers of 096 SSBNs are being build simultaneously.
Carrying 24 JL-3 missiles , each mirving 5–7 warheads.
Type 096 Tang Class SSBN
This is similar to Ohio Class
China is going to have a even Bigger Big Brother to stand beside DF-41. And even more deadly ICBM should ‘Muricans want to be funny.
The Next China Military Threat: The World's Biggest Mobile ICBM?
In addition to many Chinese satellites above, togther with 25,000 meters high flying drones Divine Eagles and Soar Dragons, and acoustic sonars on sea beds, there is this too.
News of advanced Over-the-Horizon programme for carrier fleet emerges as senior research receives China’s top science award
China’s new ‘compact’ radar will cover an area the size of India
This will be on Chinese Navy ships that will see and can see ‘Muricans carriers and Burkes and Ticos over the horizon way way before ‘Muricans can see the Chinese ships.
And if ‘Muricans chose to attack China and have war with China, this will be the way that war will take place.
Wuming Chan's answer to How long would actual intense combat last in a full scale conflict between the US armed forces and the People's Liberation Army waged in Asia?
China will never attack USA and start the war.
So how likely will it be that ‘Muricans decide to attack China and have that war?
Then you will get a war that is likely to lead to WW3.
You still looking forward to that WW3?
Still happy at steaming carriers in South China Sea that likely will escalate into WW3?
Still want to provoke wars with major countries that likely to escalate into WW3?
Will the quarrels and disagreements that lead to this war be relevant or even remembered once the war started?
Can this kind of war ever come to an end once started?
Isnt it so fucking stupid to even let the war start in the first place?
Isnt that other alternative a lot better?
Young men and women of both countries and all countries should smell roses, make love and drink and dine and laugh and go enjoy sunrises and sunsets and play with their kids and children.
How about remaining Be Nice Be Respectful and work together for a better world?
And let all those lethality toys remain toys to be admired like Hydrogen bombs . Seen and known, and never ever to be used in anger or sorrow.
Young men and women of both countries and all countries should smell roses, make love and drink and dine and laugh and go enjoy sunrises and sunsets and play with their kids and children.
China promised never be the first to use nuke
But if even one nuke land on China or Chinese forces, USA and all of USA bases around the world from Guam to Okinawa and Japan and Diego Garcia and Singapore and UK and Europe will become lakes and seas of molten glowing green and multicolored glass.
The irony is that more likely than not, China might well be the only country to have the thermonuclear bomb. China thermonuclear bombs are build to the Yu Min configuration . Which required very little maintenance. USA and Russia uses the Ulam Teller configuration requiring a lot of maintenance.
Each warhead needs to have about 200 milligrams of fresh tritium added every year. Here’s a pic showing W80s having their gas changed.
So how many of USA thermonukes are actually working in between the bouts of maintenance? Not likely you get the answer.
- Joined
- Aug 28, 2011
- Messages
- 3,990
- Points
- 63
Besides the national set of spare instant replacement satellites - 快舟 now there is yet another set of solution = 捷龙. So there are alternate plans of civilian satellites (and definitely multiple alternative replacements for the military satellites) during war time.
The usual civilian space center launching pads are totally optional during war time. Spare launching trucks will come out of warehouses from nowhere to fire many objects into space. Almost like ICBMs. You won't know if it was nuke warheads or just civilian satellites!
USA records and registered all the daily (peace time) Chinese satellites orbit / trajectories and marked them for destruction during war. But these efforts are wasted. When war starts the Chinese uses entire different set of satellites with different orbits / trajectories. And they have made ready emergency launching vehicles to launch them alike firing ICBMs. Well, they are actually replications of ICBM launching system including vehicles just changing the color from camouflage to civilian space agency's usual white rocket color.
During the wars, Americans will become too fucking confused! Unsure weather Chinese are launching civilian satellites' replacements or ICBMs hitting USA! There will be FAR TOO MANY NEW TARGETS IN THE SKY TOTALLY UNFAMILIAR! No Idea which one will spy or kill you! You will be TOTALLY CONFUSED & OVERWHELMED!
http://slide.mil.news.sina.com.cn/k/slide_8_193_73371.html#p=1
换个马甲照样认识你!中国捷龙一号火箭成功发射
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:29:58
8月17日午间,由中国航天科技集团有限公司所属中国运载火箭技术研究院抓总研制的捷龙一号遥一火箭在我国酒泉卫星发射中心成功发射,以“一箭三星”方式顺利将三颗卫星送入预定轨道,这是捷龙一号运载火箭执行的首次飞行任务。捷龙一号总长约19.5米,箭体直径1.2米,起飞重量约23.1吨,是我国固体火箭中体积最小、重量最轻的火箭。(图片来源:新华视点 人民日报)
换个马甲照样认识你!中国捷龙一号火箭成功发射
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:29:58
8月17日午间,由中国航天科技集团有限公司所属中国运载火箭技术研究院抓总研制的捷龙一号遥一火箭在我国酒泉卫星发射中心成功发射,以“一箭三星”方式顺利将三颗卫星送入预定轨道,这是捷龙一号运载火箭执行的首次飞行任务。捷龙一号总长约19.5米,箭体直径1.2米,起飞重量约23.1吨,是我国固体火箭中体积最小、重量最轻的火箭。(图片来源:新华视点 人民日报)
换个马甲照样认识你!中国捷龙一号火箭成功发射
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:29:58
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:29:58
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:29:58
Http://slide.mil.news.sina.com.cn/k/slide_8_193_73371.html#p=1
Change your vest to know you! China Jielong No. 1 rocket successfully launched
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:29:58
1 / 7
At noon on August 17th, the Jielong No. 1 remote rocket developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, affiliated to China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, was successfully launched at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in China, and successfully launched the “Three Arrows” method. The satellite was sent to the scheduled orbit, which was the first mission performed by the Jetron-1 launch vehicle. The total length of Jielong No.1 is about 19.5 meters, the diameter of the arrow is 1.2 meters, and the take-off weight is about 23.1 tons. It is the smallest and lightest rocket in China's solid rockets. (Source: Xinhua Viewpoint People's Daily)
Change your vest to know you! China Jielong No. 1 rocket successfully launched
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:29:58
2 / 7
At noon on August 17th, the Jielong No. 1 remote rocket developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, affiliated to China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, was successfully launched at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in China, and successfully launched the “Three Arrows” method. The satellite was sent to the scheduled orbit, which was the first mission performed by the Jetron-1 launch vehicle. The total length of Jielong No.1 is about 19.5 meters, the diameter of the arrow is 1.2 meters, and the take-off weight is about 23.1 tons. It is the smallest and lightest rocket in China's solid rockets. (Source: Xinhua Viewpoint People's Daily)
Change your vest to know you! China Jielong No. 1 rocket successfully launched
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:29:58
At noon on August 17th, the Jielong No. 1 remote rocket developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, affiliated to China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, was successfully launched at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in China, and successfully launched the “Three Arrows” method. The satellite was sent to the scheduled orbit, which was the first mission performed by the Jetron-1 launch vehicle. The total length of Jielong No.1 is about 19.5 meters, the diameter of the arrow is 1.2 meters, and the take-off weight is about 23.1 tons. It is the smallest and lightest rocket in China's solid rockets. (Source: Xinhua Viewpoint People's Daily)
Change your vest to know you! China Jielong No. 1 rocket successfully launched
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:29:58
At noon on August 17th, the Jielong No. 1 remote rocket developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, affiliated to China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, was successfully launched at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in China, and successfully launched the “Three Arrows” method. The satellite was sent to the scheduled orbit, which was the first mission performed by the Jetron-1 launch vehicle. The total length of Jielong No.1 is about 19.5 meters, the diameter of the arrow is 1.2 meters, and the take-off weight is about 23.1 tons. It is the smallest and lightest rocket in China's solid rockets. (Source: Xinhua Viewpoint People's Daily)
Change your vest to know you! China Jielong No. 1 rocket successfully launched
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:29:58
At noon on August 17th, the Jielong No. 1 remote rocket developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, affiliated to China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, was successfully launched at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in China, and successfully launched the “Three Arrows” method. The satellite was sent to the scheduled orbit, which was the first mission performed by the Jetron-1 launch vehicle. The total length of Jielong No.1 is about 19.5 meters, the diameter of the arrow is 1.2 meters, and the take-off weight is about 23.1 tons. It is the smallest and lightest rocket in China's solid rockets. (Source: Xinhua Viewpoint People's Daily)
At noon on August 17th, the Jielong No. 1 remote rocket developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, affiliated to China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, was successfully launched at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in China, and successfully launched the “Three Arrows” method. The satellite was sent to the scheduled orbit, which was the first mission performed by the Jetron-1 launch vehicle. The total length of Jielong No.1 is about 19.5 meters, the diameter of the arrow is 1.2 meters, and the take-off weight is about 23.1 tons. It is the smallest and lightest rocket in China's solid rockets. (Source: Xinhua Viewpoint People's Daily)
The usual civilian space center launching pads are totally optional during war time. Spare launching trucks will come out of warehouses from nowhere to fire many objects into space. Almost like ICBMs. You won't know if it was nuke warheads or just civilian satellites!
USA records and registered all the daily (peace time) Chinese satellites orbit / trajectories and marked them for destruction during war. But these efforts are wasted. When war starts the Chinese uses entire different set of satellites with different orbits / trajectories. And they have made ready emergency launching vehicles to launch them alike firing ICBMs. Well, they are actually replications of ICBM launching system including vehicles just changing the color from camouflage to civilian space agency's usual white rocket color.
During the wars, Americans will become too fucking confused! Unsure weather Chinese are launching civilian satellites' replacements or ICBMs hitting USA! There will be FAR TOO MANY NEW TARGETS IN THE SKY TOTALLY UNFAMILIAR! No Idea which one will spy or kill you! You will be TOTALLY CONFUSED & OVERWHELMED!
http://slide.mil.news.sina.com.cn/k/slide_8_193_73371.html#p=1
换个马甲照样认识你!中国捷龙一号火箭成功发射
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:29:58
8月17日午间,由中国航天科技集团有限公司所属中国运载火箭技术研究院抓总研制的捷龙一号遥一火箭在我国酒泉卫星发射中心成功发射,以“一箭三星”方式顺利将三颗卫星送入预定轨道,这是捷龙一号运载火箭执行的首次飞行任务。捷龙一号总长约19.5米,箭体直径1.2米,起飞重量约23.1吨,是我国固体火箭中体积最小、重量最轻的火箭。(图片来源:新华视点 人民日报)
换个马甲照样认识你!中国捷龙一号火箭成功发射
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:29:58
8月17日午间,由中国航天科技集团有限公司所属中国运载火箭技术研究院抓总研制的捷龙一号遥一火箭在我国酒泉卫星发射中心成功发射,以“一箭三星”方式顺利将三颗卫星送入预定轨道,这是捷龙一号运载火箭执行的首次飞行任务。捷龙一号总长约19.5米,箭体直径1.2米,起飞重量约23.1吨,是我国固体火箭中体积最小、重量最轻的火箭。(图片来源:新华视点 人民日报)
换个马甲照样认识你!中国捷龙一号火箭成功发射
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:29:58
8月17日午间,由中国航天科技集团有限公司所属中国运载火箭技术研究院抓总研制的捷龙一号遥一火箭在我国酒泉卫星发射中心成功发射,以“一箭三星”方式顺利将三颗卫星送入预定轨道,这是捷龙一号运载火箭执行的首次飞行任务。捷龙一号总长约19.5米,箭体直径1.2米,起飞重量约23.1吨,是我国固体火箭中体积最小、重量最轻的火箭。(图片来源:新华视点 人民日报)

支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:29:58
- 8月17日午间,由中国航天科技集团有限公司所属中国运载火箭技术研究院抓总研制的捷龙一号遥一火箭在我国酒泉卫星发射中心成功发射,以“一箭三星”方式顺利将三颗卫星送入预定轨道,这是捷龙一号运载火箭执行的首次飞行任务。捷龙一号总长约19.5米,箭体直径1.2米,起飞重量约23.1吨,是我国固体火箭中体积最小、重量最轻的火箭。(图片来源:新华视点 人民日报)

支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:29:58

- 8月17日午间,由中国航天科技集团有限公司所属中国运载火箭技术研究院抓总研制的捷龙一号遥一火箭在我国酒泉卫星发射中心成功发射,以“一箭三星”方式顺利将三颗卫星送入预定轨道,这是捷龙一号运载火箭执行的首次飞行任务。捷龙一号总长约19.5米,箭体直径1.2米,起飞重量约23.1吨,是我国固体火箭中体积最小、重量最轻的火箭。(图片来源:新华视点 人民日报)

- 8月17日午间,由中国航天科技集团有限公司所属中国运载火箭技术研究院抓总研制的捷龙一号遥一火箭在我国酒泉卫星发射中心成功发射,以“一箭三星”方式顺利将三颗卫星送入预定轨道,这是捷龙一号运载火箭执行的首次飞行任务。捷龙一号总长约19.5米,箭体直径1.2米,起飞重量约23.1吨,是我国固体火箭中体积最小、重量最轻的火箭。(图片来源:新华视点 人民日报)
Http://slide.mil.news.sina.com.cn/k/slide_8_193_73371.html#p=1
Change your vest to know you! China Jielong No. 1 rocket successfully launched
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:29:58
1 / 7
At noon on August 17th, the Jielong No. 1 remote rocket developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, affiliated to China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, was successfully launched at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in China, and successfully launched the “Three Arrows” method. The satellite was sent to the scheduled orbit, which was the first mission performed by the Jetron-1 launch vehicle. The total length of Jielong No.1 is about 19.5 meters, the diameter of the arrow is 1.2 meters, and the take-off weight is about 23.1 tons. It is the smallest and lightest rocket in China's solid rockets. (Source: Xinhua Viewpoint People's Daily)
Change your vest to know you! China Jielong No. 1 rocket successfully launched
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:29:58
2 / 7
At noon on August 17th, the Jielong No. 1 remote rocket developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, affiliated to China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, was successfully launched at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in China, and successfully launched the “Three Arrows” method. The satellite was sent to the scheduled orbit, which was the first mission performed by the Jetron-1 launch vehicle. The total length of Jielong No.1 is about 19.5 meters, the diameter of the arrow is 1.2 meters, and the take-off weight is about 23.1 tons. It is the smallest and lightest rocket in China's solid rockets. (Source: Xinhua Viewpoint People's Daily)
Change your vest to know you! China Jielong No. 1 rocket successfully launched
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:29:58
At noon on August 17th, the Jielong No. 1 remote rocket developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, affiliated to China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, was successfully launched at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in China, and successfully launched the “Three Arrows” method. The satellite was sent to the scheduled orbit, which was the first mission performed by the Jetron-1 launch vehicle. The total length of Jielong No.1 is about 19.5 meters, the diameter of the arrow is 1.2 meters, and the take-off weight is about 23.1 tons. It is the smallest and lightest rocket in China's solid rockets. (Source: Xinhua Viewpoint People's Daily)
Change your vest to know you! China Jielong No. 1 rocket successfully launched
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:29:58
At noon on August 17th, the Jielong No. 1 remote rocket developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, affiliated to China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, was successfully launched at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in China, and successfully launched the “Three Arrows” method. The satellite was sent to the scheduled orbit, which was the first mission performed by the Jetron-1 launch vehicle. The total length of Jielong No.1 is about 19.5 meters, the diameter of the arrow is 1.2 meters, and the take-off weight is about 23.1 tons. It is the smallest and lightest rocket in China's solid rockets. (Source: Xinhua Viewpoint People's Daily)
Change your vest to know you! China Jielong No. 1 rocket successfully launched
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:29:58
At noon on August 17th, the Jielong No. 1 remote rocket developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, affiliated to China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, was successfully launched at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in China, and successfully launched the “Three Arrows” method. The satellite was sent to the scheduled orbit, which was the first mission performed by the Jetron-1 launch vehicle. The total length of Jielong No.1 is about 19.5 meters, the diameter of the arrow is 1.2 meters, and the take-off weight is about 23.1 tons. It is the smallest and lightest rocket in China's solid rockets. (Source: Xinhua Viewpoint People's Daily)
At noon on August 17th, the Jielong No. 1 remote rocket developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, affiliated to China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, was successfully launched at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in China, and successfully launched the “Three Arrows” method. The satellite was sent to the scheduled orbit, which was the first mission performed by the Jetron-1 launch vehicle. The total length of Jielong No.1 is about 19.5 meters, the diameter of the arrow is 1.2 meters, and the take-off weight is about 23.1 tons. It is the smallest and lightest rocket in China's solid rockets. (Source: Xinhua Viewpoint People's Daily)
- Joined
- Feb 20, 2010
- Messages
- 2,818
- Points
- 48
Pathetic Taiwan want to make a dozen of these tiny 600 tons warships to dream they could stop PLA navy.
Apparently too little to laugh at, that does not even warrant using the PLA killer anti-ship ICBMs IRBMs or submarine torpedoes or ship fired anti-ship missiles. Those are meant to sink USA navy fleets.
PLA says only cheapest helicopter sweeping using tiny cheapest missiles are enough to wipe out a dozen of these 600 tons fragile light speed crafts. Call that a fishing day for tiny fish! LOL!

http://slide.mil.news.sina.com.cn/h/slide_8_203_73370.html#p=1
沱江舰引颈受戮!海军直9D挂载鹰击9反舰导弹出击
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:14:04
1 / 7
据央视报道,近日,南部战区海军某舰载直升机团组织海上实弹射击训练,检验飞行员对海目标的攻击能力。报道视频中曝光了海军直9D直升机挂载鹰击-9轻型反舰导弹出击的画面。(图片来源:沉默的山羊)
沱江舰引颈受戮!海军直9D挂载鹰击9反舰导弹出击
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:14:04
据央视报道,近日,南部战区海军某舰载直升机团组织海上实弹射击训练,检验飞行员对海目标的攻击能力。报道视频中曝光了海军直9D直升机挂载鹰击-9轻型反舰导弹出击的画面。(图片来源:沉默的山羊)
沱江舰引颈受戮!海军直9D挂载鹰击9反舰导弹出击
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:14:04
据央视报道,近日,南部战区海军某舰载直升机团组织海上实弹射击训练,检验飞行员对海目标的攻击能力。报道视频中曝光了海军直9D直升机挂载鹰击-9轻型反舰导弹出击的画面。(图片来源:沉默的山羊)
沱江舰引颈受戮!海军直9D挂载鹰击9反舰导弹出击
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:14:04
4 / 7
据央视报道,近日,南部战区海军某舰载直升机团组织海上实弹射击训练,检验飞行员对海目标的攻击能力。报道视频中曝光了海军直9D直升机挂载鹰击-9轻型反舰导弹出击的画面。(图片来源:沉默的山羊)
沱江舰引颈受戮!海军直9D挂载鹰击9反舰导弹出击
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:14:04
5 / 7
据央视报道,近日,南部战区海军某舰载直升机团组织海上实弹射击训练,检验飞行员对海目标的攻击能力。报道视频中曝光了海军直9D直升机挂载鹰击-9轻型反舰导弹出击的画面。(图片来源:沉默的山羊)
沱江舰引颈受戮!海军直9D挂载鹰击9反舰导弹出击
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:14:04
据央视报道,近日,南部战区海军某舰载直升机团组织海上实弹射击训练,检验飞行员对海目标的攻击能力。报道视频中曝光了海军直9D直升机挂载鹰击-9轻型反舰导弹出击的画面。(图片来源:沉默的山羊)
Http://slide.mil.news.sina.com.cn/h/slide_8_203_73370.html#p=1
The Lijiang River is suffering from the neck! Navy Straight 9D Mounted Eagle Strike 9 Anti-ship Missile Attack
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:14:04
1 / 7
According to CCTV reports, a ship-borne helicopter group of the Southern Theater Navy recently organized a live-fire shooting training at sea to test the pilot's ability to attack the sea target. In the report video, the Navy's straight 9D helicopter was mounted with a eagle-height-9 anti-ship missile attack. (Source: Silent goat)
The Lijiang River is suffering from the neck! Navy Straight 9D Mounted Eagle Strike 9 Anti-ship Missile Attack
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:14:04
2 / 7
According to CCTV reports, a ship-borne helicopter group of the Southern Theater Navy recently organized a live-fire shooting training at sea to test the pilot's ability to attack the sea target. In the report video, the Navy's straight 9D helicopter was mounted with a eagle-height-9 anti-ship missile attack. (Source: Silent goat)
The Lijiang River is suffering from the neck! Navy Straight 9D Mounted Eagle Strike 9 Anti-ship Missile Attack
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:14:04
3 / 7
According to CCTV reports, a ship-borne helicopter group of the Southern Theater Navy recently organized a live-fire shooting training at sea to test the pilot's ability to attack the sea target. In the report video, the Navy's straight 9D helicopter was mounted with a eagle-height-9 anti-ship missile attack. (Source: Silent goat)
The Lijiang River is suffering from the neck! Navy Straight 9D Mounted Eagle Strike 9 Anti-ship Missile Attack
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:14:04
4 / 7
According to CCTV reports, a ship-borne helicopter group of the Southern Theater Navy recently organized a live-fire shooting training at sea to test the pilot's ability to attack the sea target. In the report video, the Navy's straight 9D helicopter was mounted with a eagle-height-9 anti-ship missile attack. (Source: Silent goat)
The Lijiang River is suffering from the neck! Navy Straight 9D Mounted Eagle Strike 9 Anti-ship Missile Attack
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:14:04
5 / 7
According to CCTV reports, a ship-borne helicopter group of the Southern Theater Navy recently organized a live-fire shooting training at sea to test the pilot's ability to attack the sea target. In the report video, the Navy's straight 9D helicopter was mounted with a eagle-height-9 anti-ship missile attack. (Source: Silent goat)
The Lijiang River is suffering from the neck! Navy Straight 9D Mounted Eagle Strike 9 Anti-ship Missile Attack
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:14:04
6 / 7
According to CCTV reports, a ship-borne helicopter group of the Southern Theater Navy recently organized a live-fire shooting training at sea to test the pilot's ability to attack the sea target. In the report video, the Navy's straight 9D helicopter was mounted with a eagle-height-9 anti-ship missile attack. (Source: Silent goat)
Apparently too little to laugh at, that does not even warrant using the PLA killer anti-ship ICBMs IRBMs or submarine torpedoes or ship fired anti-ship missiles. Those are meant to sink USA navy fleets.
PLA says only cheapest helicopter sweeping using tiny cheapest missiles are enough to wipe out a dozen of these 600 tons fragile light speed crafts. Call that a fishing day for tiny fish! LOL!

http://slide.mil.news.sina.com.cn/h/slide_8_203_73370.html#p=1
沱江舰引颈受戮!海军直9D挂载鹰击9反舰导弹出击
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:14:04
1 / 7
据央视报道,近日,南部战区海军某舰载直升机团组织海上实弹射击训练,检验飞行员对海目标的攻击能力。报道视频中曝光了海军直9D直升机挂载鹰击-9轻型反舰导弹出击的画面。(图片来源:沉默的山羊)
沱江舰引颈受戮!海军直9D挂载鹰击9反舰导弹出击
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:14:04
据央视报道,近日,南部战区海军某舰载直升机团组织海上实弹射击训练,检验飞行员对海目标的攻击能力。报道视频中曝光了海军直9D直升机挂载鹰击-9轻型反舰导弹出击的画面。(图片来源:沉默的山羊)
沱江舰引颈受戮!海军直9D挂载鹰击9反舰导弹出击
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:14:04
据央视报道,近日,南部战区海军某舰载直升机团组织海上实弹射击训练,检验飞行员对海目标的攻击能力。报道视频中曝光了海军直9D直升机挂载鹰击-9轻型反舰导弹出击的画面。(图片来源:沉默的山羊)
沱江舰引颈受戮!海军直9D挂载鹰击9反舰导弹出击
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:14:04
4 / 7
据央视报道,近日,南部战区海军某舰载直升机团组织海上实弹射击训练,检验飞行员对海目标的攻击能力。报道视频中曝光了海军直9D直升机挂载鹰击-9轻型反舰导弹出击的画面。(图片来源:沉默的山羊)
沱江舰引颈受戮!海军直9D挂载鹰击9反舰导弹出击
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:14:04
5 / 7
据央视报道,近日,南部战区海军某舰载直升机团组织海上实弹射击训练,检验飞行员对海目标的攻击能力。报道视频中曝光了海军直9D直升机挂载鹰击-9轻型反舰导弹出击的画面。(图片来源:沉默的山羊)
沱江舰引颈受戮!海军直9D挂载鹰击9反舰导弹出击
支持 键翻阅图片 列表查看
全屏观看
2019.08.18 16:14:04
据央视报道,近日,南部战区海军某舰载直升机团组织海上实弹射击训练,检验飞行员对海目标的攻击能力。报道视频中曝光了海军直9D直升机挂载鹰击-9轻型反舰导弹出击的画面。(图片来源:沉默的山羊)
Http://slide.mil.news.sina.com.cn/h/slide_8_203_73370.html#p=1
The Lijiang River is suffering from the neck! Navy Straight 9D Mounted Eagle Strike 9 Anti-ship Missile Attack
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:14:04
1 / 7
According to CCTV reports, a ship-borne helicopter group of the Southern Theater Navy recently organized a live-fire shooting training at sea to test the pilot's ability to attack the sea target. In the report video, the Navy's straight 9D helicopter was mounted with a eagle-height-9 anti-ship missile attack. (Source: Silent goat)
The Lijiang River is suffering from the neck! Navy Straight 9D Mounted Eagle Strike 9 Anti-ship Missile Attack
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:14:04
2 / 7
According to CCTV reports, a ship-borne helicopter group of the Southern Theater Navy recently organized a live-fire shooting training at sea to test the pilot's ability to attack the sea target. In the report video, the Navy's straight 9D helicopter was mounted with a eagle-height-9 anti-ship missile attack. (Source: Silent goat)
The Lijiang River is suffering from the neck! Navy Straight 9D Mounted Eagle Strike 9 Anti-ship Missile Attack
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:14:04
3 / 7
According to CCTV reports, a ship-borne helicopter group of the Southern Theater Navy recently organized a live-fire shooting training at sea to test the pilot's ability to attack the sea target. In the report video, the Navy's straight 9D helicopter was mounted with a eagle-height-9 anti-ship missile attack. (Source: Silent goat)
The Lijiang River is suffering from the neck! Navy Straight 9D Mounted Eagle Strike 9 Anti-ship Missile Attack
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:14:04
4 / 7
According to CCTV reports, a ship-borne helicopter group of the Southern Theater Navy recently organized a live-fire shooting training at sea to test the pilot's ability to attack the sea target. In the report video, the Navy's straight 9D helicopter was mounted with a eagle-height-9 anti-ship missile attack. (Source: Silent goat)
The Lijiang River is suffering from the neck! Navy Straight 9D Mounted Eagle Strike 9 Anti-ship Missile Attack
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:14:04
5 / 7
According to CCTV reports, a ship-borne helicopter group of the Southern Theater Navy recently organized a live-fire shooting training at sea to test the pilot's ability to attack the sea target. In the report video, the Navy's straight 9D helicopter was mounted with a eagle-height-9 anti-ship missile attack. (Source: Silent goat)
The Lijiang River is suffering from the neck! Navy Straight 9D Mounted Eagle Strike 9 Anti-ship Missile Attack
Support button flip through pictures list view
Full screen view
2019.08.18 16:14:04
6 / 7
According to CCTV reports, a ship-borne helicopter group of the Southern Theater Navy recently organized a live-fire shooting training at sea to test the pilot's ability to attack the sea target. In the report video, the Navy's straight 9D helicopter was mounted with a eagle-height-9 anti-ship missile attack. (Source: Silent goat)
- Joined
- Sep 22, 2008
- Messages
- 80,511
- Points
- 113
But the taiwan ships are stealth. Helicopters and china navy ships are not.
Similar threads
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 201
- Replies
- 0
- Views
- 229












