- Joined
- Mar 31, 2020
- Messages
- 9,153
- Points
- 113
10 Most Common Cancers in Men and Women in Singapore
The National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS) shares the top ten cancers that affect local men and women, and offers an important tip on what is your best protection.
https://www.healthxchange.sg/cancer/mens-cancer-concerns/common-cancers-men-women-singapore#

CANCER
if detected at an early stage, may be easier to treat or cure.
Cancer: What is it?
Cancer is a disease where abnormal cells divide without control, and usually form a lump (called a tumour) as their numbers increase. Cancer cells can invade nearby tissues and can spread through the bloodstream and lymphatic systems to other parts of the body.
Cancer cases on the rise in Singapore
According to the Singapore Cancer Society, about 39 people are diagnosed with cancer every day, 15 people die of cancer every day, and 1 in 4 people may develop cancer in their lifetime.* The good news is, with early detection and treatment, it is possible to have better clinical / management outcomes.
* Singapore Cancer Registry 50th Anniversary Monograph 1968-2017 (2013-2017 mortality data)
** Other urinary refers to renal pelvis, ureter, urethra, etc.
Common cancers by gender
Lung cancer and breast cancer had the highest mortality rates in males and females respectively. Lung cancer accounted for 27.6 per cent of cancer deaths among males in Singapore and breast cancer accounted for 17.9 per cent of cancer deaths among females.
Among ethnic groups, both males and females, the incidence of cancer was highest among the Chinese, with 23,164 males and 23,925 females suffering from the disease. They were followed by the Malays, 2,326 males and 2,840 females; and then the Indians, 1,237 males and 1,423 females.
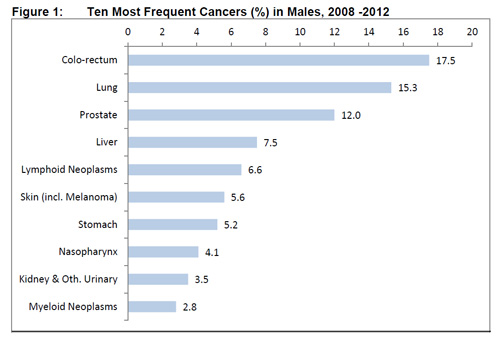
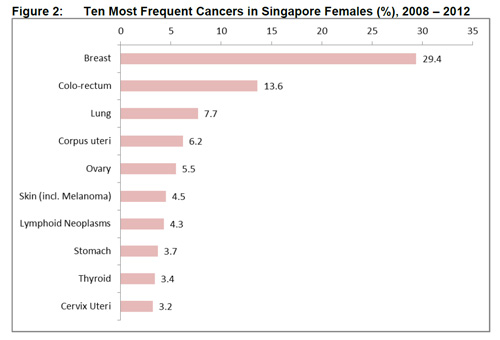
Colorectal, lung and prostate cancer were the top ranked cancers among the male resident population (Figure 1), while breast, colorectal and lung cancer were the top ranked cancers among female residents (Figure 2).
Some cancer risk factors are within your control while some are not
The majority of cancer cases are sporadic, i.e. the disease is not inherited. By pure chance, many cases of "common" cancers such as breast, colon and lung cancers can appear to run in a family. Your personal risk depends on factors such as your age, family history of cancer and your tendency to inherit cancer genes. These are beyond your control. Other risk factors that are within our control are not genetic. These include our lifestyle, diet, smoking and environmental exposure. We must work to reduce or prevent these risk factors.
Prevention and early detection of cancer
Although great advances have been made in the treatment of cancer, the impact on survival rates has been incremental rather than dramatic. Many cancer patients are also diagnosed relatively late, at which stage their treatment options are often severely limited. Prevention and early detection of cancer are therefore key strategies in cancer control efforts. You must be responsible for your own health – only you hold the key to your well-being.
Check out our comprehensive list of cancer articles:
Rise of Colorectal Cancer in Young Adults
Breast Cancer: What Puts You at Risk
Breast Cancer Screening: Your Best Protection
Tips to Keep Your Breasts Healthy
Prostate Cancer: All You Need to Know
Nose Cancer: Signs, Diagnosis and Treatment
Liver Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
Lymphoma Cancer: First Signs, Types, Treatment
Endometrial Cancer: Risk Factors, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
Ovarian Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
Cervical Cancer: Symptoms, Screening and How to Prevent
Stomach Cancer (Gastric Cancer): Symptoms and Treatment
Thyroid Cancer: Types, Symptoms and Treatment
Multiple Myeloma (Bone Marrow Cancer): Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
Skin Cancer: Types, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
Cancer Diet: Top Foods to Eat and Avoid When Undergoing Treatment
The National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS) shares the top ten cancers that affect local men and women, and offers an important tip on what is your best protection.
https://www.healthxchange.sg/cancer/mens-cancer-concerns/common-cancers-men-women-singapore#

CANCER
if detected at an early stage, may be easier to treat or cure.
Cancer: What is it?
Cancer is a disease where abnormal cells divide without control, and usually form a lump (called a tumour) as their numbers increase. Cancer cells can invade nearby tissues and can spread through the bloodstream and lymphatic systems to other parts of the body.
Cancer cases on the rise in Singapore
According to the Singapore Cancer Society, about 39 people are diagnosed with cancer every day, 15 people die of cancer every day, and 1 in 4 people may develop cancer in their lifetime.* The good news is, with early detection and treatment, it is possible to have better clinical / management outcomes.
| Men | Age-standardised incldence (%) | Women | Age-standardised incidence (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colorectal | 38.2% | Breast | 69.8% |
| Lung | 32.6% | Colorectal | 27.2% |
| Prostate | 31.8% | Lung | 15.4% |
| Liver & Intrahepatic Bile Ducts | 17.7% | Corpus Uteri (Uterus) | 16.9% |
| Lymphoid Neoplasms | 17.8% | Ovary & Fallopian Tube | 13.1% |
| Non-Melanoma Skin | 12.3% | Lymphoid Neoplasms | 12.3% |
| Stomach | 10.2% | Non-Melanoma Skin | 8% |
| Kidney and Other Urinary Organs** | 9.4% | Thyroid | 10.3% |
| Myeloid Neoplasms | 8.1% | Stomach | 6.2% |
| Nasopharynx | 7.5% | Cervix Uteri | 7.1% |
** Other urinary refers to renal pelvis, ureter, urethra, etc.
Common cancers by gender
Lung cancer and breast cancer had the highest mortality rates in males and females respectively. Lung cancer accounted for 27.6 per cent of cancer deaths among males in Singapore and breast cancer accounted for 17.9 per cent of cancer deaths among females.
Among ethnic groups, both males and females, the incidence of cancer was highest among the Chinese, with 23,164 males and 23,925 females suffering from the disease. They were followed by the Malays, 2,326 males and 2,840 females; and then the Indians, 1,237 males and 1,423 females.
Colorectal, lung and prostate cancer were the top ranked cancers among the male resident population (Figure 1), while breast, colorectal and lung cancer were the top ranked cancers among female residents (Figure 2).


Some cancer risk factors are within your control while some are not
The majority of cancer cases are sporadic, i.e. the disease is not inherited. By pure chance, many cases of "common" cancers such as breast, colon and lung cancers can appear to run in a family. Your personal risk depends on factors such as your age, family history of cancer and your tendency to inherit cancer genes. These are beyond your control. Other risk factors that are within our control are not genetic. These include our lifestyle, diet, smoking and environmental exposure. We must work to reduce or prevent these risk factors.
Prevention and early detection of cancer
Although great advances have been made in the treatment of cancer, the impact on survival rates has been incremental rather than dramatic. Many cancer patients are also diagnosed relatively late, at which stage their treatment options are often severely limited. Prevention and early detection of cancer are therefore key strategies in cancer control efforts. You must be responsible for your own health – only you hold the key to your well-being.
Check out our comprehensive list of cancer articles:
Rise of Colorectal Cancer in Young Adults
Breast Cancer: What Puts You at Risk
Breast Cancer Screening: Your Best Protection
Tips to Keep Your Breasts Healthy
Prostate Cancer: All You Need to Know
Nose Cancer: Signs, Diagnosis and Treatment
Liver Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
Lymphoma Cancer: First Signs, Types, Treatment
Endometrial Cancer: Risk Factors, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
Ovarian Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
Cervical Cancer: Symptoms, Screening and How to Prevent
Stomach Cancer (Gastric Cancer): Symptoms and Treatment
Thyroid Cancer: Types, Symptoms and Treatment
Multiple Myeloma (Bone Marrow Cancer): Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
Skin Cancer: Types, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
Cancer Diet: Top Foods to Eat and Avoid When Undergoing Treatment

